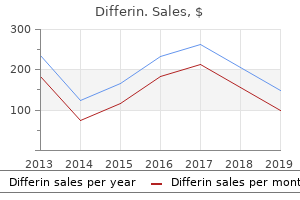
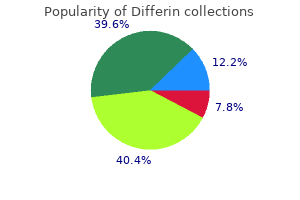
Differin
"Discount differin on line, skin care japan".
By: I. Georg, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Program Director, University of Central Florida College of Medicine
Although some aspects of treatment may need to be adjusted to conform with unique aspects of correctional settings (Tamburello et al acne face buy line differin. While in the correctional system skin care products reviews by dermatologists order differin 15 gr with amex, individuals with schizophrenia may be withdrawn, disorganized, or behave in a disruptive manner. These behaviors may result in disciplinary infractions, which may lead the individual with schizophrenia to be placed in a locked-down setting. Such units are often called "administrative segregation", "disciplinary segregation", or "restricted housing units" (Krelstein 2002; Semenza and Grosholz 2019) and have been conceptualized as having three main characteristics: social isolation, sensory deprivation, and confinement (Zubek et al. Each of these elements can vary significantly, but inmates typically spend an average of 23 hours per day in a cell, have limited human interaction and minimal or no access to programs, and are maintained in an environment that is designed to exert maximum control over the person, which has raised broader ethical considerations about the long-term use of such settings (Ahalt and Williams 2016; Ahalt et al. In addition, mental health clinicians working in such facilities frequently report that inmates without preexisting serious mental disorders develop irritability, anxiety, and other dysphoric symptoms when housed in these units for long periods of time (Metzner 2002). Difficulties in providing appropriate and adequate access to mental health care and treatment are especially problematic in any segregation environment and are related to logistical issues that 49 frequently include inadequate office space and limited access to inmates because of security issues (Metzner 2003; Metzner and Fellner 2010). In addition, because of their inherently punitive structure, such units typically provide very little support, access to relevant treatment modalities, or a therapeutic milieu. Furthermore, rates of self-injury and suicide appear to be higher in such settings than elsewhere in the correctional system (Baillargeon et al. Consequently, persons with schizophrenia should generally not be placed in a 23-hour/day lockdown for behaviors that are directly related to schizophrenia, because such an intervention is likely to exacerbate rather than reduce psychotic symptoms, as well as increase rather than reduce disruptive behaviors (American College of Correctional Physicians 2013; American Psychiatric Association 2012, 2016b; American Public Health Association 2013; National Commission on Correctional Heath Care 2016). Individuals with schizophrenia, like other individuals with serious mental illness, are at increased risk for symptom relapse and gaps in treatment upon release from a correctional setting. Services are often needed to reduce the likelihood of recidivism and maintain continuity of care for treatment of schizophrenia and concomitant disorders. Thus, discharge planning is a crucial aspect of care for inmates with schizophrenia, particularly for those who have been incarcerated for significant periods of time. Often, inmates with schizophrenia have been alienated from systems of care and psychosocial supports prior to arrest, and this estrangement is compounded by incarceration. As a result, inmates will likely need assistance around the time of discharge, which can encompass various domains including housing, treatment needs, financial support and obtaining supplemental security income/social security disability and related Medicaid benefits (American Psychiatric Association 2009c; Angell et al. Balancing of Potential Benefits and Harms in Rating the Strength of the Guideline Statement Benefits Development and documentation of a comprehensive, person-centered treatment plan assures that the clinician has considered the available nonpharmacological and pharmacological options for treatment and has identified those treatments that are best suited to the needs of the individual patient, with a goal of improving overall outcome. It may also assist in forming a therapeutic relationship, eliciting patient preferences, permitting education about possible treatments, setting expectations for treatment, and establishing a framework for shared decision-making. Documentation of a treatment plan promotes accurate communication among all those caring for the patient and can serve as a reminder of prior discussions about treatment. Harms the only identifiable harm from this recommendation relates to the time spent in discussion and documentation that may reduce the opportunity to focus on other aspects of the evaluation. The level of research evidence is rated as low because no information is available on the harms of such an approach. There is also minimal research on whether developing and documenting a specific treatment plan improves outcomes as compared with assessment and documentation as usual. However, indirect evidence including expert opinion supports the benefits of comprehensive treatment planning. Review of Available Guidelines from Other Organizations Information from other guidelines (Addington et al. Quality Measurement Considerations It is not known whether psychiatrists and other mental health professionals typically document a comprehensive and person-centered treatment plan that includes evidence-based nonpharmacological and pharmacological treatments, and there is likely to be variability. Although a well-defined and scientifically-sound quality measure could be developed to assess for the implementation of an evidence-based treatment plan that meets consensus-based features of person-centered care, clinical judgment would still be needed to determine whether a documented treatment plan is comprehensive and adapted to individual needs and preferences. Manual review of charts to evaluate for the presence of such a person-centered treatment plan would be burdensome and time-consuming to implement. A quality measure could assess the presence or absence of text in the medical record that would reflect treatment planning. When considering the development of such quality measures, there should be a thorough examination of the potential for unintended negative consequences, such as increased documentation burden or overuse of standardized language that meets the quality measure criteria but would inaccurately reflect what occurred in practice.
