Dilantin
"Purchase 100 mg dilantin overnight delivery, symptoms 2 days after ovulation".
By: T. Rozhov, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Deputy Director, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine
Primary outcomes at 12-month follow-up were Oswestry Disability Index and pain intensity symptoms gallstones cheap 100 mg dilantin fast delivery, measured with numeric rating scale medications erectile dysfunction purchase dilantin 100mg otc. Inclusion criteria were as follows: age between 18 and 65 years, diagnosed with non-specific chronic low back pain for >3 months, localized pain from T12 to gluteal folds, provoked with postures, movement and activities. A total of 121 patients were randomized to either classification-based cognitive functional therapy group n = 62) or manual therapy and exercise group (n > = 59). Results: the classification-based cognitive functional therapy group displayed significantly superior outcomes to the manual therapy and exercise group, both statistically (p < 0. For Oswestry Disability Index, the classification-based cognitive functional therapy group improved by 13. For pain intensity, the classification-based cognitive functional therapy improved by 3. Conclusions: the classification-based cognitive functional therapy produced superior outcomes for non-specific chronic low back pain compared with traditional manual therapy and exercise. The patients were recruited from March 2006 to June 2008 from private physiotherapy outpatient practices, general practitioners and the outpatient spine clinic at the Haukeland University Hospital. Classification-based cognitive functional therapy patients were presented with written information about the study with its aims and procedures. Here, it was clearly stated that there were two active comparable treatment arms, and that based on current knowledge, we did know which was superior. The patients gave a written informed consent prior to proceeding to the clinical examination. A lack of compliance of greater than 50% was set as a withdrawal criterion based on programme compliance forms. When the patients had been examined and classified and a blinded examiner had collected baseline data, the patient drew the envelope containing their allocation and details of procedure in relation to their allocation. All subjects first underwent a comprehensive interview and full physical examination at the Department of Public Health and Primary Health Care, UiB. During the interview, subjects were guided in questioning to inform: their history of pain, pain area and nature, pain behaviour (aggravating/easing movements and activities), their primary functional impairments, disability levels, activity levels and sleep patterns. Their degree of pain focus, pain coping strategies, stress response and its relationship to pain, and their pain beliefs were also questioned as was any history of anxiety and depression. Finally, their beliefs and goals regarding management of their disorder were ascertained. These factors were then considered within the context of the movement behaviours and lifestyle factors, i. The physical examination process involved a systematic process of assessment of pain provocative postures (such as sleeping, sitting, standing and bending) and functional movement tasks (such as sit to stand, single-leg stand, spinal movements and lifting) and any other specific tasks nominated by the patient as pain provocative or that they avoided. In Supporting Information Appendix S2, all the included subjects and their subsequent classification are outlined. The intervention took place at 3 different private clinics and lasted for 12 weeks. After the 12-week intervention period, participants were permitted to seek alternative care, and the frequency and type of treatment were monitored in the follow-up questionnaires. A tester blinded to allocation, pretreatment and at 3-month follow-up distributed the questionnaires. All instructions for subjects were written, and they were asked to complete the programme on a daily basis and complete a daily diary outlining if they had complied with each aspect of the intervention. These therapists were specialists in orthopaedic manual therapy with an average of 25. The motor control exercises involved isolated contractions of the deep abdominal muscles in different functional positions as previously described (Richardson et al. The therapists in this group generally spent 1 h with the patients for the initial consultation and 30 min for follow-ups.
Any point-of-care test that is available and used in primary care settings for diagnostic purposes with the ability to provide results within a reasonable period of time (e symptoms 6 dpo trusted 100 mg dilantin. System level strategies such as clinician reminders (paper-based or electronic) medicine identifier purchase line dilantin, clinician audit and feedback, financial or regulatory incentives for clinicians or patients, antimicrobial stewardship programs, and pharmacist review. Multifaceted approaches that include numerous elements of one or more of the above strategies. Standard care without a strategy for improving appropriate use of antibiotics: We use the terms usual care and standard care synonymously. Although practice probably varies considerably between settings, usual and standard practice likely includes maintaining hydration and use of decongestants, cough suppressant, etc. Full-text of all citations deemed potentially eligible for inclusion by at least one reviewer were obtained for further evaluation. Full-text articles were reviewed by two reviewers, with differences in judgment on eligibility resolved through consensus or inclusion of a third party. Results published only in abstract form were not included because inadequate details were available for assessing quality. In general, at full-text level, studies were excluded for one or more of the following reasons: ineligible population, ineligible intervention, ineligible comparator, ineligible outcome, ineligible setting (e. All citations were entered in an electronic database (Endnote X7, Thomson Reuters) and screening decisions for each citation were also tracked in the database. Appendix B lists all studies included at full text, while all studies excluded at full text are listed in Appendix C. Data Extraction the following data were abstracted from included studies: study design, number of participants randomized or enrolled, patient and provider population criteria, intervention strategy and comparator characteristics, patient characteristics (e. One reviewer abstracted study data, and a second reviewer appraised the abstractions. Preventive Services Task Force and the National Health Service Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (United Kingdom). The internal validity of observational studies were rated based on criteria specific to these study designs: the adequacy of the patient selection process, whether there was important differential loss to followup or overall high loss to followup, the adequacy of event ascertainment, whether