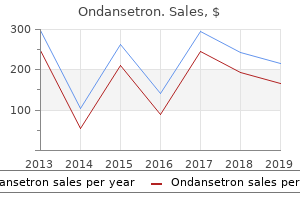
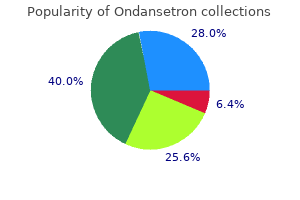
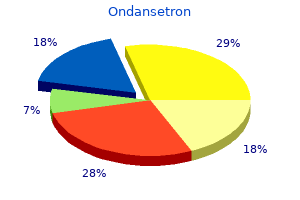
Ondansetron
"Purchase genuine ondansetron on-line, when administering medications 001mg is equal to".
By: C. Givess, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Medical Instructor, University of California, Merced School of Medicine
Measles vaccination as a risk factor for inflammatory bowel disease [letter; comment} treatment 5th metatarsal avulsion fracture buy ondansetron 4 mg line. Unilateral total deafness as a complication of the measlesmumpsrubella vaccination treatment 2nd degree burn purchase generic ondansetron. Miller E, Andrews N, Stowe J, Grant A, Waight P, Taylor B Risks of convulsion and aseptic meningitis following measles-mumps-rubella vaccination in the United Kingdom. A controlled trial for evaluating two live attenuated mumps-measles vaccines (Urabe Am 9-Schwarz and Jeryl Lynn-Moraten) in young children. Rajantie J, Zeller B, Treutiger I, Rosthцj S; Vaccination associated thrombocytopenic purpura in children. Myosite aiquл sйvиre et transitoire aprиs vaccination ourlienne (Imovax-Oreillons). IgE antibody to gelatin in children with immediate-type reactions to measles and mumps vaccines. Absence of an association between rubella vaccination and arthritis in under-immune postpartum women. Measles, mumps, and rubella vaccination and bowel problems or developmental regression in children with autism: population study. Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study on adverse effects of rubella immunization in seronegative women. Recurrent thrombocytopenic purpura after repeated measlesmumpsrubella vaccination. Ileal lymphoid nodular hyperplasia, non-specific colitis, and regressive developmental disorder in children. Acute encephalopathy followed by permenant brain injury or death associated with further-attenuated measles vaccines: a review of claims submitted to the National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program. Association of autistic spectrum disorder and the measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine: a systematic review of current epidemiological evidence. Information displayed has been developed using primary sources such (Plotkin et al 2008, Institute of Medicine of the National Academies 2011) and from data derived from a literature search on Pubmed in 2008 using key words "vaccine antigen", "Safety" and "adverse events". Data of different vaccines that may be found in this product should only be compared if there is indication that a comparative randomised controlled trial has been undertaken. The information sheets will be updated as new information may become available at the following web link. A group of admissions for patients with related condition categories or procedure categories; this measure includes seven cohorts, each with its own risk model (see Section 2. A variable in the risk-adjustment model intended to account for patient comorbid conditions or age. The variation among hospitals in the types of conditions they care for and procedures they provide. While it is helpful to assess readmission rates for specific groups of patients, these conditions account for only a small minority of total readmissions. Briefly, we developed the measure as an all-condition measure designed to capture unplanned readmissions within 30 days of discharge. The measure includes all admissions except those for which a subsequent readmission would not be considered a quality signal. The measure does not count planned readmissions in the measure outcome, since they do not represent a quality signal. The overall risk-standardized readmission rate is derived from a composite of seven statistical models built for groups of admissions that are clinically related. The seven risk adjustment models will be tested for reliability in a split sample dataset combining two calendar years (2007 and 2008), and the stability of the measure over time will be tested using data from 2009. Although we developed the measure using Medicare data, the measure will also be tested in and adapted for all-payer datasets. Some readmissions are unavoidable and result from inevitable progression of disease or worsening of chronic conditions.
