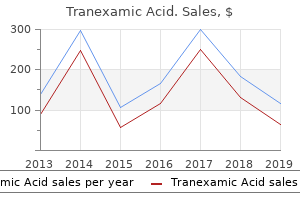
Tranexamic Acid
"Buy generic tranexamic 500 mg on line, medicine 93 7338".
By: A. Aldo, M.B.A., M.D.
Professor, Duke University School of Medicine
Palliative radiotherapy Bone metastases usually respond well to single fractions of external beam radiotherapy symptoms quiz order discount tranexamic. Treatment can be hazardous in patients who have poor bone marrow reserve because it may cause prolonged thrombocytopenia symptoms 8 days after ovulation buy tranexamic pills in toronto. Palliative treatments Hormone treatments for metastatic disease Patients who present with metastatic disease should be started on hormonal therapy because the majority (80%) respond well. Occasionally patients present as an emergency with spinal cord compression before having any hormone therapy. In most cases surgical intervention to the spine can be deferred at this stage unless there is neurological deterioration. Radiotherapy to the spine is often given, although it is uncertain whether it provides any additional benefit over hormone therapy alone. Patients who have prolonged responses to primary hormone therapy have a good chance of responding to second-line hormone therapy such as bicalutamide 50 mg. A combination of docetaxel (75 mg/m2 every 3 weeks) and prednisolone appears to confer a 2 to 3 month survival benefit compared to a combination of mitoxantrone and prednisolone (Tannock et al. Some patients can achieve a substantial palliative benefit, but many have insufficient bone marrow reserve, or are too unwell, to tolerate cytotoxic chemotherapy. In addition, pamidronate appears to have little or no activity in metastatic disease, and zoledronate only weak activity (Saad et al. Use of bisphosphonates in this setting has been shown to Prostate improve bone mineral density but its effect on fracture rate has not yet been reported. Prognosis Prognostic groupings for localised prostate cancer (N0 M0) Many groups have developed their own definitions and groupings for evaluating prostate cancer. Defining biochemical failure after radiotherapy with and without androgen deprivation for prostate cancer. Randomized trial comparing two fractionation schedules for patients with localized prostate cancer. Preliminary results of a randomized radiotherapy dose-escalation study comparing 70 Gy with 78 Gy for prostate cancer. Long-term efficacy of zoledronic acid for the prevention of skeletal complications in patients with metastatic hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Docetaxel plus prednisone or mitoxantrone plus prednisone for advanced prostate cancer. A reduction in rectal toxicity may improve patient outcomes, but longer follow-up is required to show whether there is an effect on survival. The management has changed little over the past 20 years, there is a high degree of consensus about treatment, and standard protocols are well developed. Nonetheless, patients with testicular cancer are best managed by specialised multidisciplinary teams. Testicular maldescent (cryptorchidism) is associated with an approximately ten-fold increased risk of a testicular tumour. Orchidopexy, if done when the child is young enough (probably before 2 years of age), partially reduces this risk. The mechanism of carcinogenesis is unknown, but it is likely that a loss of inhibitory feedback to the pituitary gland from the abnormal germinal epithelium may predispose a person to cancer by continued hormonal stimulation of the germ cells. It is standard practice to perform orchidopexy on maldescended testes because this is thought to reduce their malignant potential. Screening There is no evidence that population screening for testicular cancer reduces mortality, which would be expected in a rare disease with effective treatment available. Testicular cancer patients should all be taught testicular self-examination, because they run a particularly high risk of second, contralateral cancers. Germ cell tumours are the most common malignant tumours that occur in men between the ages of 25 and 35; there is a second peak between the ages of 55 to 65 years. Theories range from the impact of environmental oestrogens, related to oral contraceptive use, to the increased scrotal temperatures resulting from the use of disposable diapers in infancy.
