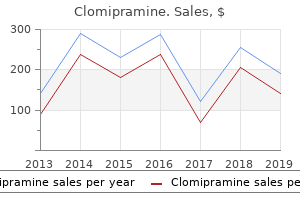
Clomipramine
"Discount 50 mg clomipramine, depression signs".
By: Q. Lares, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Co-Director, Universidad Central del Caribe School of Medicine
Glycemic memory has several important clinical implications: 1 Early tight control is very important; 2 Cure of diabetes may not prevent subsequent development of complications; and 3 Novel therapies that reverse hyperglycemic memory may be needed mood disorder prevalence discount clomipramine uk. Hyperglycemia-induced mitochondrial superoxide production may provide an explanation for the continuing progression of tissue damage after the correction of hyperglycemia ("hyperglycemic memory") depression vs recession discount clomipramine online master card. Both the epigenetic changes and the gene expression changes persist for at least 6 days of subsequent normal glycemia. Hyperglycemia-induced epigenetic changes and increased p65 expression are prevented by normalizing mitochondrial superoxide production or superoxide-induced methylglyoxal (Figure 35. These results highlight the dramatic and long-lasting effects that short-term hyperglycemic spikes can have on vascular cells and suggest that transient spikes of hyperglycemia may be an HbA1c-independent risk factor for diabetic complications. This reduces inhibition of p65 gene expression, and thus acts synergistically with the activating methylation of histone 3 lysine 4 [156]. A continued benefit was evident during the 10-year post-trial follow-up Determinants of individual susceptibility to hyperglycemia-induced damage As with all complex diseases, the occurrence and progression of diabetic complications vary markedly among patients. The control of blood glucose, as well as blood pressure and blood lipid profiles, are important factors in predicting the risk of complications, but they only partially explain the risk of complications for an individual patient. Therefore, genetic factors have been investigated for their influence on the risk of developing complications. Familial clustering studies strongly support a role for genetic determinants of susceptibility to hyperglycemic damage. By contrast, the risk was only 17% or 22% if the index patient did not have diabetic nephropathy [160,161] or 566 Pathogenesis of Microvascular Complications Chapter 35 retinopathy. Numerous associations have been made between various genetic polymorphisms and the risk of various diabetic complications. The odds ratio for risk of severe retinopathy in diabetic relatives of positive versus negative subjects from the conventional treatment group is 5. In the same cohort, an association of multiple superoxide dismutase 1 variants is associated with the development and progression of diabetic nephropathy [168]. In the future, the challenge will be to identify specific genes involved in the varying clinical severity of diabetic complications. Recent emphasis in human disease genetics has been on so-called modifying genes, i. This means that one gene changes the whole phenotype in an all-or-nothing fashion, in contrast with the incremental effects seen with changes in a large number of non-modifier genes. Many examples of modifier genes are known in model organisms, and several have been identified in humans [169,170]. These results provide a basis for the rational design of new therapeutics to normalize impaired ischemia-induced vasculogenesis in patients with diabetes such as occurs in non-healing foot ulcers. Hemodynamic factors Hypertension is one of the most significant secondary risk factors for the development of microvascular vascular diabetic complications. In both retina and glomerulus, reduction of vascular surface area appears to occur first in microvessels with high perfusion pressure, and in patients with unilateral ophthalmic or renal artery stenosis there is a pronounced decrease in the severity of retinopathy or nephropathy on the affected side. In the kidney, glomerular hypertension occurs with diabetes as a result of altered afferent and efferent arteriolar tone, increasing renal damage. Together, these data suggest that hypertension contributes to diabetic microvascular complications by further increasing intracellular hyperglycemia. Diabetes significantly impairs this process in tissues whose cells develop intracellular hyperglycemia. This concept originated from a feature of the unifying 567 Part 7 Microvascular Complications in Diabetes mechanism. Two of these glycolytic intermediates, fructose-6-phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, are also the final products of the transketolase reaction, which is the rate-limiting enzyme in another metabolic pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway [177]. Because in diabetes the concentration of these two glycolytic intermediates is high, activating transketolase could reduce their concentration by converting them to pentose phosphates. This would divert their flux away from three of the damaging pathways normally activated by hyperglycemia. Although thiamine itself only activated transketolase by 25% in arterial endothelial cells, the thiamine derivative benfotiamine activated transketolase 250% in arterial endothelial cells.
