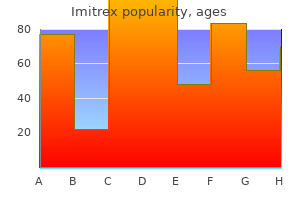
Imitrex
"Generic 25 mg imitrex, spasms right before falling asleep".
By: G. Cobryn, M.A., Ph.D.
Professor, George Washington University Medical School
Most of the studies that met criteria for evidence evaluated interventions providing sensory aids spasms muscle pain purchase imitrex us, hearing aids muscle relaxant otc usa imitrex 25mg low price, tactile aids, or cochlear implants to infants and young children. The effects of hearing loss and age of intervention on some language metrics in young hearing-impaired children. Early referral for hearing testing and hearing aid fitting is correlated with better levels of expressive spoken language for children with mild to severe hearing loss. For children with moderate hearing loss who are fitted with hearing aids, the highest correlation with better language outcomes is the age of referral. Cochlear Implants this section evaluates the use of cochlear implants in infants and young children. Enhancement of expressive language in prelingually deafened children with cochlear implants. Children who receive cochlear implants at 2 to 3 years of age appear to have similar expressive and receptive language scores when compared with children who had implants between 3 and 5 years of age. Both groups show improvement in speech production and language acquisition over time (although the use of other interventions after implantation may influence outcomes) (Brackett 1998). Children receiving cochlear implantation at a mean age of 50 months can significantly improve their language development rate as measured at 12 months postimplantation (although timing of the intervention, the use of additional interventions, and demographics such as age of onset of hearing loss may influence outcomes) (Miyamoto 1997/Robbins 1997). Children who receive cochlear implants at a young age have more improvement in speech perception and speech intelligibility during the first 24 months postimplantation (Nikolopoulos 1999). Children who receive cochlear implants can improve in recognition of speech sound units (phonemes) when using both oral and total communication regardless of the intervention program (Svirsky 1999). Children who receive cochlear implantation have greater improvement in vocal and auditory communication than children who use hearing aids as measured one year after implantation have (Tait 1994). Children who receive cochlear implants have significantly higher receptive language scores over time than do pair-matched children who use hearing aids. This seems to occur even when the implantation group has worse pure-tone audiometric thresholds and statistically significant lower receptive language development curves than the control group has prior to implantation. However, individual maturation and duration of deafness may influence outcomes (Truy 1998). Communication Interventions this section evaluates the use of communication interventions for infants and young children. Early intervention and language development in children who are deaf and hard of hearing. The Deaf Mentor Experimental Project for young children who are deaf and their families. The development of deaf and hard of hearing children identified early through the high-risk registry. Panel Conclusions (Communication Interventions) Effects of early intervention on communication, language, and general development 1. Early intervention can improve outcomes in children with identified hearing impairments regardless of the degree of hearing loss, mode of communication, cognitive ability, or socio-economic status (YoshinagaItano 1998B). Early diagnosis, early intervention, and family involvement are important factors in achieving better language outcomes regardless of the age of onset, degree of hearing loss, or type of intervention (Moeller 2000). Children who are identified with hearing loss by the age of 6 months who receive intervention within 2 to 3 months of diagnosis have better receptive language outcomes than do children who are identified and receive intervention after the age of 18 months. However, it is not clear whether the delay is due to receiving more total intervention or beginning the intervention at an earlier age (Yoshinaga-Itano 1998A). For children with severe and profound hearing loss, the age of enrollment in a generic early intervention program has a significant effect on receptive language when measured at 3 to 5 years of age.
