Asacol
"Buy asacol with a visa, treatment molluscum contagiosum".
By: M. Thorald, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, University of California, Riverside School of Medicine
A previously healthy 6-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of a 1-week history of right knee pain and swelling medicine you cannot take with grapefruit order asacol master card. He went camping with his father in eastern Pennsylvania approximately 2 months ago medications ending in pam order asacol with visa. Two weeks after the trip, he had a solid red rash that slowly spread over most of his right thigh and resolved spontaneously 2 weeks later. Examination of the right knee shows swelling, an effusion, and mild tenderness to palpation. An 8-year-old boy is brought to the physician by his mother for a well-child examination. His mother reports that she is exhausted because he is constantly "on the go," is increasingly difficult to manage, and needs constant supervision. Last week, he climbed out on the roof of their house "just to see how high up it was. His mother says that he wakes up cheerful and full of energy each morning and that he says he will "really try to be good. After the examination, his mother becomes tearful and says she does not know what to do. A previously healthy 10-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his parents immediately after the sudden onset of difficulty breathing that began when he was stung on the arm by a bee. A 16-year-old girl is brought to the physician because of severe acne over her face and upper back for 6 months. Examination shows numerous papules and pustules with widespread erythema over the face and upper back. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial step prior to treatment with isotretinoin A 3-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department 2 days after the onset of fever, profuse watery diarrhea, and progressive lethargy. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step to decrease the risk of acute renal failure in this patient A 3-year-old girl with Down syndrome is brought to the physician because of a 1-week history of frequent nosebleeds, decreased appetite, and lethargy. Laboratory studies show: Hemoglobin Hematocrit Leukocyte count Segmented neutrophils Atypical lymphocytes Platelet count 6. Her blood pressure is 140/80 mm Hg in the left arm and 105/70 mm Hg in the left leg. A grade 2/6 systolic murmur is heard best over the upper back to the left of the midline. Breast development is Tanner stage 2, and pubic hair development is Tanner stage 1. An 11-year-old girl with cystic fibrosis is admitted to the hospital 18 hours after the onset of shortness of breath. During the past 11 years, she has had more than 20 episodes of respiratory exacerbations of her cystic fibrosis that have required hospitalization. Current medications include an inhaled bronchodilator, inhaled corticosteroid, oral pancreatic enzyme, and oral multivitamin. A 3-week-old infant is brought to the physician by his mother because of a 1-week history of increasingly frequent vomiting. She says that at first he vomited occasionally, but now he vomits after every feeding. A 15-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her mother because of a 1-year history of monthly cramps that begin 2 days before menses and last 3 days. She is unable to practice with her volleyball team because of the pain and typically misses 2 days of school monthly.
Three conserved histidine residues (positions 131 medicine q10 purchase 400 mg asacol free shipping, 133 symptoms of colon cancer purchase generic asacol canada, and 135) shown in green comprise a "histidine triad" motif (HxHxH), which may mediate the 296 Walt Ream 4. This interaction is specific for the C-terminal region of VirD2, which includes the nuclear localization sequence (Figure 8-4), and it may affect nuclear import of VirD2. Phosphorylation of serine residues near a nuclear localization sequence can simulate nuclear import. The cyclophilin CypA binds amino acids 274-337, whereas Roc1 binds amino acids 174-337. A deletion that removes amino acids 338-356 does not affect VirD2 function (Shurvinton et al. The cellular function of these cyclophilins is not known, but they may act as chaperones that assist protein folding. CypA interacts strongly with residues 274-337 of VirD2, whereas Roc1 interacts weakly