In general treatment 4 water 8 mg ondansetron visa, a unilateral reduction of the alpha rhythm suggests a lesion of the underlying occipital cortex symptoms 0f food poisoning discount ondansetron on line, but in the case of the alpha rhythm an amplitude reduction may also be seen with distant lesions in the frontal or parietal cortices or the ipsilateral thalamus. Here, in conditions where the skull has been breached, for example with a burr hole or fracture (regardless of how much scar tissue has formed), an excessive amplitude is seen on the side with the breach, making the normal amplitude activity on the other side appear low by comparison (Cobb et al. Focal slowing Focal slowing may consist of either theta or delta activity, and is seen in a variety of focal conditions, including infarcts and tumors (Daly and Thomas 1958; Gastaut et al. Generalized slowing Generalized slowing appears in the theta or delta range and may be either bilaterally asynchronous or synchronous. Asynchronous generalized slowing is most commonly seen in metabolic or toxic delirium (Pro and Wells 1977; Romano and Engel 1944). Metabolic deliria accompanied by generalized asynchronous slowing include hepatic encephalopathy and uremic encephalopathy, and the deliria occurring secondary to hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, hypernatremia, hyponatremia, hypercalcemia, or hypocalcemia. Toxic deliria associated with similar slowing include those due to phenytoin (Roseman 1961), valproate (Adams et al. Interestingly, however, the delirium of delirium tremens, rather than slowing, is accompanied by an increase of beta activity (Kennard et al. The delirium seen with bacterial meningitis or viral encephalitis is also marked by generalized slowing. A mild degree of generalized asynchronous slowing may also be seen as a normal variant in a small minority of subjects; furthermore, occasional scattered theta transients are not at all abnormal in normal subjects over the age of 60 years (Kooi et al. Generalized slowing also, of course, occurs with sleep, and thus slowing in a drowsy patient who is slipping in and out of sleep is of little significance. Interictal activity Interictal activity consists of what are known as epileptiform discharges. These paroxysmal transients may consist of isolated spikes or sharp waves or may appear as complexes, such as spike-and-sharp wave, spike-and-slow wave, sharp-and-slow wave, polyspikes, or polyspike-and-wave discharges. Although epileptiform activity may be seen in a very small percentage of subjects who have never had a seizure (Ajmone-Marsan and Zivin 1970; Gibbs et al. Focal epileptiform activity strongly suggests an underlying focal epileptogenic lesion. The task of localizing focal epileptiform activity is facilitated by having in mind a spatial image of the electrical activity itself. With this image in mind, one can understand the changes produced on either a referential or bipolar montage. Thus, proceeding from Fp1 to F3 the depth falls, from F3 to C3 it continues to fall to its nadir, from C3 to P3 it rises, and from P3 to O1 it continues to rise back to the surface. Furthermore, assume also that electrode F3, being over the gently downsloping wall of the chasm, sees a potential of 50 V, and that electrode C3, being over the nadir of the chasm, sees a potential of 100 V. Electrode P3, being over the following wall of the chasm, sees 50 V, and electrode O1 encompasses the normal landscape of 25 V. As noted earlier, in a referential recording each scalp, or active electrode, is paired with the same reference electrode, in this example the ipsilateral ear; thus, in this example, as Fp1 F7 F3 Fz Cz Fp2 F8 F4 A1 T3 C3 100 V C4 T4 A2 P3 T5 50 V Pz P4 T6 O1 25 V O2 Figure 1. Thus, with referential recordings, it is the channel showing the greatest amplitude that serves to localize the focus of the electrical paroxysm. The situation with bipolar recordings is quite different: here, it is not amplitude that is important but a phenomenon known as phase reversal (Knott 1985; Lesser 1985). Take the same example of an electrical paroxysm as used above, but this time cover it, as illustrated in Figure 1. For channel Fp1 F3, one looks down from Fp1 at 25 to F3 at 50, for a difference of 25 V. For the next channel, F3 C3, one continues to look down into the electrical chasm, now looking down from 50 to 100, for a difference of 50 V. Similarly, for the next channel, P3 O1, one continues to look up, but here from 50 to 25, for a difference of 25 V. As may be noted, both channels Fp1 F3 and Fp1 F7 F3 Fz Cz Fp2 F8 F4 Fp1 Fp2 F8 F3 Fz Cz F4 A1 T3 C3 C4 T4 A2 F7 P3 T5 O1 Pz P4 T6 O2 A1 T3 C3 C4 T4 A2 P3 T5 O1 Pz P4 T6 O2 Fp1A1 F3A1 Fp1F3 C3A1 F3C3 P3A1 C3P3 O1A1 P3O1 Figure 1.
