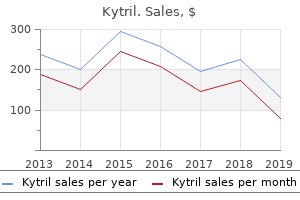
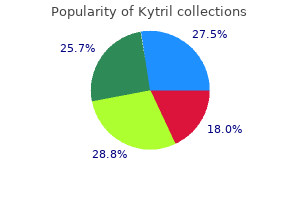
Kytril
"Purchase 1 mg kytril visa, symptoms norovirus".
By: R. Milten, M.B. B.CH., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Professor, University of Texas Medical Branch School of Medicine
After age 70 medications 5 rs cheap 1 mg kytril mastercard, people of the same age increasingly display variability in physiological functioning and physical activity medicine used for uti order 2 mg kytril amex. This is demonstrated by age-related declines in nutrient absorption and renal function. This variability may be most applicable to nutrients for which requirements are related to energy expenditure. Pregnancy and Lactation Recommendations for pregnancy and lactation may be subdivided because of the many physiological changes and changes in nutrient need that occur during these life stages. Moreover, nutrients may undergo net losses due to physiological mechanisms regardless of the nutrient intake. Reference Heights and Weights Use of Reference Heights and Weights Reference heights and weights are useful when more specificity about body size and nutrient requirements are needed than that provided by life stage categories. In some cases, where data regarding nutrient requirements are reported on a body-weight basis, it is necessary to have reference heights and weights to transform the data for comparison purposes. Frequently, where data regarding adult requirements represent the only available data. Besides being more current, these new reference heights and weights are more representative of the U. In addition, to provide guidance on the appropriate macronutrient distribution thought to decrease risk of disease, including chronic disease, Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Ranges are established for the macronutrients. These reference values have been developed for life stage and gender groups in a joint U. It also provides recommendations for physical activity and energy expenditure to maintain health and decrease risk of disease. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Zinc. Studies in human lactation: Milk volumes in lactating women during the onset of lactation and full lactation. Randomized trial of varying mineral intake on total body bone mineral accretion during the first year of life. Specific subcomponents, such as some amino acids and fatty acids, are required for normal growth and development. Other subcomponents, such as fiber, play a role in decreasing risk of chronic disease. For example, under normal circumstances the brain functions almost exclusively on glucose (Dienel and Hertz, 2001). To a large extent, the body can synthesize de novo the lipids and carbohydrates it needs for these specialized functions. An exception is the requirement for small amounts of carbohydrate and n-6 and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Otherwise, there are no specific "dietary requirements"1 for fat or carbohydrate for specific functions. Of course, some mixture of fat and carbohydrate is required as a source of fuel to meet the energy requirements of the body. It was also necessary to provide quantitative guidance on proportions of specific sources of required energy based on evidence of decreased risk of disease (which, in most cases, is chronic disease). Thus, a fundamental question to be addressed when reviewing the role of these nutrients in health is, What is the most desirable mix of energy sources that maximizes both health and longevity Because individuals can live apparently healthy lives for long periods with a wide range of intakes of specific energy nutrients, it is not surprising that this optimal mix of such sources may be difficult to define. There are no clinical trials that compare various energy sources with longevity in humans. For this reason, recommendations about the desirable composition of energy sources must be based on either short-term trials that address specific health or disease endpoints, or surrogate markers (biomarkers) that correlate well with these endpoints. A large number of research studies have been carried out to examine the effects of the composition of energy sources on surrogate markers, and these have provided a basis for making recommendations. Because diets with specific ratios of carbohydrate to fat, or specific ratios of subcomponents of each, have associations with the risk of various clinical endpoints. For any given diet consumed by an individual, the sum of the contribution to energy intake as a percentage of total intake for carbohydrate, fat, protein, and alcohol must equal 100 percent. The acceptable range of macronutrient intake is a range of intakes for a particular nutrient or class of nutrients that will confer decreased risk of disease and provide the most desirable long-term health benefits to apparently healthy individuals. Basic biological research, often involving animal models, provides critical information on mechanisms that may link nutrient consumption to beneficial or adverse health outcomes.