On average bipolar depression and christianity order 50mg clomipramine with visa, it takes 36 hours mood disorder related to general medical condition order discount clomipramine online, with an upper limit of 65 hours, to transfer contents from the cecum to the rectum. Compared to the stomach and small intestine, colonic transit is relatively prolonged, permitting digestion of fiber and absorption of water and electrolytes to be completed. Insulin or pancreas transplantation improved glycemic control and the axonopathy affecting autonomic nerves in rats with diabetic autonomic neuropathy [19]. Overexpression of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor, a trophic factor for enteric neurons, in transgenic mice reversed hyperglycemia-induced apoptosis of enteric neurons, improved gastric emptying and intestinal transit [22]. Pathophysiology of diabetic enteropathy: insights from animal studies In animal models, extrinsic neural dysfunction has been primarily implicated to a loss of myelinated and unmyelinated fibers without much neuronal loss [16,17]. In theory, this reduction in nitrergic inhibitory functions may contribute to impaired gastric accommodation and accelerated intestinal transit in diabetes. Reduced sympathetic inhibition may also contribute to accelerated intestinal transit. Several mechanisms, including apoptosis, oxidative stress, advanced glycation end products and neuroimmune mechanisms may be responsible for neuronal loss and gut dysmotility [12]. A vagal neuropathy can cause antral hypomotility and/or pylorospasm, which may delay gastric emptying [23]. The pathophysiology of rapid gastric emptying in diabetes is less well understood. Conceivably, impaired gastric accommodation resulting from a vagal neuropathy [24] may increase gastric pressure and thereby accelerate gastric emptying of liquids. The relationship between vagal neuropathy and impaired post-prandial accommodation is unclear because accommodation may be preserved even in people with diabetes and vagal neuropathy [25], perhaps reflecting non-vagal adaptive mechanisms involving enteric neurons [26]. Some patients with diabetes and gastroparesis also have small intestinal dysmotility, more frequently characterized by reduced than by increased motility [27]. Diabetic diarrhea It is useful to categorize the pathophysiology of diabetic diarrhea into conditions that are associated with malabsorption and those that are not (Figure 46. Involvement of sympathetic fibers, which normally inhibit motility and facilitate absorption via 2adrenergic receptors, can result in accelerated small intestinal transit and cause diarrhea [38]. Patients with rapid ileal transit may have bile acid malabsorption [39,40] and deconjugated bile acids induce colonic secretion. Features suggestive of malabsorption such as anemia, macrocytosis or steatorrhea should prompt consideration of bacterial overgrowth, small bowel mucosal disease or pancreatic insufficiency. Small intestinal dysmotility predisposes to bacterial overgrowth, which can cause bile salt deconjugation, fat malabsorption and diarrhea. Chronic pancreatic insufficiency may result from pancreatic atrophy, disruption of cholinergic enteropancreatic reflexes, or elevated serum hormonal levels of glucagon, somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide, which reduce pancreatic enzyme secretion [42]. Nevertheless, the association between chronic pancreatic insufficiency and diabetes is uncommon. Cross-sectional studies suggest that higher glycated hemoglobin concentrations are associated with a higher prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms and slower gastric emptying among people with diabetes in the community [6,35]. While strict glycemic control improves neural, renal and retinal functions in diabetes, the impact on gastric emptying is unclear [36]. In addition to hyper- 764 Gastrointestinal Manifestations of Diabetes Chapter 46 only 10% of pancreatic function is sufficient for normal digestion. Because of the high prevalence of coronary atherosclerosis in diabetes, testing for coronary artery disease should be considered when necessary in patients with chest pain. Fecal incontinence Loose stools and anorectal dysfunctions contribute to fecal incontinence in diabetic diarrhea. Compared to continent people with diabetes and healthy controls, patients with diabetes and fecal incontinence have a higher threshold for rectal perception of balloon distention, a marker of reduced sensation [43,44]. A sympathetic neuropathy may impair internal anal sphincter function and anal resting pressures while a pudendal neuropathy may result in reduced anal squeeze pressure.
Purchase 75mg clomipramine. What is bipolar disorder? - Helen M. Farrell.