acceptable statistical techniques were used to minimize potential 12 confounding factors, and whether the duration of followup was reasonable to capture investigated events. All assessments were done at the overall study level and resulted in a rating of good, fair, or poor. We utilized a dual rating procedure for study quality, where all studies were first rated by one reviewer and then checked by another reviewer. Data Synthesis Evidence tables were constructed to illustrate the study characteristics, quality ratings, and results for all included studies (Appendixes D through I). A hierarchy-of-evidence approach was used, where the best evidence is the focus of our synthesis for each question, population, intervention, and outcome addressed. High-quality systematic reviews that had a similar scope to our review were used as primary evidence where possible; where a review included all studies of an intervention, population, and outcome we summarized the findings of the review as our evidence. Where an eligible review did not include all identified studies we noted the review and its findings, but undertook a new synthesis to incorporate the newer studies not included in the review. For assessing overall and appropriate prescribing and use, we accepted and recorded all definition and measurement methods. Particularly for appropriate prescribing outcomes, we grouped together studies that use similar definitions of appropriateness and evaluated whether the comparative effectiveness of strategies differed across categories. Where appropriate, we synthesized outcome data quantitatively using meta-analysis to pool outcomes, with odds ratio as the principle summary measure. Data from poor-quality studies were generally excluded from the synthesis, except to undertake sensitivity analyses or to note where high risk of bias studies constitute the only evidence for an important outcome. To determine the appropriateness of meta-analysis, we considered the internal validity of the studies and the heterogeneity among studies in design, patient population, interventions, and outcomes. The Q statistic and the I2 statistic (the proportion of variation in study estimates due to heterogeneity) were calculated to assess heterogeneity in effects between studies. Forest plots were used when applicable to graphically summarize the results of individual studies and of the pooled analysis. Since most data was not suitable for pooling, we largely summarized the data qualitatively. Qualitative synthesis involved grouping studies by similarity of population and/or intervention characteristics, including the sources of variation or heterogeneity listed above. When definition of appropriate antibiotic use and/or prescription were provided, we grouped together studies that used similar definitions of appropriateness and categorized the different groups based on concordance (e. We then evaluated whether the comparative effectiveness of strategies differed across categories.
Discount 100mg dilantin free shipping. Headache and Irregular menstruation (Medical Symptom).
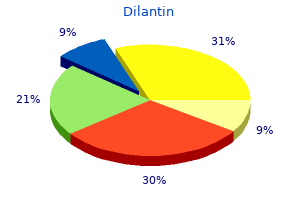
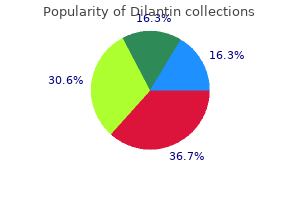
Pot Barley (Barley). Dilantin.
- What is Barley?
- Bronchitis, cancer prevention, diarrhea, swelling (inflammation) of the stomach or bowel, boils, increasing strength and energy, weight loss, and other conditions.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Dosing considerations for Barley.
- Preventing stomach cancer.
- High cholesterol.
- How does Barley work?
- Preventing cancer of the colon (bowels) or rectum.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96777
Prevalence and influence of diagnostic tests for acute respiratory tract infections in primary care medications gerd purchase genuine dilantin online. A case study of nurse management of upper respiratory tract infections in general practice gas treatment purchase dilantin 100mg online. Effectiveness of multifaceted educational programme to reduce antibiotic dispensing in primary care: practice based randomised controlled trial. Impact of the rapid antigen detection test in diagnosis and treatment of acute pharyngotonsillitis in a pediatric emergency room. White blood cell count can aid judicious antibiotic prescribing in acute upper respiratory infections in children. Impact of the French campaign to reduce inappropriate ambulatory antibiotic use on the prescription and consultation rates for respiratory tract infections. Procalcitonin guidance of antibiotic therapy in community-acquired pneumonia: a randomized trial. Empirical management of community-acquired pneumonia: impact of concurrent A/H1N1 influenza pandemic on guideline implementation. Can a patient information sheet reduce antibiotic use in adult outpatients with acute bronchitis? A community-based intervention to reduce antibiotic use for upper respiratory tract infections in regional South Australia. Use of procalcitonin measurement to identify bacterial co-infection in patients with H1N1 influenza. Evaluating the evidence for the implementation of C-reactive protein measurement in adult patients with suspected lower respiratory tract infection in primary care: a systematic review. Reducing antibiotic use for acute bronchitis by giving patients written information. Diagnosis and treatment of upper respiratory tract infections in the primary care setting. Effects of an education and training intervention on caregiver knowledge of nonurgent pediatric complaints and on child health services utilization. Performance of a bedside C-reactive protein test in the diagnosis of community-acquired pneumonia in adults with acute cough. Cluster randomised controlled trial of tailored interventions to improve the management of urinary tract infections in women and sore throat. Delayed antibiotic prescribing and associated antibiotic consumption in adults with acute cough. Increasing adherence to a community-based guideline for acute sinusitis through education, physician profiling, and financial incentives. Implementing practice guidelines for appropriate antimicrobial usage: a systematic review. Physician specialty is associated with adherence to treatment guidelines for acute otitis media in children. Implementing the delayed antibiotic therapy approach significantly reduced antibiotics consumption in Israeli children with first documented acute otitis media. Addressing antibiotic use for acute respiratory tract infections in an academic family medicine practice. Diagnostic accuracy and the observation option in acute otitis media: the Capital Region Otitis Project. Prescribed medications and pharmacy interventions for acute respiratory tract infections in Swiss primary care. Changes before and after a policy to restrict antimicrobial usage in upper respiratory infections in Taiwan. Procalcitonin to guide duration of antibiotic therapy in intensive care patients: a randomized prospective controlled trial. Evaluation of the implementation of a rapid streptococcal antigen test in a routine primary health care setting: from recommendations to practice.