In a case of "semantic sleight-of-hand" (Korngold 2007 symptoms of anxiety buy discount kytril, 20) medications nursing buy kytril 2mg overnight delivery, the latter type of arrangement was termed an easement in order to avoid the restrictions linked to covenants under U. In 1981, the Uniform Law Commission approved and recommended the Uniform Conservation Easement Act for all U. Conservation easements are voluntarily pursued by landowners-not mandated by governments-who seek to benefit from an arrangement that allows them to preserve the natural integrity of the land in perpetuity while still productively using the land. Nonprofit Sector the involvement of the nonprofit sector, and par- ticularly the land trust movement, has been a critical factor in the success of the U. Nonprofit organizations provide the stewardship that maintains the conservation benefits enjoyed by society. Because the public invests in conservation through the tax benefits that accompany the creation of such easements, nonprofits must in effect be accountable for the investment of public funds. Perpetual Stewardship the restrictions placed on the property in or- der to preserve its natural integrity may be for a specified period of time or in perpetuity. It is important to note that many of the financial incentives offered by the government only apply when landowners place restrictions on their property in perpetuity, making these forms of conservation easements more popular. Elsewhere in the world, however, the provision of these fi nancial incentives has been a challenge. In Latin America, many countries have been unable or unwilling to take such measures, especially during the recent financial crisis; the only country in the region that has been able to offer and maintain substantial financial incentives for conservation easements is Costa Rica (Environmental Law Institute 2003). Although there is an ongoing initiative to formalize and legislate an incentive scheme to encourage conservation by private landowners (Ministry of Natural Resources and the Environment 2010), the lack of a financial structure leaves the effort at a great disadvantage. Unlike Belize, and despite the absence of a policy and legislative framework to support conservation easements, Trinidad has a financial structure in place that could potentially be used to promote easement creation: the Green Fund, established by the government in 2001 under the Miscellaneous Taxes Act. This stipulation suggests that the use of the Green Fund to provide financial incentives to private landowners who use conservation easements to achieve biodiversity protection and the maintenance of ecosystem ser vices on private lands is a policy-supported option. Despite the obstacles to meeting this prerequisite, Trinidad and Tobago can learn from nearby success stories when considering ways to enact their own conservation easements. As part of the program, landowners have the option of entering into one of three types of contracts that creates legal easements that remain with the property even if it is sold. The three types of contracts provide varying degrees of financial incentives (all in the form of monetary payments) based on the level of conservation activities on the property: forest conservation, reforestation, or sustainable forest management. Legal Requirements In the United States, clear and strong legal support has been critical to the success of the conservation easement movement. Within Latin America, the lack of a secure legal framework to support private conservation programs has been a primary challenge to implementation of this system. Despite the lack of any national law that recognizes the use of perpetual easements for conservation purposes or the creation of in gross easements that involve an independent third party, countries have still found ways to use these instruments (Environmental Law Institute 2003). Environmental nonprofits have been creatively using traditional appurtenant easements under the civil code to form easements with conservation-minded landowners. Costa Rica pioneered the use of traditional laws to facilitate the creation of easements in 1992, and these efforts have now spread to other Latin American countries (Swift et al. Environmental law groups in Latin America have made progress in seeking legislative reform that allows for in gross easements that can be held by third-party entities such as nonprofits in order to provide the necessary support for effective private land conservation in the region (Environmental Law Institute 2003). Countries such as Chile, Costa Rica, and Ecuador have introduced proposed laws authorizing in gross easement. Rather than borrow an instrument from another legal system, this tool has been created to serve as a functional, flexible, and enforceable legal instrument especially for private conservation initiatives in Chile (Levitt 2010). Because it is adaptable to any nation with a Napoleonic legal system, it is under review by countries such as Argentina, which has large tracts of privately owned land requiring protection. In Belize, representatives from environmental management organizations have drafted a framework that would provide legal support for an existing system of private protected areas and private landowner initiatives to conserve land.
