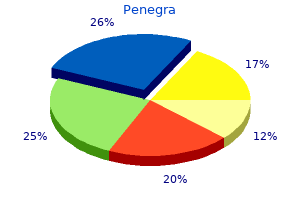
Penegra
"Buy penegra without prescription, mens health life".
By: G. Tom, M.A., M.D.
Vice Chair, University of Miami Leonard M. Miller School of Medicine
Early intervention is extremely important to beneficial long-term outcome in those infants at highest risk for disability androgen hormone up regulation trusted 50mg penegra. These resources should be accessed before discharge in preparation for outpatient follow-up man health policy buy discount penegra 50mg on line. Appointments at a neonatal follow-up clinic for monitoring growth and development, with input from a dietitian, social worker, physiotherapist, and developmentalist, are mandatory for very high-risk infants. At the request of the physician, follow-up house visits by a home health nurse to check clinical status, to repeat tests, and to ensure weight gain should be arranged for finite periods, depending on the needs of the individual infant and family. Have all screening tests, laboratory evaluations, radiologic evaluations, and appropriate immunizations been completed Brainstem auditory evoked response assessment is essential in other clinical conditions in which there is an increased risk for hearing loss and for which progressive losses are possible. Screening at birth for phenylketonuria, hypothyroidism, and galactosemia is almost universal. Other tests, such as sickle cell screen and cystic fibrosis screen, vary regionally based on prevalence. All initial newborn screens should be done per state protocol but essentially at 48 hours after birth and preferably after 24 hours of protein feeding. The galactosemia test is valid at birth and invalid after blood transfusion for at least 60 days. Hematocrit at the time of discharge should be >22% (controversial), and the reticulocyte count should be >5% (controversial), with adequate supplementation of iron and multivitamins added to the normal dietary intake. Folic acid, B12, and fat-soluble vitamin supplementation may be necessary in infants with short-gut syndrome or loss of distal ileum, including ileocecal valve during surgery. Extremely premature infants and low birthweight infants must have these parameters checked during inpatient stay and at discharge, along with radiographs of the bones to rule out rickets of prematurity. Vitamin D3 (1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol) supplementation may be considered in these infants, often as part of a multivitamin (controversial). Infants being discharged home on medications such as phenobarbital or theophylline should have levels tested before discharge, and the results should be recorded with dose adjustment as necessary. Clearly record the findings of the scans in chronologic order, with emphasis on hemorrhage, ventricular size, and areas of echogenicity suggestive of periventricular leukomalacia and porencephalic cysts. All newborns should be vaccinated against hepatitis B before discharge from the hospital. Use infant-only car safety seats with 3-point harness systems or convertible car safety seats with 5-point harness systems. Blanket rolls may be placed on both sides of the infant, and a rolled diaper or blanket can be used between the crotch strap and the infant to reduce slouching. Parents need to bring the car seat before discharge for training on seating the infant, proper positioning, and support. Record the results, if done more than once, in chronologic order, indicating assessment of cerebral function in infants with seizures. Documentation is useful in cases of congenital heart defect, supraventricular tachycardias, or metabolic problems. Record the findings and recommendations on pneumograms, barium contrast studies, and so on. A concise list of all the diagnoses for a patient, listed in chronologic order of occurrence, including procedures, should be generated. Perform a complete physical examination, paying careful attention to note any significant changes or findings. No follow-up screen is required, but the pediatrician should follow-up per standard practice. Before discharge, every infant should be assessed for the risk of developing severe hyperbilirubinemia.