This results in potential shortcomings related to a poor definition of diabetes and hidden diabetes anxiety 504 purchase clomipramine with american express, actual glucose lowering therapy and also a risk for selection biases with an overrepresentation of less severe diabetes mood disorder and diabetes buy cheap clomipramine on-line. With these limitations in mind, available data favor a proportionately similar efficacy in patients with and without diabetes. Because the absolute prognosis is considerably worse in patients with diabetes, the impact of therapy expressed as number of patients needed to treat to avoid an event. It is worthy of note that the relative risk reduction following metoprolol is similar in the two groups. The remaining event rate is still substantially higher in the diabetic cohort than among those without diabetes. Diuretics and aldosterone antagonists Diuretics are mandatory for symptomatic relief of fluid overload. As already underlined, they should not be used in excess because they induce neurohormonal activation [94]. Loop diuretics are recommended rather than diuretics that may further impair glucose metabolism. The European guidelines for the management of diabetes recommend that HbA1c should be <6. Further studies are yet to be conducted on this category of patient before aggressive glucose normalization can be recommended as a possibility to improve their situation. Currently, it seems as if such assumptions reflect information from epidemiologic studies showing increased risk with increasing levels of plasma glucose and HbA1c starting well below what has currently been labeled as normal. Glucose lowering agents Regarding specific glucose lowering agents, there is some information available of importance for the choice of treatment in patients with or at risk for heart failure. The main effect of insulin is to decrease blood glucose, but it may also increase myocardial blood flow, decrease heart rate and cause a modest increase in cardiac output [137,138]. Beneficial effects on myocardial function have been reported, but also that insulin may be associated with increased morbidity [139] and mortality [140,141]. Diastolic congestive heart failure Impaired myocardial diastolic function and endothelial dysfunction are early expressions of diabetes-related cardiovascular involvement causing a decreased myocardial blood flow reserve. It has been suggested that hyperglycemia-related early myocardial and microcirculatory disturbances are dynamic and that they may be reversed by improved metabolic control [143]. It should be underlined that it is still too early to abandon the hypothesis of a favorable relation between glycemic control and myocardial diastolic dysfunction. Accordingly, such protocols must include detailed examinations of the patients with this in mind. Risk factors for heart failure in the general population: the study of men born in 1913. Evolving trends in the epidemiologic factors of heart failure: rationale for preventive strategies and comprehensive disease management. Congestive heart failure predicts the development of non-insulindependent diabetes mellitus in the elderly. How to diagnose diastolic heart failure: a consensus statement on the diagnosis of heart failure with normal left ventricular ejection fraction by the Heart Failure and Echocardiography Associations of the European Society of Cardiology. Epshteyn V, Morrison K, Krishnaswamy P, Kazanegra R, Clopton P, Mudaliar S, et al. Geneva: World Health Organization, Department of Noncommunicable Disease Surveillance, 1999. Glucose tolerance and blood pressure in a population-based cohort study of males and females: the Reykjavik Study. Heart failure in the general population of men: morbidity, risk factors and prognosis. Prevalence of heart failure and left ventricular dysfunction in the general population: the Rotterdam Study. A type 2 diabetes screening program by general practitioners in a Belgian at risk population.
Although psychopharmacology is the first and most widely used treatment for bipolar disorders bipolar depression worse in the morning order clomipramine discount, occasionally psychological interventions are also paired with medication as psychotherapy alone is not a sufficient treatment option mood disorder in teens cheap clomipramine 75mg with amex. Majority of psychological interventions are aimed at medication adherence, as many bipolar patients stop taking their mood stabilizers when they "feel better" (Advokat et al. Social skills training and problem-solving skills are also helpful techniques to address in the therapeutic setting as individuals with bipolar disorder often struggle in this area. As we have discussed, major depressive disorder has a variety of treatment options, all found to be efficacious. However, research suggests that while psychopharmacological interventions are more effective in rapidly reducing symptoms, psychotherapy, or even a combined treatment approach, are more effective in establishing longterm relief of symptoms. Lithium and other mood stabilizers are very effective in managing symptoms of patients with bipolar disorder. Unfortunately, it is the adherence to the medication regimen that is often the issue with these patients. Bipolar patients often desire the euphoric highs that are associated with manic and hypomanic episodes, leading them to forgo their medication. A combination of the two main approaches often works best, especially in relation to maintenance of wellness. Treatment of bipolar disorder involves mood stabilizers such as Lithium and psychological interventions with the goal of medication adherence, as well as social skills training and problem-solving skills. In regard to depression, psychopharmacological interventions are more effective in rapidly reducing symptoms, while psychotherapy, or even a combined treatment approach, is more effective in establishing long-term relief of symptoms. Discuss the effectiveness of the different pharmacological treatments for mood disorders. Be sure you are clear on what makes them different from one another in terms of their clinical presentation, epidemiology, comorbidity, and etiology. Prior to discussing these clinical disorders, we will explain what stressors are, as well as identify common stressors that may lead to a stressor-related disorder. Be sure you refer Modules 1-3 for explanations of key terms (Module 1), an overview of models to explain psychopathology (Module 2), and descriptions of various therapies (Module 3). A stress disorder occurs when an individual has difficulty coping with or adjusting to a recent stressor. Stressors can be any event-either witnessed firsthand, experienced personally, or experienced by a close family member-that increases physical or psychological demands on an individual. These events are significant enough that they pose a threat, whether real or imagined, to the individual. While many people experience similar stressors throughout their lives, only a small percentage of individuals experience significant maladjustment to the event that psychological intervention is warranted. Among the most commonly studied triggers for trauma-related disorders are combat and physical/sexual assault. Symptoms of combat-related trauma date back to World War I when soldiers would return home with "shell shock" (Figley, 1978). Physical assault, and more specifically sexual assault, is another commonly studied traumatic event. Unfortunately, this statistic likely underestimates the actual number of cases that occur due to the reluctance of many individuals to report their sexual assault. Of the reported cases, it is estimated that nearly 81% of female and 35% of male rape victims report both acute stress disorder and posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms (Black et al. It does not have to be personally experienced but can be witnessed or occur to a close family member and have the same effect. Only a small percentage of people experience significant maladjustment due to these events. The most studied triggers for trauma-related disorders include physical/sexual assault and combat.