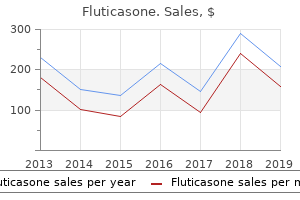
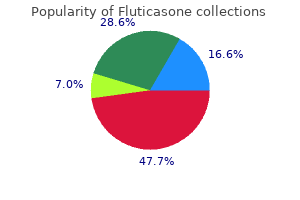
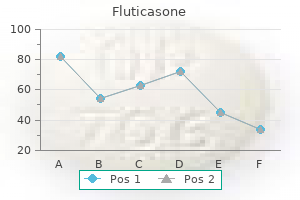
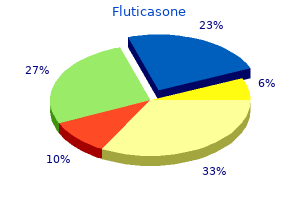
Fluticasone
"Generic fluticasone 250 mcg otc, asthma lung pain".
By: P. Volkar, M.A.S., M.D.
Professor, Touro University Nevada College of Osteopathic Medicine
The level of pharmacologic paralysis is adjusted based on serum levels and the assessed parameters asthma exercise order 500 mcg fluticasone otc. Potential complications include hypotension due to decreased sympathetic tone and myocardial depression (Greenberg asthma definition images discount fluticasone 500 mcg without a prescription, 2001). Readings taken from a catheter residing in the jugular outflow tract theoretically allow for a comparison of arterial and venous oxygen saturation, and the balance of cerebral oxygen supply and demand is demonstrated. This type of monitoring appears beneficial in the management of patients at risk for cerebral ischemia; however, the invasive nature of this type of monitoring and current limitations in technology mandate caution in its use. More study is needed before SjO2 monitoring can be considered a valid and reliable tool for the management of cerebral ischemia (Clay, 2000). Because the patient is critically ill, ongoing assessment will Chapter 61 be more focused, including pupil checks, assessment of selected cranial nerves, frequent measurements of vital signs and intracranial pressure, and use of the Glasgow Coma Scale. Repeated assessments of the patient are made (sometimes minute by minute) so that improvement or deterioration may be noted immediately. The head is kept in a neutral (midline) position, maintained with the use of a cervical collar if necessary, to promote venous drainage. Elevation of the head is maintained at 0 to 60 degrees to aid in venous drainage unless otherwise prescribed (Sullivan, 2000). When moving or being turned in bed, the patient can be instructed to exhale (which opens the glottis) to avoid the Valsalva maneuver. Before suctioning, the patient should be preoxygenated and hyperventilated using 100% oxygen on the ventilator (Hickey, 2003). High levels of positive end-expiratory pressure are avoided because they may decrease venous return to the heart and decrease venous drainage from the brain through increased intrathoracic pressure (Hickey, 2003). The patient is hyperoxygenated before and after suctioning to maintain adequate oxygenation. The lung fields are auscultated at least every 8 hours to determine the presence of adventitious sounds or any areas of congestion. Elevating the head of the bed may aid in clearing secretions as well as improving venous drainage of the brain. Increased pressure on the frontal lobes or deep midline structures may result in Cheyne-Stokes respirations, whereas pressure in the midbrain may cause hyperventilation. When the lower portion of the brain stem (the pons and medulla) is involved, respirations become irregular and eventually cease. Hyperextension, rotation, or hyperflexion of the neck causes decreased venous return. To keep secretions loose and easy to suction or expectorate Soft bowel movements will prevent straining or Valsalva maneuver. Skin turgor, mucous membranes, and serum and urine osmolality are monitored to assess fluid status. If fluids are given intravenously, the nurse ensures they are administered at a slow to moderate rate with an intravenous infusion pump to prevent too-rapid administration and avoid overhydration. For the patient receiving mannitol, the nurse observes for the possible development of heart failure and pulmonary edema, because the intent of treatment is for fluid to shift from the intracellular compartment to the intravascular system, thus controlling cerebral edema. For patients undergoing dehydrating procedures, vital signs, including blood pressure, must be monitored to assess fluid volume status. An indwelling urinary catheter is inserted to permit assessment of renal function and fluid status. An output greater than 200 mL/hr for 2 consecutive hours may indicate the onset of diabetes insipidus (Cruz, 1998). These patients also need careful oral hygiene because mouth dryness is associated with dehydration. Frequently rinsing the mouth, lubricating the lips, and removing encrustations relieve dryness and promote comfort. Most health care facilities have written protocols for managing these systems and maintaining their sterility; strict adherence to them is essential.