Training should be in accordance with specialty skin care in your 20s differin 15 gr with amex, organization skin care trends order 15gr differin mastercard, or institutional specific guidelines. Physicians should render a diagnostic interpretation in a time frame consistent with the management of acute renal pathology, as outlined above. They are paired structures that lie oblique to every anatomic plane and at different levels on each side. The long axis of the kidney approximates the intercostal spaces and longitudinal scans may be facilitated by placing the transducer plane parallel to the intercostal space. By convention, the probe indicator is always toward the head or the vertebral end of the rib on both the right and left sides. Transverse views of the kidneys are therefore usually transverse to the ribs, resulting in prominent rib shadows that may make visualizing the kidneys more difficult unless a small footprint or phased array probe is available. The kidneys are retroperitoneal in location and are usually above the costal margin of the flanks in the region of the costovertebral angle. A general-purpose curved array abdominal probe with a frequency range of between 2. A small footprint or phased array probe may facilitate scanning between the ribs, but may require several windows in the longitudinal plane if the kidney is long, or superficial. Images of both kidneys should be obtained in the longitudinal and transverse planes for purposes of comparison and to exclude absence of either kidney. The bladder should be imaged to assess for volume, evidence of distal ureteral obstruction and for calculi. The right kidney may be visualized with an anterior subcostal approach using the liver as a sonographic window. Imaging may be facilitated by having the patient in the left lateral decubitus position or prone. Asking the patient to take and hold a deep breath may serve to extend the liver window so that it includes the inferior pole of the kidney. Despite these techniques, parts or the entire kidney may not be seen in this view due to interposed loops of bowel, in which case the kidney should be imaged using an intercostal approach in the right flank between the anterior axillary line and midline posteriorly. For this approach, the patient can be placed in the decubitus position with a bolster under the lower side with the arm of the upper side fully abducted, thus spreading the intercostal spaces. Separate views of the superior and inferior poles are often required to adequately image the entire kidney in its longitudinal plane. Once in the transverse plane, the transducer can be moved superiorly and medially, or inferiorly and laterally to locate the renal hilum. Images cephalad to the hilum represent the superior pole and those caudad represent the inferior pole. The left kidney lacks the hepatic window, necessitating an intercostal approach similar to the one described above for the right flank. Ideally, the bladder is scanned prior to voiding and again post-void if outlet obstruction is a concern. To measure bladder volume, one must obtain the maximal length (longitudinal), width (transverse) and height (anteroposterior) measurements of the bladder. The length is only obtainable in the sagittal plane, and width only in the transverse plane. The height can be measured in either sagittal or transverse planes; however, it should only be measured once. All three measurements are multiplied in centimeters by a coefficient (shape-dependent, with a common default of 0. The kidneys should be studied for abnormalities of the renal sinus and parenchyma. Under normal circumstances, the renal collecting system contains no urine, so that the renal sinus is a homogeneously hyperechoic structure. Other abnormalities identified including cysts, masses and bladder abnormalities may require additional diagnostic evaluation. Measurements may be made of the dimensions of abnormal findings and the length and width of the kidneys.
Discount differin 15 gr visa. My FULL Day + Night Skincare Routine 💦 | allanaramaa.
Several uncontrolled studies (historical controls acne knitwear order differin toronto, retrospective review) suggested that it is effective in reducing the risk for contrast-induced nephropathy skin care professionals purchase 15gr differin fast delivery, and the results of a pilot trial were promising (for review, see Stacul et al. On the other hand, when intermittent dialysis is used after these therapeutic interventions, the extracorporeal removal of potassium will be reduced and the post-treatment rebound of serum potassium will be more pronounced. The association of early initiation of dialysis with survival benefit was first suggested by case series with historical controls conducted in the 1960 s and 1970 s. However, these studies mostly combined early start with more-intensive dialysis and late start with less-intensive dialysis. Ideally, therapeutic interventions should be designed to achieve the above goals and a systematic assessment of all these factors is key to determining the optimal timing for initiating dialysis (Table 17). Patients dialyzed for control of both azotemia and volume overload experienced the worst outcome. Survivors had lower fluid accumulation at dialysis initiation compared to nonsurvivors (8. Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin was shown to have an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0. Pediatric and adolescent patients range in age from the premature neonate to 25 years of age, with a size range of 1. Dialysis for hyperkalemia is effective in removing potassium; however, it requires frequent monitoring of potassium levels and adjustment of concurrent medical management to prevent relapses. Life-threatening indications Hyperkalemia Acidemia Pulmonary edema Uremic complications (pericarditis, bleeding, etc. Intraoperative fluid removal using modified ultrafiltration has been shown to improve outcomes in pediatric cardiac surgery patients. A detailed discussion of the specific pediatric clinical situations is beyond the scope of 91 chapter 5. This study also found a significantly higher mortality in patient with 420% fluid overload (58%) vs. Among the 15 nonsurvivors, only 6 (40%) had percentage fluid accumulation o10% at the time of death. Not surprisingly, the predictive ability of urine output was negatively affected by the use of diuretics. It is, however, not clear whether failure to wean is simply a marker of illness severity or contributed by itself to the adverse outcome. The incidence of withdrawal of life-support treatments in critically ill patients with multiorgan failure has increased over the last decade. Evidence from large observational studies suggests that large variation in practice exists. These benefits have to be weighed against the risk of bleeding, and economic issues, such as workload and costs. On the other hand, prolonged clotting times can also point to a consumptive coagulopathy based on the presence of an activated coagulation. In these patients, frequent filter clotting will occur and necessitate a switch to some form of anticoagulation. The doses of low-molecular-weight heparin, as provided by the manufacturers, should be adapted to the bleeding risk of the individual patient. Dose reduction may also be required in patients receiving daily dialysis, which increases the risk of accumulation.