Identification of an additional two-cysteine containing type I interferon in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss provides evidence of a major gene duplication event within this gene family in teleosts holistic medicine purchase ondansetron 8 mg with amex. Alpha interferon and not gamma interferon inhibits salmonid alphavirus subtype 3 replication in vitro treatment wrist tendonitis cheap 4 mg ondansetron otc. Antiviral activity of salmonid gamma interferon against infectious pancreatic necrosis virus and salmonid alphavirus and its dependency on type I interferon. Functional analysis of an orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) interferon gene and characterisation of its expression in response to nodavirus infection. Promoters of type I interferon genes from Atlantic salmon contain two main regulatory regions. Characterization of the interferon genes in homozygous rainbow trout reveals two novel genes, alternate splicing and differential regulation of duplicated genes. Conservation and divergence of gene families encoding components of innate immune response systems in zebrafish. Atlantic salmon possesses two clusters of type I interferon receptor genes on different chromosomes, which allows for a larger repertoire of interferon receptors than in zebrafish and mammals. Mutant U5A cells are complemented by an interferon-alpha beta receptor subunit generated by alternative processing of a new member of a cytokine receptor gene cluster. Multiple regions within the promoter of the murine Ifnar-2 gene confer basal and inducible expression. Structural linkage between ligand discrimination and receptor activation by type I interferons. Hydrophobic cluster analysis reveals duplication in the external structure of human alpha-interferon receptor and homology with gammainterferon receptor external domain. An interferon-induced mouse protein involved in the mechanism of resistance to influenza viruses Its purification to homogeneity and characterization by polyclonal antibodies. Susceptibility of Xenopus laevis tadpoles to infection by the ranavirus Frog-Virus 3 correlates with a reduced and delayed innate immune response in comparison with adult frogs. No enhanced influenza virus resistance of murine and avian cells expressing cloned duck Mx protein. Native antiviral specificity of chicken Mx protein depends on amino acid variation at position 631. Association of Mx1 Asn631 variant alleles with reductions in morbidity, early mortality, viral shedding, and cytokine responses in chickens infected with a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus. Asparagine 631 variants of the chicken Mx protein do not inhibit influenza virus replication in primary chicken embryo fibroblasts or in vitro surrogate assays. Susceptibility of different chicken lines to H7N1 highly pathogenic avian influenza virus and the role of Mx gene polymorphism coding amino acid position 631. Mx is dispensable for interferon-mediated resistance of chicken cells against influenza A virus. Immune responses elicited in rainbow trout through the administration of infectious pancreatic necrosis viruslike particles. Antigen dose and humoral immune response correspond with protection for inactivated infectious pancreatic necrosis virus vaccines in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L). Inhibition of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus replication by atlantic salmon Mx1 protein. Enhanced grass carp reovirus resistance of Mxtransgenic rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus). Protective roles of grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella Mx isoforms against grass carp reovirus. Survey of transcript expression in rainbow trout leukocytes reveals a major contribution of interferonresponsive genes in the early response to a rhabdovirus infection. Rock bream (Oplegnathus fasciatus) viperin is a virusresponsive protein that modulates innate immunity and promotes resistance against megalocytivirus infection. Viperin protein expression inhibits the late stage of respiratory syncytial virus morphogenesis. Equine viperin restricts equine infectious anemia virus replication by inhibiting the production and/or release of viral gag, env, and receptor via distortion of the endoplasmic reticulum.