However prostate cancer stages buy penegra cheap, the most common fate of gene duplication is that one copy acquires a mutation that renders it nonfunctional man health latam order 100mg penegra, giving rise to a pseudogene. Pseudogenes are common in the genomes of complex eukaryotes; the human genome is estimated to contain as many as 20,000 pseudogenes. Horizontal gene transfer Most organisms acquire their genomes through vertical transmission-transfer through the reproduction of genetic information from parents to offspring. This process is especially common among bacteria, and there are a number of documented cases in which genes are transferred from bacteria to eukaryotes. The extent of horizontal gene transfer among eukaryotic organisms is controversial, with few well-documented cases. Horizontal gene transfer can obscure phylogenetic relationships and make the reconstruction of phylogenetic trees difficult. Whole-genome duplication In addition to the duplication of individual genes, whole genomes of some organisms have apparently duplicated in the past. For example, a comparison of the genome of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae with the genomes of other fungi reveals that S. Genes can be passed among distantly related organisms through horizontal gene transfer. It is a two-step process: (1) genetic variation arises and (2) genetic variants change in frequency. The neutral-mutation hypothesis proposes that molecular variation is selectively neutral and is shaped largely by mutation and genetic drift. The balance hypothesis proposes that molecular variation is maintained largely by balancing selection. With the passage of time, the two populations acquire genetic differences that may lead to reproductive isolating mechanisms. In general, those parts that have the least effect on function evolve at the highest rates. Then various evolutionary forces cause changes in the frequency of genetic variants. Genetic drift can bring about changes in the allelic frequencies of populations and lead to genetic differences among populations. Genetic differentiation is the cause of postzygotic and prezygotic reproductive isolation between populations that leads to speciation. As a measure of genetic variation, why is the expected heterozygosity often preferred to the observed heterozygosity Why does protein variation, as revealed by electrophoresis, underestimate the amount of true genetic variation What is the key difference between the neutral-mutation hypothesis and the balance hypothesis Briefly describe differences among the distance approach, the maximum parsimony approach, and the maximum likelihood approach to the reconstruction of phylogenetic trees. Outline the different rates of evolution that are typically seen in different parts of a protein-encoding gene. What is the difference between prezygotic and postzygotic reproductive isolating mechanisms. What is the basic difference between allopatric and sympatric modes of speciation Briefly explain how switching from hawthorn fruits to apples has led to genetic differentiation and partial reproductive isolation in Rhagoletis pomonella. Briefly discuss the differences in these two patterns, particularly in regard to the role of cladogenesis in evolutionary change. The table below gives allelic frequencies for several loci and populations studied by Levin. Calculate the percentage of polymorphic loci and the expected heterozygosity for each species. For the expected heterozygosity, calculate the mean for all loci in a population, and then calculate the mean for all populations. What tentative conclusions can you draw about the effect of self-fertilization on genetic variation in these flowers
There is also a predilection for vasculitis androgen hormone zit cheap penegra 50 mg with mastercard, which may lead to hemorrhage androgen insensitivity hormone generic penegra 100 mg amex, thrombosis, and infarction. In the very low birthweight infant, coagulase-negative staphylococci need to be considered as causative organisms in bacterial meningitis. Many unusual organisms, including Ureaplasma, fungi, and anaerobes, have been described in case reports of neonatal meningitis. The clinical presentation is usually nonspecific and indistinguishable from those caused by sepsis. Meningitis must be excluded in any infant being evaluated for sepsis or infection. Signs and symptoms of meningitis include temperature instability (the most common), lethargy, irritability, poor tone, seizures, feeding intolerance, vomiting, respiratory distress, apnea, or cyanotic episodes. Seizures, often focal, can be the presenting manifestation in up to 50% of the cases. Gram-stained smear can be helpful in making a more rapid definitive diagnosis and identifying the initial classification of the causative agent. Imaging studies are recommended to detect the complications of meningitis, especially when the clinical course is complicated. Infection with certain microorganisms such as Citrobacter koseri and Enterobacter sakazakii predispose for the development of brain abscesses. The most useful and noninvasive method of imaging is ultrasonography, which provides information regarding ventricular size, inflammation (echogenic strands), and the presence of hemorrhage. General supportive measures like ventilation/oxygenation, cardiovascular support, intravenous