The newer serotonergic antidepressants seem not to be as effective for the treatment of chronic neuropathic pain (see review by McQuay and colleagues) medications via endotracheal tube tranexamic 500 mg fast delivery, but these agents have not yet been extensively investigated in this clinical condition medicine grace potter order genuine tranexamic. Anticonvulsants have a beneficial effect on many central and peripheral neuropathic pain syndromes but are generally less effective for causalgic pain due to partial injury of a peripheral nerve. The mode of action of phenytoin, carbamazepine, gabapentin, levetiracetam, and other anticonvulsants in suppressing the lancinating pains of tic douloureux and certain polyneuropathies as well as pain after spinal cord injury and myelitis is not fully understood, but they are widely used. Their action has been attributed to the blocking of excess sodium channels, thereby reducing the evoked and spontaneous activity in nerve fibers. The full explanation is certainly more complex and related to separate central and peripheral sites, as summarized by Jensen. Often, large doses must be attained- for example, more than 2400 mg per day for gabapentin for full effect- but the soporific and ataxic effects may be poorly tolerated. The use of analgesic (nonnarcotic and narcotic), anticonvulsant, and antidepressant drugs in the management of chronic pain is summarized in Table 8-3. Treatment of Cancer Pain If the patient is ridden with disease and will not live longer than a few weeks or months, is opposed to surgery, or has widespread pain, surgical measures are out of the question. However, pain from widespread osseous metastases, even in patients with hormone-insensitive tumors, may be relieved by radiation therapy or by hypophysectomy. If these are not feasible, opioid medications are required and are effective, but they must be utilized in adequate doses. Usually, nerve section is not a satisfactory way of relieving restricted pain of the trunk and limbs because the overlap of adjacent nerves prevents complete denervation. Other procedures to be considered are the regional delivery of narcotic analogues, such as fentanyl or ketamine, by means of an external pump and a catheter that is implanted percutaneously in the epidural space in proximity to the dorsal nerve roots in the affected region; this device can be used safely at home. Treatment of Neuropathic Pain the treatment of pain induced by nerve root or intrinsic peripheral nerve disease is a great challenge for the neurologist and, as previously mentioned, utilizes several techniques that are generally administered by an anesthesiologist. One usually resorts first to one of the anticonvulsants discussed earlier and listed in Table 8-3. The next simplest treatments are topical; if the pain is regional and has a predominantly burning quality, capsaicin cream can be applied locally, care being taken to avoid contact with the eyes and mouth. These preparations may provide considerable relief in postherpetic neuralgia and some painful peripheral neuropathies, but they are totally ineffective in others. Aspirin mixed with chloroform in cold cream is said to be very effective in the topical treatment of postherpetic neuralgia, as suggested by King (see Chap. Several types of spinal injection, epidural, root, and facet, have long been used for the treatment of pain. Injections of epidural corticosteroids or mixtures of analgesics and steroids are helpful in selected cases of lumbar or thoracic nerve root pain and occasionally in painful peripheral neuropathy, but precise criteria for the use of this measure are not well established. Several studies do not support a beneficial effect, but there is little doubt, in our view, that a few patients are helped, if only for several days or weeks (see Chap. Root blocks with lidocaine or with longer-acting local anesthetics are sometimes helpful in establishing the precise source of radicular pain. Their main therapeutic use in our experience has been for thoracic radiculitis from shingles, chest wall pain after thoracotomy, and diabetic radiculopathy. Injection of analgesic compounds into and around facet joints and the extension of this procedure, radiofrequency ablation of the small nerves that innervate the joint, are as controversial as epidural injections; most studies failing to find a consistent benefit. Despite these drawbacks, we have found both of these approaches very useful when pain can be traced to a derangement of these joints, as discussed in Chap. The intravenous infusion of lidocaine has a brief beneficial effect on many types of pain, including neuropathic varieties, localized headaches, and facial pain; it is said to be useful in predicting the response to longer-acting agents such as mexiletine, its oral analogue, although this relationship has been erratic in our experience (see Table 8-1). Mexiletine is given in an initial dose of 150 mg per day and slowly increased to a maximum of 300 mg three times daily; it should be used very cautiously in patients with heart block. A variant of this technique utilizes regional intravenous infusion of a sympathetic blocking drug (bretylium, guanethidine, reserpine) into a limb that is isolated from the systemic circulation by the use of a tourniquet. This is known as a "Bier block," after the developer of regional anesthesia for single-limb surgery. The use of these techniques, as well as the administration of clonidine by several routes and the intravenous infusion of the adrenergic blocker phentolamine, is predicated on the concept of "sympathetically sustained pain," meaning pain that is mediated by the interaction of sympathetic and pain nerve fibers or by the sprouting of adrenergic axons in partially damaged nerves.