A right ventricular lift spasms nose order imitrex australia, elevated neck veins muscle relaxant hair loss order 100mg imitrex amex, ascites and edema are later signs of right ventricular overload with pulmonary hypertension. Digoxin: is indicated for patients with atrial fibrillation to control the heart rate, since tachycardia will further decrease left ventricular filling, reduce cardiac output and increase left atrial pressure, leading to more symptoms. This compensated phase of mitral regurgitation varies in duration but may last many years. The prolonged state of volume overload may eventually lead to decompensate mitral regurgitation. This phase is characterized by impaired left ventricular function, decreased ejection fraction and pulmonary congestion. An S3 gallop indicates severe disease but does not necessarily indicate heart failure There may be displacement of the left ventricular impulse A holosystolic murmur that may radiate to the axilla, the upper sternal borders or the subscapular region is apparent on physical examination. Salt restriction Vasodilators: afterload reduction with vasodilators has been shown to improve left ventricular performance. Treatment of atrial fibrillation if it occurs Endocarditis prophylaxis is important essential. Therefore, surgery is indicated if left ventricular dysfunction has begun to develop, even in the absence of symptoms. Mitral Valve Prolapse Mitral valve prolapse occurs when varying portions of one or both leaflets of the mitral valve extend or protrude abnormally above the mitral annulus into the left atrium. The clinical course is often benign Most patients are asymptomatic and may remain so for their entire lives. Some patients may manifest with features of Mitral regurgitation Arrhythmias like premature ventricular contractions and ventricular tacycardias may occur as complications. The mid-systolic click, often accompanied by a late systolic murmur, is the auscultatory hallmark of mitral valve prolapse. Successful management of patients with valvular heart disease requires an evidence-based approach to echocardiography and to surgical intervention. Most patients with acquired valvular heart disease are at risk for developing endocarditis and should receive prophylactic antibiotics. Infective Endocarditis Learning objectives: at the end of this lesson the student will be able to: 1) Define valvular heart Infective endocarditis. The intracardiac effects of this infection include severe valvular insufficiency, which may lead to intractable congestive heart failure and myocardial abscesses. Infective endocarditis affects not only the heart, but also produces a wide variety of systemic signs and symptoms through several mechanisms, including both sterile and infected emboli and a variety of immunological phenomena. Classification of Infective endocarditis: depending on the type of valve affected 1. However Native valve endocarditis is the commonest type of Infective endocarditis in Ethiopia and other developing countries. The course is insidious even in untreated cases which may extend over many months. Group D streptococci: the source for this bacterium is the gastrointestinal or genitourinary tract. Pathophysiology: All cases of infective endocarditis develop from a commonly shared process: 1.
Fulminant muscle relaxant gel purchase discount imitrex, fatal viral pneumonia may occur and death may follow as soon as 48 hr after onset muscle relaxant list by strength purchase imitrex 50mg overnight delivery. Prophylaxis: Vaccines that include the prevalent strains of influenza viruses effectively reduce the incidence of infection. Amantadine 100mg orally bid (for adults) can be used prophylactically against influenza A. It may develop after a common cold or other viral infection of the nasopharynx, throat or tracheobronchial tree, often with secondary bacterial infection. Scattered rhonchi and wheezes may be heard, as well as occasional crepitations at the bases. In persons who do not respond to antibiotics, gram stain and sputum culture is necessary. Specific Treatment Antibiotics should be given when purulent sputum and persistent fever are present. Pneumonia Learning Objective: At the end of this unit the student will be able to 1. Refer complicated cases of Pneumonia Pneumonia is an acute infection of lung parenchyma including alveolar spaces and interstitial tissue. Other means include hematogenous dissemination, via the lymphatics, or directly from contiguous infections. Microbial Pathogen that cause Pneumonia: depend on the setting in which pneumonia is acquired 1. Community-acquired pneumonia o o o o o o o o Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcal pneumonia) commonest cause Mycoplasma pneumoniae Chlamydia pneumoniae Haemophilus influenza Oral anaerobic bacteria Staphylococcus aureus Legionella pneumophila Mycobacterium tuberculosis 2. Aspiration pneumonia: this occurs when large amount of oropharyngeal or gastric contents are aspirated into the lower respiratory tract. Hospital-acquired pneumonia: a patient is said to have hospital acquired pneumonia if the symptoms begin 48 hours after hospital admission and not incubating at the time of admission. Clinical Presentation of community acquired pneumonia Community acquired pneumonia can have typical or atypical presentations. There will be pulmonary signs of consolidation (lobar pneumonia), which are Increased tactile fremitus and vocal fremitus, dullness on percussion Bronchial breath sound, egophony, wispering pectoriloquy, crackles and pleural friction rub. Some viruses like influenza virus, Varicella zoster virus and cytomegalovirus may cause "atypical" pneumonia. Prominence of systemic symptoms like headache, malign, fatigue, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. Chest findings on physical examination are minimal even though X-ray changes are marked. Presumptive diagnosis can be made from history, changes on chest x-ray, blood and sputum culture and sputum Gram stains. If a patient does not improve, the following factors should be considered: Wrong etiologic diagnosis Adverse drug reaction Far advanced case or superinfection Inadequate host defenses due to associated condition Non-compliance to the drug regimen in outpatients Antibiotic resistance of the strain and Complications like empyema requiring drainage, or metastatic foci of infection requiring higher doses.