Sleeper cardiac surgery medicine dictionary pill identification cheap 8 mg ondansetron with visa, catheterization procedures treatment abbreviation effective ondansetron 4 mg, myocardial contusions from blunt chest trauma, electrical injuries occurring during cardioversion, ablation procedures, or defibrillation. This allows patients that normally would be monitored in the hospital for 13 days to be discharged early. Elevations of cTn have also been shown to be sensitive in detecting cardiac injury in dogs and cats with blunt chest trauma, although further studies are needed to determine if cTn levels can aid in the clinical management of veterinary patients with chest trauma. In humans, elevated cTn values during sepsis are associated with left ventricular dysfunction. A study involving septic foals showed that cTnT values were significantly elevated compared with healthy foals but there was no difference in levels among survivors compared with nonsurvivors. Elevations in cTnI can be used to determine cardiac involvement in babesiosis and there is an association between cTnI levels and clinical severity and mortality. A study of dogs in Brazil naturally infected with Ehrlichia canis showed that 44% of patients had elevated cTnI concentrations without clinically apparent heart disease suggesting myocardial involvement. The evolution of the clinical entity of heart failure is accompanied by cardiac remodeling as a result of hypertrophy of myocardial myocytes, death of cardiac myocytes consisting of both cell necrosis and apoptosis, and formation of fibrotic replacement tissue. These are all a consequence of the complex interaction between mechanical, neurohumoral, inflammatory, and ischemic alterations within the myocardium. A correlation was also found between & Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care Society 2008, doi: 10. Unfortunately, as described above, cTnI comparisons between different machines are not possible and limit the use of this data. Little research involving cardiac disease and cTn levels has been performed in horses but there are reports of elevated cTnI levels in horses with ventricular arrhythmias. Reports of 2 horses with ventricular tachycardia showed that 1 had a ruptured aortic jet lesion and another had severe myocardial necrosis of unknown cause. Chemotherapy Cardiomyopathy secondary to chemotherapy, particularly anthracyclines such as doxorubicin, is irreversible and usually fatal. Development of cardiomyopathy is related to the cumulative dose throughout the course of chemotherapy. Clinical signs of cardiac disease may be delayed, occurring after chemotherapy is finished. A retrospective study showed that cTnI levels were elevated in 32 of 44 dogs during doxorubicin chemotherapy for lymphoma and osteosarcoma, but the elevations did not predict development of cardiac disease based primarily on physical exam findings and thoracic radiographs. Further prospective studies are needed to determine if troponins will be useful in the clinical management of patients receiving chemotherapy. Pericardial Disease Pericardial disease has been shown to cause elevations in troponin levels in both humans and veterinary patients. Decreased coronary perfusion during tamponade may also be the cause of troponin release. Two studies have shown that dogs with pericardial effusion have significantly higher cTnI levels than normal dogs. This study prospectively evaluated 26 dogs in which a definitive cause of pericardial effusion was identified. A significantly higher cTnI level was found in dogs with hemangiosarcoma versus dogs with idiopathic pericardial effusion. Troponin release in these cases may be from the cytosolic pool rather than structurally bound troponin. A report on serum chemistry alterations in Alaskan sled dogs during endurance exercise showed elevations in cTnI, with 241 & Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care Society 2008, doi: 10. The resultant increase in right ventricular pressure leads to decreased myocardial perfusion and oxygen supply. These changes, in addition to hypoxemia with pulmonary thromboembolism, can cause cardiac damage and cTn leakage. Results of the second study were similar with increased cTnI and cTnT values in 93% and 57% of patients, respectively. Renal Failure Cardiac disease is a common cause of death in humans with end-stage renal disease. Regardless of cause, elevations of troponin I and T in patients with renal disease and patients on hemodialysis were found to be indicators of mortality.
Buy cheap ondansetron 4mg online. Depression : डिप्रेसन के हो ? | कसरि डिप्रेसन बाट मुक्ति पाउने.