with residues 174-337 (Deng et al. In addition, most of this region is very poorly conserved among different VirD2 proteins (Figure 8-4), and it adjoins a region not required for VirD2 function (residues 338-356) (Shurvinton et al. Cyclosporin A, which disrupts the interaction of VirD2 with cyclophilins, also inhibits Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of plant cells (Deng et al. This approach is important for species recalcitrant to regeneration from tissue culture, because cells within embryos can be transformed. This provides an opportunity to obtain marker-free transgenic plants by transient selection of kanamycin-resistant plant cells (Rommens et al. Plant cells that express the kanamycin resistance gene transiently (but fail to inherit this gene stably) can be selected by temporary growth on medium containing kanamycin, and a significant fraction of these cells are stably transformed with the desired transgene (Rommens et al. Although such homologous recombination events can occur during plant transformation, they constitute a very small fraction of the total number of integration events. The chromosomal location of a transgene can affect expression of both the transgene and chromosomal genes at the site of insertion. Usually, plant scientists must examine hundreds (or thousands) of transformed plants to find one that exhibits appropriate transgene expression without affecting other important agronomic traits. An efficient integration system based on homologous recombination would allow engineers to place transgenes at specific chromosomal locations that allow good transgene expression without affecting host genes. For these reasons, an efficient transformation method that allows control over transgene insertion site is an important tool that plant genetic engineers currently lack. J Mol Biol 271: 718-727 Citovsky V, Warnick D, Zambryski P (1994) Nuclear import of Agrobacterium VirD2 and VirE2 proteins in maize and tobacco. Mol Cell Biol 18: 3907-3914 Covacci A, Rappuoli R (1993) Pertussis toxin export requires accessory genes located downstream from the pertussis toxin operon. Science 294: 23232328 Guyon P, Chilton M-D, Petit A, Tempe J (1980) Agropine in "null-type" crown gall tumors: evidence for the generality of the opine concept. J Bacteriol 182: 1541-1548 Hansen G, Chilton M-D (1996) "Agrolistic" transformation of plant cells: integration of T-strands generated in planta. Mol Microbiol 43: 1523-1532 Kunik T, Tzfira T, Kapulnik Y, Gafni Y, Dingwall C, Citovsky V (2001) Genetic transformation of HeLa cells by Agrobacterium. J Biol Chem 267: 20471-20480 Lessl M, Lanka E (1994) Common mechanisms in bacterial conjugation and Timediated transfer to plant cells. Plant Cell 8: 873-886 Otten L, DeGreve H, Leemans J, Hain R, Hooykass P, Schell J (1984) Restoration of virulence of vir region mutants of Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain B6S3 by coinfection with normal and mutant Agrobacterium strains. Mol Gen Genet 190: 204-414 Petit A, Tempe J, Kerr A, Holsters M, Van Montagu M, Schell J (1978) Substrate induction of conjugative activity of Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res 12: 6031-6041 Sheng J, Citovsky V (1996) Agrobacterium-plant cell interaction: have virulence proteins - will travel. Science 279: 873-876 Wang K, Herrera-Estrella A, Van Montagu M (1990) Overexpression of virD1 and virD2 genes in Agrobacterium tumefaciens enhances T-complex formation and plant transformation. The T4S systems are structurally complex machines assembled from a dozen or more membrane proteins often in response to environmental signals. Christie picture of the VirB/D4 T4S system as multifunctional and structurally dynamic.
Buy discount asacol. How to Spot the Symptoms of Autism | Child Psychology.
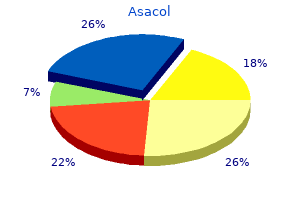
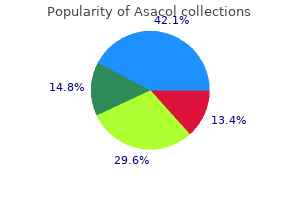
Mora De La India (Morinda). Asacol.
- Colic, seizures, cough, diabetes, urinary problems, menstrual problems, fever, liver problems, constipation, vaginal discharge, nausea, smallpox, enlarged spleen, kidney disorders, swelling, asthma, bone and joint problems, cancer, eye cataracts, colds, depression, digestion problems, stomach ulcers, heart trouble, high blood pressure, infections, migraine, stroke, pain, reducing signs of aging, and other conditions.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Noni?