Sometimes the lacerations may completely sever the fibers of the anal sphincter (complete tear) asthma treatment otc order 250 mcg fluticasone overnight delivery. Prolapse (if complete prolapse occurs asthma treatment images generic fluticasone 250 mcg, it may also be referred to as procidentia) results from a weakening of the support structures of the uterus itself; the cervix drops and may protrude from the vagina. The patient should have the pessary removed, examined, and cleaned by her health care provider at prescribed intervals. At this checkup, vaginal walls are examined for pressure points or signs of irritation. Normally, the patient experiences no pain, discomfort, or discharge with a pessary, but if chronic irritation occurs, alternative measures may be needed. The procedure to repair the anterior vaginal wall is called anterior colporrhaphy, repair of a rectocele is called a posterior colporrhaphy, and repair of perineal lacerations is called a perineorrhaphy. These repairs are frequently performed laparoscopically, resulting in short hospital stays and good outcomes. A laparoscope is inserted through a small abdominal incision, the pelvis is visualized, and surgical repairs are performed. Clinical Manifestations Because a cystocele causes the anterior vaginal wall to bulge downward, the patient may report a sense of pelvic pressure, fatigue, and urinary problems such as incontinence, frequency, and urgency. The symptoms of rectocele resemble those of cystocele, with one exception: instead of urinary symptoms, the patient may experience rectal pressure. Constipation, uncontrollable gas, and fecal incontinence may occur in patients with complete tears. Individual variations may result in an anterior, middle, or posterior uterine position. A backward positioning of the uterus, known as retroversion and retroflexion, is not uncommon. Chart 47-4 Medical Management Kegel exercises, which involve contracting or tightening the vaginal muscles, are prescribed to help strengthen these weakened muscles. Kegel exercises are easy to do and are recommended for all women, including those with strong pelvic floor muscles (Chart 47-4). This device is inserted into the vagina and positioned to keep an organ, such as the bladder, uterus, or intestine, properly aligned when a cystocele, rectocele, or prolapse has occurred. Pessaries are usually ringshaped or doughnut-shaped and are made of various materials, such as rubber or plastic. Become aware of pelvic muscle function by "drawing in" the perivaginal muscles and anal sphincter as if to control urine or defecation, but not contracting the abdominal, buttock, or inner thigh muscles. Sustain contraction of the muscles for up to 10 seconds, followed by at least 10 seconds of relaxation. Chapter 47 Management of Patients With Female Reproductive Disorders 1425 If the structures that support the uterus weaken (typically from childbirth), the uterus may work its way down the vaginal canal (prolapse) and even appear outside the vaginal orifice (procidentia). As the uterus descends, it may pull the vaginal walls and even the bladder and rectum with it. Symptoms include pressure and urinary problems (incontinence or retention) from displacement of the bladder. The problems are aggravated when the woman coughs, lifts a heavy object, or stands for a long time. The patient is encouraged to void within a few hours after surgery for cystocele and complete tear. If the patient does not void within this period and reports discomfort or pain in the bladder region after 6 hours, she will need to be catheterized. Some physicians prefer to leave an indwelling catheter in place for 2 to 4 days, so some women may return home with a catheter in place. After each voiding or bowel movement, the perineum is cleansed with warm, sterile saline solution and dried with sterile absorbent material if a perineal incision has been made. After an external perineal repair, several methods are used in caring for the sutures.
Vaccines are made of antigen preparations in a suspension and are intended to produce a human immune response to protect the host from future encounters with the organism asthma treatment images fluticasone 500mcg low cost. When live organisms are used as antigen asthma symptoms 7 dpo order fluticasone with paypal, the actual disease (often with a modified course) may follow. These guidelines detail studied experience with allergy and other complications and provide crucial information about refrigeration, storage, dosage, and administration. For example, although the first dose of measles vaccine is recommended at the age of 12 to 15 months, babies in developing countries (where measles contributes significantly to childhood morbidity and mortality) should be vaccinated at 9 months. Vaccine recommendations for adults are designed to protect those with underlying diseases that increase infection risk, those with potential for occupational exposure, and those who may be exposed to infectious agents during travel. Immunosuppressed adults (including those who have had splenectomy) should be vaccinated for pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae), meningococcus (Neisseria meningitidis), and Haemophilus influenzae. Health care workers should be immune to measles, mumps, rubella, hepatitis B, and varicella. It is strongly recommended that all of the previously described adult groups and those with asthma or other chronic respiratory conditions receive annual influenza vaccine. Information about individual vaccines or the most current vaccine schedules may be found on the Internet (. Advice about optimal vaccination for travelers is available on the Internet Nurses should ask parents or adult vaccine recipients to provide information about any problems encountered after vaccination. The incidence of vaccine-preventable diseases, such as measles, mumps, rubella, and diphtheria, is affected by immigration from developing countries. Vaccine campaigns in developing countries are often financially and logistically constrained, and immigrants from such areas may be more likely than U. Individual risk and epidemic risk are reduced when vaccination campaigns reach all communities, including those with a high proportion of immigrants. The measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine should not be administered to pregnant women. All public health departments are encouraged to vigorously promote vaccination for all children and for susceptible adults unless contraindicated. All who work in health care should demonstrate immunity to these three viruses by one of the following: birth date before 1957, documented administration of two doses of vaccine, laboratory evidence of immunity, or documentation of physician-diagnosed measles or mumps. Epidemiologic evidence supports that the risk for side effects is greater in nonimmune vaccine recipients than in those receiving repeat doses. Patients should be advised that fever, transient lymphadenopathy, or hypersensitivity reaction might occur. In its natural state, the varicella virus attacks most individuals as children, causing disseminated disease in the form of chickenpox. Any dose not given at the recommended age should be given at any subsequent visit when indicated and feasible. Blue shading indicates age groups that warrant special effort to administer those vaccines not previously given. Monovalent or combination vaccine containing HepB may be used to complete the series. The second dose should be given at least 4 weeks after the first dose, except for combination vaccines which cannot be administered before age 6 weeks. The third dose should be given at least 16 weeks after the first dose and at least 8 weeks after the second dose. The last dose in the vaccination series (third or fourth dose) should not be administered before age 6 months. The last dose in the vaccination series should not be administered before age 6 months. Varicella vaccine is recommended at any visit at or after age 12 months for susceptible children, ie, those who lack a reliable history of chickenpox.