dextrose, and anticonvulsant therapy are considered essential components of managing the neonate with bacterial meningitis. Optimal antibiotic selection depends on culture and sensitivity testing of the causative organisms. Ampicillin and gentamicin are usually started as empirical therapy for suspected early sepsis. Lastly, for the infant <60 days who is coming from home to the emergency department, the empiric therapy consists of ampicillin and cefotaxime. Because of the increased prevalence of methicillinresistant staphylococci both in the nosocomial setting and in the community, vancomycin should be substituted for penicillin or ampicillin as initial coverage. Most clinicians would use ampicillin plus cefotaxime plus an aminoglycoside as initial therapy. There is an emerging problem with multidrug-resistant enteric microorganisms (especially Klebsiella pneumoniae); for this situation, the drug of choice is meropenem. Persistence of infection may indicate a focus, such as obstructive ventriculitis, subdural empyema, or multiple smallvessel thrombi. External ventricular drainage may be indicated in certain cases complicated by ventriculitis. Treatment should continue until 14 days after cultures are negative or for 21 days, whichever is longer. Contrary to childhood meningitis, dexamethasone does not seem to improve the outcome of neonatal meningitis. Other therapies focusing on enhancing the immune system in the newborn, such as hematopoietic growth factors or intravenous immune globulins, do not seem to help either. Head circumference should be measured daily, and neurologic examination should be performed frequently. Hearing and vision evaluation should be done in all neonates who develop meningitis. Group B streptococcal meningitis: cerebrospinal fluid parameters in the era of intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis.

Physical examination shows a normal female body habitus prostate exam guidelines buy cheap penegra online, normal breast development prostate cancer quiz and answers penegra 50mg, and normal appearing external genitalia. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for the clinical presentation A 16-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of a 3-day history of abdominal pain and vomiting; he also has had decreased appetite during this period. Examination of peritoneal fluid from this patient will most likely show which of the following organisms A 45-year-old woman comes to the office because of a 6-month history of hot flashes, night sweats, and insomnia. She thinks she is going through menopause and asks the physician if there are any medications that will alleviate her symptoms. The physician explains that hormone therapy likely will help and explains the risks to the patient. A randomized controlled trial is conducted to assess the risk for development of gastrointestinal adverse effects using azithromycin compared with erythromycin in the treatment of pertussis in children. Of the 100 children with pertussis enrolled, 50 receive azithromycin, and 50 receive erythromycin. Results show vomiting among 5 patients in the azithromycin group, compared with 15 patients in the erythromycin group. Which of the following best represents the absolute risk reduction for vomiting among patients in the azithromycin group A 34-year-old woman with a 10-year history of hepatitis C comes to the physician because of progressive fatigue during the past month. Which of the following mechanisms is the most likely cause of the ongoing hepatocyte injury in this patient Her blood pressure was 145/100 mm Hg and 145/95 mm Hg, respectively, at two previous visits. Today, her pulse is 75/min, respirations are 15/min, and blood pressure is 150/95 mm Hg. If left untreated, which of the following is most likely to decrease in this patient A 62-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up examination after he was diagnosed with chronic inflammatory interstitial pneumonitis. Following pulmonary function testing, a biopsy specimen of the affected area of the lungs is obtained. A 31-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus comes to the physician because of an oozing, foul-smelling wound on her foot for 2 days. Physical examination shows a 4-cm, necrotizing wound with a purplish black discoloration over the heel. The causal organism most likely produces which of the following virulence factors A 4-month-old boy with severe combined immunodeficiency receives a bone marrow transplant. Six days later, he develops a widespread, erythematous, maculopapular rash over the trunk. Examination of a skin biopsy specimen shows diffuse vacuolar degeneration of basal epidermal cells with a mononuclear inflammatory cell infiltrate. A 37-year-old woman with right lower extremity edema is evaluated because of the sudden onset of shortness of breath and pleuritic chest pain. Which of the following signs, if present on physical examination, would be the most specific indicator of pulmonary arterial hypertension in this patient A 43-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus is brought to the emergency department because of a 12-hour history of nausea and vomiting. She says that it began after drinking champagne at a birthday party the previous night.
Purchase penegra american express. General Knowledge About Food & Health | Food & Health | General Knowledge Quiz.