- Dosing considerations for Noni.
- How does Noni work?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96740
In relatively industrialized nations treatment hpv proven asacol 400 mg, the neurologic reflections of Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome are frequently associated with chronic alcoholism with limited food consumption (9) symptoms 6 days before period due buy asacol 800mg on-line. Some cases of thiamin deficiency have been observed with patients who are hypermetabolic, are on parenteral nutrition, are undergoing chronic renal dialysis, or have undergone a gastrectomy. Thiamin deficiency has also been observed in Nigerians who ate silk worms, Russian schoolchildren (in Moscow), Thai rural elderly, Cubans, Japanese elderly, Brazilian Xavante Indians, French Guyanense, Southeast Asian schoolchildren who were infected with hookworm, Malaysian detention inmates, and people with chronic alcoholism. Hence, when there is insufficient thiamin, the overall decrease in carbohydrate metabolism and its inter-connection with amino acid metabolism (via -keto acids) have severe consequences, such as a decrease in the formation of acetylcholine for neural function. Biochemical indicators Indicators used to estimate thiamin requirements are urinary excretion, erythrocyte transketolase activity coefficient, erythrocyte thiamin, blood pyruvate and lactate, and neurologic changes. The excretion rate of the vitamin and its metabolites reflects intake, and the validity of the assessment of thiamin nutriture is improved with load test. Thiamin status has been assessed by measuring urinary thiamin excretion under basal conditions or after thiamin loading, transketolase activity, and free and phosphorylated forms in blood or serum (6, 9). Although overlap with baseline values for urinary thiamin was found with oral doses below 1 mg, a correlation of 0. In some cases the activity coefficient may appear normal after prolonged deficiency (14). This measure seemed poorly correlated with dietary intakes estimated for a group of English adolescents (15). Certainly, there are both inter-individual and genetic factors affecting the transketolase (16). Factors affecting requirements Because thiamin facilitates energy utilisation, its requirements have traditionally been expressed on the basis of energy intake, which can vary depending on activity levels. Intakes below this amount lead to irritability and other symptoms and signs of deficiency (24). Taking into account an increased growth in maternal and foetal compartments, an overall additional requirement of 0. Because the deficiency almost invariably occurs combined with a deficiency of other B-complex vitamins, some of the symptoms. The major cause of hypo-riboflavinosis is inadequate dietary intake as a result of limited food supply, which is sometimes exacerbated by poor food storage or processing. Children in developing countries will commonly demonstrate clinical signs of riboflavin deficiency during periods of the year when gastrointestinal infections are prevalent. Decreased assimilation of riboflavin also results from abnormal digestion such as that which occurs with lactose intolerance. This condition is highest in African and Asian populations and can lead to a decreased intake of milk as well as an abnormal absorption of the vitamin. Absorption of riboflavin is also affected in some other conditions, for example, tropical sprue, celiac disease, malignancy and resection of the small bowel, and decreased gastrointestinal passage time. In relatively rare cases the causes of deficiency are inborn errors in which the genetic defect is in the formation of a flavoprotein. Also at risk are those receiving phototherapy for neonatal jaundice and perhaps those with inadequate thyroid hormone. Some cases of riboflavin deficiency were also observed in Russian schoolchildren (Moscow) and Southeast Asian schoolchildren (infected with hookworm). Toxicity Riboflavin toxicity is not a problem because of limited intestinal absorption. Biochemical indicators Indicators used to estimate riboflavin requirements are urinary flavin excretion, erythrocyte glutathione reductase activity coefficient, and erythrocyte flavin. The urinary flavin excretion rate of vitamin and metabolites reflects intake; validity of assessment of riboflavin adequacy is improved with load test.