For example medications given for bipolar disorder order 500 mg tranexamic fast delivery, in the head and neck medicine 3 sixes discount tranexamic 500mg with visa, the tumour volumes may shrink during radiotherapy. These natural variations are inevitable, but the size of the variation can to some extent be estimated and accounted for. Techniques to reduce tumour movement have been used in thorax treatments such as breath hold, active breathing control, or depressing the chest to reduce the movement. Lung tumour motion can be in the order of 2 cm during a normal breathing cycle, depending on the lobe of the lung affected (Seppenwoolde et al. The function of serial organs may be seriously affected if even a small portion is irradiated above a tolerance dose. The effect of radiation on the function of parallel organs is more dependent on the volume irradiated. For a serial organ, the accuracy of treatment planning and delivery are important to ensure that tolerance is not exceeded. Principles of the isodose plan: photons Basic beam data It is important that the concepts of basic beam data are understood. The width of the radiation beam increases linearly with distance from the treatment head. At the edge of the radiation beam, the dose reduces over the distance of some millimetres. With megavoltage beams the dose is deposited by secondary electrons, which travel primarily in a forward direction. As a result there is buildup of dose below the skin surface before dmax is reached. The radial profile of a megavoltage beam changes with depth due to the differential hardening across the beam. This means that, if an asymmetric beam is created, the shape of the profile may also be noticeably asymmetric. As the distance from the treatment machine to the patient increases, the crosssectional area of the beam increases because of divergence. The inverse-square law causes the intensity of the radiation beam to decrease but the percentage depth doses below dmax to increase. As the field size increases, the central axis receives more radiation per monitor unit because of increased scatter from the machine head and within the patient. Beam arrangements Typical beam arrangements are as follow: r A single beam is used for superficial tumours such as skin cancers, or for tumours that are not at or near the midplane. It is also important to understand beam weighting so that the relative proportion of dose delivered to the tumour from each beam can be adjusted (Williams and Thwaites, 2000). In prostate planning, an anterior beam is combined with two wedged lateral fields. Use of lateral fields, rather than posterior obliques, allows beam shaping to be more effective in reducing the dose to the rectum. In head and neck treatments, the exit beams should avoid such critical structures as the contralateral eye and spinal cord. Non-coplanar beam arrangements can be achieved easily by linear accelerators, by rotating the table and the gantry, but it is important to ensure that the beam direction can be achieved. Isodose shapes for combinations of beams the directions of the beams will influence the shape of the treated volume. The global hot spot in a balanced multibeam treatment is likely to lie close to the centre of the treated volume. For example, with radical oesophagus treatments, delivering the dose entirely by anterior and posterior parallelopposed fields would exceed spinal cord tolerance. Similarly, using oblique laterals instead of the posterior beam would cause an excessive dose to the lungs. A two-phase technique that combines both of these approaches can prevent tolerance doses from being Beam 1 Beam 3 Figure 4. The shaded area represents the volume that received the highest radiation dose, and it is formed by the edges of the beams. It is possible to top up the beam with a small amount of dose from the contralateral side, but this obviously has implications for the dose to normal tissue on that side.
Purchase tranexamic paypal. 누난 너무 예뻐 (Replay/Boom Track ) - SHINee (Replay (mini-album)).