Order generic kytril on-line. Trigeminal Neuralgia Symptoms.
Potential threats include the loss of knowledge associated with traditional food-processing practices that are in decline and the effects of climate change on microbial communities treatment ulcerative colitis order kytril online from canada. Key tasks include improving frameworks for quality control of microbial products and for evaluating potential risks to human health or to the environment treatment using drugs purchase kytril overnight delivery, improving registration policies for microbial products, improving education and awarenessraising, and strengthening research and conservation networks. Considerable progress has been made in this regard in recent years, but fundamental knowledge gaps remain to be addressed. Genetic-improvement activities Genetic-improvement programmes for domesticated crops and livestock are well established globally, although many species and within-species populations are neglected. Programmes for trees and species used in aquaculture are becoming more widespread. There could be benefits in extending domestication and genetic-improvement activities to other invertebrate species that contribute to food and agriculture, including stingless bees, which have been found to be more effective pollinators than honey bees for certain crops, and insects that can be raised for human consumption or as animal feed. Efforts are also being made to develop methods for assisted evolution of climate resilience in corals. Especially with respect to ex situ conservation, there are still technical barriers to the long-term conservation of some species. Overcoming these gaps and constraints will often require increased funding, better training of relevant personnel and better provision of technical resources. Where skills are concerned, improving capacity in the fields of taxonomy and systematics is a widespread priority. Conservation-related education, training and awareness-raising activities for stakeholders at all levels from producers to policy-makers need to be strengthened. Maintenance and transfer of relevant traditional knowledge should be supported and facilitated. Productive landscapes and seascapes need to include the habitat features necessary to support the associatedbiodiversity species that underpin food and agricultural production. Ensuring that this is the case will, in places, require the restoration of degraded habitats and maintaining or recreating wildlife corridors linking patches of habitat. Given their focus on integrated action across multiple scales and on accounting for the interests and concerns of a wide range of stakeholders, ecosystem, landscape or seascape approaches (see above) may provide useful frameworks. Strategies need to be put in place that allow nutritional benefits to be realized in a sustainable way and threats such as overharvesting to be identified and addressed. Synergies between the food and agriculture and environmental sectors, in particular, need to be strengthened. Constraints to cooperation often relate to a lack of mechanisms for exchanging information among and between stakeholder groups or a lack of participatory decision-making processes. Mechanisms for involving small-scale producers, and women and youth in particular, in decision-making processes need to be improved. Training and awareness-raising on the organization of collaborative initiatives is also needed. Improving coordination and linkages between institutes nationally, and at regional and international levels, potentially provides opportunities both to strengthen interdisciplinary work and to allow more efficient use of resources and information. Links between research and practical management at production-system level also need to be improved. Biodiversityrelated issues tend not to be well integrated into higher-education courses on food and agriculture or on other aspects of land use. Courses related to biodiversity conservation are often disconnected from those related to the use of biodiversity. There is often also a need to improve the supply of graduates trained in specific fields such as taxonomy, economic valuation and cryoconservation. Ongoing capacity development among professionals and technicians is also essential. Research programmes need to be strengthened and the necessary research infrastructure put in place, including by addressing shortages of specialists in relevant fields. This in turn creates the need to strengthen educational curricula and improve training (see next subsection). All these measures will require adequate funding, as will improving the dissemination of research results. Strengthening research-related information systems, such as systems for monitoring the status and trends of components of biodiversity or for managing relevant geographical data, is a widespread priority, both as a means of disseminating research outputs and as a means of making relevant information available to researchers. Improving the state of education and training will require addressing shortfalls in funding and improving cooperation and exchange of information between educational institutions and between them and other stakeholder groups.