After the stone is extracted asthma symptoms young children discount fluticasone 250 mcg on line, the percutaneous nephrostomy tube is left in place for a time to ensure that the ureter is not obstructed by edema or blood clots asthma treatment latest purchase fluticasone 250mcg free shipping. The most common complications are hemorrhage, infection, and urinary extravasation. Chemolysis, stone dissolution using infusions of chemical solutions (eg, alkylating agents, acidifying agents) for the purpose of dissolving the stone, is an alternative treatment sometimes used in patients who are at risk for complications of other types of therapy, who refuse to undergo other methods, or who have stones (struvite) that dissolve easily. A percutaneous nephrostomy is performed, and the warm irrigating solution is allowed to flow continuously onto the stone. The irrigating solution exits the renal collecting system by means of the ureter or the nephrostomy tube. Several of these treatment modalities may be used in combination to ensure removal of the stones (Bihl & Meyers, 2001; Joshi, Kumar & Timoney, 2001; Liou & Streem, 2001). Surgical intervention is indicated if the stone does not respond to other forms of treatment. It may also be performed to correct anatomic abnormalities within the kidney to improve urinary drainage. If the stone is in the kidney, the surgery performed may be a nephrolithotomy (incision into the kidney with removal of the stone) or a nephrectomy, if the kidney is nonfunctional secondary to infection or hydronephrosis. Stones in the kidney pelvis are removed by a pyelolithotomy, those in the ureter by ureterolithotomy, and those in the bladder by cystotomy. If the stone is in the bladder, an instrument may be inserted through the urethra into the bladder, and the stone is crushed in the jaws of this instrument. Such a procedure is called a cystolitholapaxy (Maheshwari, Oswal & Bansal, 1999; Monga & Oglevie, 2000; Streem, 2000). Management of Patients With Urinary Disorders 1341 stones and measures to prevent their occurrence or recurrence is also assessed. The pain level is monitored closely, and increases in severity are reported promptly to the physician so that relief can be provided and additional treatment initiated. The patient is prepared for other treatment (eg, lithotripsy, percutaneous stone removal, ureteroscopy, or surgery) if severe pain is unrelieved and the stone is not passed spontaneously. Increased fluid intake is encouraged to prevent dehydration and increase hydrostatic pressure within the urinary tract to promote passage of the stone. If the patient cannot take adequate fluids orally, intravenous fluids are prescribed. Ambulation is encouraged as a means of moving the stone through the urinary tract. Patients with calculi require frequent nursing observation to detect the spontaneous passage of a stone. Any blood clots passed in the urine should be crushed and the sides of the urinal and bedpan inspected for clinging stones. The patient is instructed to report any sudden increases in pain immediately because of the possibility of a stone fragment obstructing a ureter. Analgesic medications are administered as prescribed for the relief of pain and discomfort. The severity and location of pain are determined, along with any radiation of the pain. The history focuses on factors that predispose the patient to urinary tract stones or that may have precipitated the current episode of renal or ureteral colic. Predisposing factors include family history of stones, the presence of cancer or bone marrow disorders or the use of chemotherapeutic agents, inflammatory bowel disease, or a diet high in calcium or purines. Factors that may precipitate stone formation in the patient predisposed to renal calculi include episodes of dehydration, prolonged immobilization, and infection. All infections should be treated with the appropriate antibiotic agent before efforts are made to dissolve the stone (DeLeskey & Massi-Ventura, 2000). One facet of prevention is to maintain a high fluid intake because stones form more readily in concentrated urine. A patient who has shown a tendency to form stones should drink enough fluid to excrete greater than 2,000 mL of urine every 24 hours (preferably 3,000 to 4,000 mL), should adhere to the prescribed diet, and should avoid sudden increases in environmental temperatures, which may cause a fall in urinary volume.
Cheap generic fluticasone canada. Asthma | Symptoms | Attack | Medications | Inhalers| Treatments..