Diminution or absence of deep tendon reflexes can occur with lower motor neuron disorders muscle relaxant drug list cheap imitrex 25 mg online, whereas increased reflexes and an abnormal plantar reflex can be signs of upper motor neuron dysfunction spasms multiple sclerosis generic imitrex 25mg without a prescription. Neuromotor dysfunction can be accompanied by sensory deficits and should be assessed by testing touch and pain sensation. In older children, difficulties with sequential motor planning, or praxis, should be differentiated from strength and extrapyramidal problems. Dyspraxia refers to the inability to formulate, plan, and execute complex movements. Assessment includes the presence and quality of age-appropriate gross motor skills (stair climb, 1-foot stand, hop, run, skip, and throw) and fine motor skills (button, zip, snap, tie, cut, use objects, and draw). Measure Creatine Phosphokinase and Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Concentrations When low to normal tone is identified, especially with concomitant weakness, investigations should target diseases of the lower motor neurons or muscles. As an X-linked disorder, there may be a family history of other affected male family members on the maternal side. Other neuromuscular disorders include diseases of the peripheral motor nerves or muscles, such as myotonic dystrophy, spinal muscular atrophy, mitochondrial disorders, and congenital myasthenia gravis. Testing for these diseases should be performed by subspecialists, because these patients often require electrodiagnostic or specific genetic testing. After identifying concerns of motor development, primary care clinicians can perform key diagnostic tests. Family history is also important to identify any other relatives with developmental or motor issues, recurrent pregnancy loss, stillbirth, or infant death, which may lead to identification of an underlying genetic etiology. Findings on physical examination, such as unusual facial features or other known visceral anomalies, may suggest a specific genetic condition. The state-mandated newborn screening laboratory results should be reviewed, because normal results exclude many disorders and avoid unnecessary testing. Although newborn screening is comprehensive, it does not test for all inborn biochemical disorders. Table 3 lists "red flags" that should prompt the primary care pediatrician to expedite referral to diagnostic resources. Consider Neuroimaging Increased tone in a child with neuromotor delay suggests an upper motor neuron problem, such as cerebral palsy. It is reasonable to perform thyroid function studies (thyroxine [T4] and thyroidstimulating hormone) as part of the general laboratory evaluation for children with low tone or neuromuscular weakness, even without classic signs of thyroid disease. Cerebral palsy classically presents with spasticity, dystonia, or athetosis, but may also result in hypotonia. Children with cerebral palsy may have a history of perinatal insult with concomitant abnormalities on brain imaging. Other causes of hypotonia should be considered before the diagnosis of hypotonic cerebral palsy is given to a child with an uneventful perinatal history and normal brain imaging. It can affect gait, handwriting, sports and academic participation, and self-help skills. The American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics recommends microarray testing as the first-line chromosome study. Routine chromosome testing may be appropriate for children with weakness suspected as having recognizable disorders, such as Down syndrome (including mosaic Down syndrome), Turner syndrome, and Klinefelter syndrome. Fragile X syndrome is the most common inherited cause of cognitive impairment, and children with fragile X syndrome may have some element of motor delay. Genetic testing for fragile X syndrome should be considered in both boys and girls, whether they have dysmorphic facial features or a family history. Noonan syndrome is genetically heterogeneous and may be caused by mutations in genes in the ras pathway. Refer to Early Intervention/Child Find, and Consult/Refer to Appropriate Pediatric Subspecialists, and Perform Remainder of Bright Futures Health Supervision Examination Observation Mild abnormalities that are not accompanied by "red flag" findings (red flag conditions necessitate prompt referral) may be closely followed through "observation," but a plan for new or worsening symptoms as well as a time-definite follow-up plan must be developed.
Order imitrex 50 mg online. Black Seed Cream - Africa Imports.