Pairing of strains with Different A medicine for anxiety order asacol australia, different B idiomorphs (dikaryon) Events observed 1 Septal dissolution 2 Nuclear migration 3 Clamp branches arise and fuse with hypha 1 Septa dissolve 2 Nuclei migrate 1 Septa remain intact 2 No nuclear migration 3 Clamp branches arise but do not fuse 1 No septal dissolution 2 No nuclear migration 3 No clamp connections Common A symptoms joint pain fatigue purchase 800 mg asacol fast delivery, different B idiomorphs Common B, different A idiomorphs Common A, common B idiomorphs and a successful mating will occur between any two strains that differ from one another at each locus. This greatly increases the chances of finding a mate, compared with fungi that have only two idiomorphs. Strains derived from haploid basidiospores are monokaryons and they can fuse with other compatible monokaryons to form a dikaryon. All subsequent growth involves the synchronous division of the two nuclei in each hyphal compartment and their regular distribution as nuclear pairs throughout the mycelium. In several members of the group this regular arrangement is aided by the production of clamp connections (see. Eventually, the dikaryotic colony will produce a fruitbody, and nuclear fusion and meiosis occur in the basidia. By experimentally pairing strains with the same A or the same B ideomorph, it has been possible to deduce the regulatory roles of the A and B loci (Casselton et al. In pairings of strains with the same A and same B (common A, common B) there is no septal breakdown, no nuclear migration, no dikaryotization, and no clamp connections. Pairings of strains with different A but common B loci show nuclear pairing, synchronous division of the nuclei and formation of clamp branches; but the dolipore septa do not break down, and the clamp branches do not fuse with the parent hypha. Pairings of strains with different B but common A lead to septal dissolution but none of the other events. Septal dissolution coincides with a marked increase in the activity of -glucanase in the hyphae, indicating that the B locus controls the derepression of glucanase genes. Development of fruitbodies the toadstools, brackets and other fruitbodies of Basidiomycota are the largest and most complex differentiated structures in the fungal kingdom. Here we consider one example where a start has been made to dissect this process at the biochemical and molecular level, and we end with a discussion of commercial mushroom production because of its economic importance. Further development from the primordia occurs when carbon nutrients are depleted from the medium, and is then fuelled by carbon reserves within the mycelium. Early in this process the mycelial storage compounds such as glycogen are converted to sugars, which are translocated to the developing primordia. Then, as the sugar levels in the hyphae decline, the hyphal walls begin to break down and the breakdown products are translocated to the primordia. The wall glucans seem to provide the major source of sugars, because fruitbody development is associated with a marked rise in glucanase activity in the mycelia. We have already seen that synthesis of this enzyme is derepressed by the B mating-type locus, but it is still subject to catabolite repression by sugars; so its generalized activity in the hyphae, as opposed to its localized activity in degrading septa, depends on depletion of the mycelial sugar reserves. The breakdown of hyphal walls to recycle nutrients for differentiation is, in fact, quite common in fungi. The breakdown of wall glucans also fuels the developing ascocarps of Emericella nidulans. Wessels and his colleagues (see Wessels 1992) identified several differentiation-associated genes in S. In order to do this, they crossed and repeatedly back-crossed strains to generate monokaryons that were essentially isogenic except for the mating-type locus. All these comparisons were made in two sets of conditions: (i) for 2-day-old colonies, when the monokaryons and dikaryons were growing as mycelia with similar colony morphology, and (ii) for 4-day-old colonies grown in light, when the monokaryon had produced copious aerial hyphae but the dikaryon had produced numerous small fruitbodies. Some of these 37 occurred only in the fruitbodies; others were found in both the fruitbodies and the mycelium of the dikaryon. They were scarce in young vegetative colonies of both strains, and they remained scarce in the monokaryon, but they increased in the dikaryon when this began to fruit. Hydrophobin genes have been shown to contain a putative signal peptide sequence at the N-terminus, a feature associated with secretion from the hyphal tips.