Women with highest level of dietary calcium intake had 20 percent lower risk of breast cancer symptoms juvenile diabetes purchase genuine kytril line. For estrogen receptor positive tumors symptoms ulcerative colitis buy kytril visa, higher levels of dietary calcium, vitamin D, and dairy were each associated with 20-30 percent decreased risk of breast cancer. This study did not inquire about sun exposure or measure serum levels of vitamin D. The Ecology of Breast Cancer 130 risk of breast cancer than those with levels < 13 ng/mL. A recent meta-analysis of 9 studies (5 case-control; 4 nested case-control) reported that seven of the nine studies showed a lower incidence of breast cancer with higher serum levels of vitamin D. This finding supports the hypothesis that there is a threshold effect of vitamin D on breast cancer risk and that intervention trials should be designed to use enough vitamin D to raise serum levels at least into the 30-35 ng/mL range. After an average follow up of 7 years, there was no difference in breast cancer incidence in the two groups. However, further analysis of data showed that women who were not taking vitamin D or calcium supplements at the time the study began and who were assigned to the vitamin D-calcium supplement intervention group had 14-20 percent decreased risk of all cancer, breast cancer, and invasive breast cancer over seven years of follow up. Compared to women taking placebo, the risk of any cancer was 60 percent lower in the vitamin D plus calcium group and 47 percent lower in the calcium-only group. Detailed information was collected about the amount of time spent out of doors at various ages. A decreased risk of breast cancer was associated with increasing time spent outdoors (>21 vs < 6 hrs/ week) during the teenage years (29 percent lower risk), 20s-30s (36 percent lower risk), 40s-50s (26 percent lower risk), and 60s-75 years (50 percent lower risk), all statistically significant. Cod liver oil is a rich source of vitamin D and milk a source of both vitamin D and calcium. Vitamin D post-diagnosis and recurrence A study of 12,019 breast cancer survivors from four different cohorts in the U. However, people of color, particularly African-Americans, and older people are among those with significantly lower levels. Dietary reference intakes are intended to improve public health in the general population and provide recommendations for adequate and safe daily intakes of nutrients consumed over many years, possibly a lifetime. Thus, the committee said, the need for sound, causal evidence to make recommendations is essential. The Ecology of Breast Cancer 134 the major hypothesized mechanism by which shift work and disrupted circadian rhythm might influence breast cancer risk is through alteration in melatonin levels. Melatonin is a hormone secreted by the pineal gland, located in the middle of the brain. People who are blind tend to have reduced spikes of melatonin, but higher baseline levels that vary considerably among individuals. People who work at night may spend less time outdoors in sunlight during the day and thereby have lower vitamin D levels. Most studies have examined breast cancer risk as it relates to shift work although some have also investigated prostate, colon, and uterine cancer risks. Six of those studies, including two prospective cohort studies in nurses, showed a modestly increased risk of breast cancer in long-term employees who worked night shifts. A more recent systematic review and meta-analysis identified 12 case-control and four cohort studies examining night shift work as a risk factor for breast cancer. This analysis excluded studies of airline crews because of other potentially com135 the electromagnetic spectrum and breast cancer plicating exposures such as cosmic radiation and time-zone changes. The authors reported a nine percent increased risk per five years of night-shift work in case control studies but no increased risk in cohort studies. Of six studies that have investigated sleep duration and breast cancer, three found no association,55,56,57 one reported an increased risk with increased sleep duration58, one found an increased risk with short sleep duration (<6 hrs/day),59 and one reported a decreased risk with increasing sleep duration and no association with sleep quality. Erren proposed a "sleep-years" index to assess cumulative sleep over decades as a possible approach. In the 20th century it became clear that ionizing radiation could cause mammary gland tumors in laboratory animals and breast cancer in women who had undergone chest fluoroscopy for tuberculosis or X-irradiation for mastitis and in survivors of the atomic bombing in Japan. Some people believe that current regulations, promulgated in 1996 with minor updates in 2003, are out-of-date and not based on more current information that looks beyond thermal effects of exposure. The field abounds with skeptics convinced that radiation of insufficient energy to break chemical bonds, ionize atoms, and at least produce heat cannot possibly be harmful.