In general terms medications related to the integumentary system buy dilantin 100 mg with amex, each demonstration project has four aspects: assessing whether knowledge and attitudes of the population are adequate symptoms 9 days after ovulation buy cheap dilantin on line, correcting misinformation and increasing awareness of epilepsy and how it can be treated; assessing the number of people with epilepsy and estimating how many of them are appropriately treated; ensuring that people with epilepsy are properly served by health personnel equipped for their task; analysing the outcome and preparing recommendations for those who wish to apply the findings to the improvement of epilepsy care in their own and other countries. Up to 70% of people with epilepsy could lead normal lives if properly treated, but for an overwhelming majority of patients this is not the case. The worldwide incidence, prevalence and mortality of epilepsy are not uniform and depend on several factors, which include the structure of the local population, the basic knowledge of the disease, the socioeconomic and cultural background, the presence of environmental risk factors, and the distribution of infrastructure, financial, human and material resources. As epileptic seizures respond to drug treatment, the outcome of the disease depends on the early initiation and continuity of treatment. Difficulties with availability of or access to treatment (the treatment gap) may seriously impair the prognosis of epilepsy and aggravate the social and medical consequences of the disease. In low income countries the treatment gap needs to be seen in the context of the local situation, with inadequate resources for all forms of health delivery as well as education and sanitation. Integration of epilepsy care in national health systems needs to be promoted by developing models for epilepsy control worldwide. Systematic review and meta-analysis of incidence studies of epilepsy and unprovoked seizures. Socioeconomic characteristics of childhood seizure disorders in the New Haven area: an epidemiologic study. Comparative epidemiology of epilepsy in Pakistan and Turkey: population-based studies using identical protocols. Epilepsy in developing countries: a review of epidemiological, sociocultural, and treatment aspects. The cost of epilepsy in the United States: an estimate from population-based and survey data. The cost of epilepsy in the United Kingdom: an estimation based on the results of two population-based studies. Cost-effectiveness of first-line anti-epileptic drug treatments in the developing world: a population-level analysis. Report of the Ad Hoc Committee on Health Research related to Future Intervention Options. Increased prevalence of epilepsy associated with severe falciparum malaria in children. New York, Demos Medical Publishing, 2005 (World Federation of Neurology: Seminars in Clinical Neurology). Epilepsy in developing countries: a review of epidemiological, sociocultural and treatment aspects. Medical risks in epilepsy: a review with focus on physical injuries, mortality, traffic accidents and their prevention. Headache also occurs as a characteristic symptom of many other conditions; these are termed secondary headache disorders. Collectively, headache disorders are among the most common disorders of the nervous system, causing substantial disability in populations throughout the world. Others, such as the more prevalent tensiontype headache and the more disabling so-called chronic daily headache syndromes, have received less attention. Furthermore, few population-based studies exist for developing countries, where limited funding and large and often rural (and therefore less accessible) populations, coupled with the low profile of headache disorders compared with communicable diseases, prevent the systematic collection of information. Nevertheless, despite regional variations, headache disorders are thought to be highly prevalent throughout the world, and recent surveys add support to this belief. Sufficient studies have been conducted to establish that headache disorders affect people of all ages, races, income levels and geographical areas (Figure 3. Four of them - three primary headache disorders and one secondary - have particular public health importance. Note: All studies were conducted in general population or community-based adult samples of at least 500 participants. Migraine Tension-type headache Cluster headache and other trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias Other primary headaches Secondary Headache attributed to head and/or neck trauma Headache attributed to cranial or cervical vascular disorder Headache attributed to non-vascular intracranial disorder Headache attributed to a substance or its withdrawal Headache attributed to infection Headache attributed to disorder of homoeostasis Headache or facial pain attributed to disorder of cranium, neck, eyes, ears, nose, sinuses, teeth, mouth or other facial or cranial structures 12. Headache attributed to psychiatric disorder Neuralgias and other headaches Source: (1). It almost certainly has a genetic basis (4), but environmental factors play a significant role in how the disorder affects those who suffer from it. Pathophysiologically, activation of a mechanism deep in the brain causes release of pain-producing inflammatory substances around the nerves and blood vessels of the head.