Accuracy of Reported Lab Findings Lab results must be performed correctly skin care 50s discount differin 15 gr, and clinical and laboratory personnel must invest time to understand the lab tests on site and minimize human error skin care wiki generic differin 15 gr overnight delivery. A welldesigned referral system for lab samples will minimize confusion and allow rapid turnaround. Once a result is available, it must be carefully communicated to both patient and provider. Access An understanding of what tests are required to diagnose patients does not ensure that patients can get tested and enroll into care. For diagnostic protocols to function, patients need to be able to find their way to informed providers, and those providers need to have access to the materials needed for appropriate laboratory testing. Advocacy: Opt-Out and Provider-Initiated Diagnostic Testing In addition to maximizing access to care, providers should promote access to testing by instituting an opt-out policy. Another anticipatory strategy to maximize access to diagnostic testing is called provider-initiated testing, meaning that it Monitoring Diagnostic testing is important to both individual patients and the population as a whole. In 2006, the World Health Organization updated several easy-to-use tables for this purpose. This staging system is used in many countries to determine eligibility for antiretroviral therapy. Fungal paronychia (painful, red and swollen nail bed) or onycholysis (painless separation of the nail from the nail bed). Clinical Diagnosis recurrent oral ulceration unexplained persistent parotid enlargement Lineal gingival erythema Herpes zoster Current event plus at least one previous episode in past 6 months. Aphthous Clinical Diagnosis ulceration, typically with a halo of inflammation and yellow-grey pseudomembrane. Asymptomatic bilateral swelling that may spontaneously resolve and recur, in absence of other known cause, usually painless. Erythematous band that follows the contour of the free gingival line; may be associated with spontaneous bleeding Painful rash with fluid-filled blisters, dermatomal distribution, can be haemorrhagic on erythematous background, and can become large and confluent. Clinical Diagnosis Clinical Diagnosis Clinical Diagnosis recurrent upper Current event with at least 1 episode in the past 6 months. Symptom respiratory tract infection complex; fever with unilateral face pain and nasal discharge (sinusitis) or painful swollen eardrum (otitis media), sore throat with productive cough (bronchitis), sore throat (pharyngitis) and barking croup-like cough (laryngotracheal bronchitis). Reports of fever or night sweats for longer than one month, either intermittent or constant, with reported lack of response to antibiotics or antimalarial agents. How to Diagnose Microscopy or culture Clinical diagnosis Clinical diagnosis Lymph node tuberculosis Non-acute, painless "cold" enlargement of peripheral lymph nodes, localized to one region. Cough with fast breathing, chest indrawing, nasal flaring, wheezing, and grunting. Isolation of bacteria from appropriate clinical specimens (induced sputum, bronchoalveolar lavage and lung aspirate) Severe recurrent bacterial pneumonia Symptomatic lymphocytic No presumptive interstitial pneumonia clinical diagnosis Cxr: bilateral reticulonodular interstitial pulmonary infiltrates present for more than 2 months with no response to antibiotic treatment and no other pathogen found. How to Diagnose Culture and/or histology esophageal candidiasis Difficulty in swallowing, or pain on swallowing (food and fluids). Not required but may be confirmed by: 1) typical red-purple lesions seen on bronchoscopy/ endoscopy; 2) dense masses in lymph nodes, viscera, or lungs by palpation or radiology; and 3) histology. Clinical features of organs involved, such as sterile pyuria, pericarditis, ascites, pleural effusion, meningitis, arthritis, or orchitis, pericardial or abdominal kaposi sarcoma Typical appearance in skin or oropharynx of persistent, initially flat, patches with a pink or blood-bruise color, skin lesions that usually develop into nodules. Computed tomography scan (or other neuroimaging) showing single or multiple lesions with mass effect or enhancing with contrast. For classification purposes, once a category C condition has occurred, the person will remain in category C. Differentiation of opportunistic infections from immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome is necessary.