The earliest feeling of drowsiness should prompt the patient to pull off the road and take a nap medications with acetaminophen order tranexamic on line. Idiopathic Hypersomnia (Essential Hypersomnolence; Independent Narcolepsy) As has been indicated medicine zolpidem generic tranexamic 500 mg otc, recurrent daytime sleepiness may be the presenting symptom in a varied number of disorders other than narcolepsy and cataplexy. When chronic daytime sleepiness occurs repeatedly and persistently without known cause, it is classified as essential or idiopathic hypersomnolence. Admittedly, this condition proves difficult to distinguish from narcolepsy unless laboratory studies exclude the latter, and even then there is overlap between the two syndromes in some cases (Bassetti and Aldrich). Idiopathic hypersomnia, as defined in this manner, proves to be a rare syndrome once narcolepsy and all other causes of daytime sleepiness have been excluded. Pathologic Wakefulness this state, as remarked earlier, has been induced in animals by lesions in the tegmentum (median raphe nuclei) of the pons. Comparable states are known to occur in humans but are very rare (Lugaresi et al; see page 340). The commonest causes of asomnia in hospital practice are delirium tremens and certain drugwithdrawal psychoses. We have seen a number of patients with a delirious hyperalertness lasting a few days to a week or more after temporofrontal trauma or in association with a hypothalamic tumor (lymphoma). None of the various treatments we have tried has been successful in suppressing this state. Sleep Palsies and Acroparesthesias Several types of paresthetic disturbances, sometimes distressing in nature, may arise during sleep. Pressure of the nerve against the underlying bone may interfere with intraneural function in the compressed segment of nerve. Sustained pressure may result in a sensory and motor paralysis- sometimes referred to as sleep or pressure palsy. Usually, this condition lasts only a few hours or days, but if compression is prolonged, the nerve may be severely damaged, so that recovery of function awaits remyelination or regeneration. Deep sleep or stupor, as in alcohol intoxication or anesthesia, renders patients especially liable to pressure palsies merely because they do not heed the discomfort of a sustained unnatural posture. The patient, after being asleep for a few hours, is awakened by numbness or a tingling, prickling, "pins-and-needles" feeling in the fingers and hands. There are also aching, burning pains or tightness and other unpleasant sensations. With vigorous rubbing or shaking of the hands or extension of the wrists, the paresthesias subside within a few minutes, only to return later or upon first awakening in the morning. At first, there is a suspicion of having slept on an arm, but the frequent bilaterality of the symptoms and their occurrence regardless of the position of the arms dispels this notion. Usually the paresthesias are in the distribution of the median nerves, and almost invariably they prove to be due to carpal tunnel syndrome (see page 1167). An enuretic episode is most likely to occur 3 to 4 h after sleep onset and usually but not necessarily in stages 3 and 4 sleep. It is preceded by a burst of rhythmic delta waves associated with a general body movement. Imipramine (10 to 75 mg at bedtime) has proved to be an effective agent in reducing the frequency of enuresis. A series of training exercises designed to increase the functional bladder capacity and sphincter tone may also be helpful. Sometimes all that is required is to proscribe fluid intake for several hours prior to sleep and to awaken the patient and have him empty his bladder about 3 h after going to sleep. One interesting patient, an elderly physician with lifelong enuresis, reported that he had finally obtained relief (after all other measures had failed) by using a nasal spray of an analogue of antidiuretic hormone (desmopressin) at bedtime. Diseases of the urinary tract, diabetes mellitus or diabetes insipidus, epilepsy, sleep apnea syndrome, sickle cell anemia, and spinal cord or cauda equina disease must be excluded as causes of symptomatic enuresis. Relation of Sleep to Other Medical Illnesses the high incidence of thrombotic stroke that is apparent upon awakening, a phenomenon well known to neurologists, has been studied epidemiologically by Palomaki and colleagues. These authors have summarized the evidence for an association between snoring, sleep apnea, and an increased risk for stroke. Bruxism Nocturnal grinding of the teeth, sometimes diurnal as well, occurs at all ages and may be as distressing to the bystander as it is to the patient. It may also cause serious dental problems unless the teeth are protected in some way.