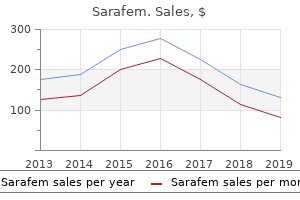
Sarafem
"Purchase sarafem without prescription, breast cancer yoga mat".
By: O. Khabir, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, University of South Carolina School of Medicine Greenville
It suggests that the activation areas are not exclusively related to the chills menstrual ovulation order 10mg sarafem mastercard, rather helped to feel chill when subjects listened to chill-inducing music menstrual like cramps at 33 weeks sarafem 20mg visa. Based on our research, the activation in the caudate could be important for the chill sensation. In addition, the activation in the putamen, the insula and the parahippocampus could be involved in general musical sensation, such as whether they listened to original or noisy music. Much of this research has focused on long-term effects occurring over the course of multiple sessions and many of the studies have focused on behavioral variables such as self-reported changes in mood that result from music intervention. The purpose of this Stress Reduction with a Musical Intervention study was to expand the previous work in two major ways. We wanted to compare the stress reducing effects of music listening versus music playing. Secondly, we utilized psychophysiological measures of stress in addition to self-report measures. We were also interested in changes that occur in one session (as opposed to multiple sessions). Behavioral and physiological results from post stressor and post recovery were compared. We performed a manipulation check by comparing baseline behavioral and physiological data versus post stressor data for each subject to ensure that we successfully stressed the participants. Results indicated that participants exhibited significant increase in behavioral and physiological stress response as a result of the stressor task. In comparing the groups, behavioral data was mixed while the physiological data showed a trend towards greater stress reduction for both experimental groups. Emotion Support: Faculty Research Council Grant Title: Measuring physiological markers of restorative landscapes using virtual reality environments Authors: *M. Research has shown that even minimal exposure to natural environments has been associated with increases in cognitive performance, attention and mood. Additionally, studies have shown significant decreases in stress after such exposure. What remains unknown, however, are the physiological responses during nature exposure and their relationship to these post-exposure changes in stress and behavior. Each subject was exposed to four environments (design using Unity software): an open valley, a narrow forest, an open plaza, and a narrow street. Within each environment, participants were transported to six locations for 30s within the environment. Participants were asked to remain seated and refrain from excessive movement below the neckline, but they were encouraged to look around within their environment and to take pictures of beautiful views. Given that people tend to have some control over their environment, pinpointing the physiological mechanisms underlying the benefits of natural environments is important to making changes that increase our health, cognitive abilities, and psychological well-being. However, yet little is known regarding the neural mechanism of how focusing on slow breathing modulates time course of emotional responses. Before the experiment, all the participants were instructed to practice slow breathing for 3 minutes. In the breath-focused condition but not in the viewing condition, P1 amplitudes for emotional minus neutral pictures correlated positively with the ability to focus attention measured by the Attentional Control Scale; N2 amplitudes for emotional minus neutral pictures correlated positively with individual differences in dispositional mindfulness measured by the Mindful Attention Awareness Scale. These observations suggest that even in the face of emotional stimulation, focusing on slow breathing induces attention-concentrated mindful states that increase the stability of attention and promote early emotion regulation, which deepens our understanding of the temporal processing mechanism of breath-focused mindfulness. Low threshold, unmyelinated C-tactile afferents respond preferentially to this type of touch. In two studies, we investigated both neural and autonomic (heart rate variability) responses during long-lasting slow stroking. Methods: In both studies, stroking was performed with a brush on the forearm for ~ 40 minutes at 3 cm/s (the velocity that optimally activates C-tactile fibres). In study 2, we added a control group (20 subjects) that received vibration stimulation. In both studies, pleasantness ratings for the brush stroking (and vibration in study 2) were collected.
The results appeared random: A third fired faster breast cancer 49ers generic sarafem 10mg visa, a third fired slower breast cancer month generic sarafem 20 mg line, and the remaining third were unresponsive. This was also the best understood region of the brain in terms of cellular circuitry. While visiting the Karolinska Institute in 1971 (the year Axelrod was awarded the Nobel Prize), I learned from Lars neurons are the most quiet during sleep. The locus coeruleus and the raphe nuclei are part of a venerable concept called the ascending reticular activating system, which implicates the reticular "core" of the brain stem in processes that arouse and awaken the forebrain. This simple idea has been refined and redefined in countless ways since it was introduced in the 1950s, but its basic sense remains. Raphe neurons seem to be intimately involved in the control of sleepwake cycles, as well as the different stages of sleep. It is important to note that several other transmitter systems are involved in a coordinated way as well. We will discuss the involvement of the diffuse modulatory systems in sleep and wakefulness in Chapter 19. Serotonergic raphe neurons have also been implicated in the control of mood and certain types of emotional behavior. We will return to serotonin and mood when we discuss clinical depression in Chapter 22. For many years, neuroscientists thought that dopamine existed in the brain only as a metabolic precursor for norepinephrine. After moving to the Salk Institute, I worked with Steve Foote and Gary Aston-Jones to record the firing patterns of the locus coeruleus neurons in awake behaving rats and squirrel monkeys. These experiments revealed that the locus coeruleus neurons have brief phasic responses to novel sensory signals of all modalities, progressively slowing with loss of attention and becoming silent during rapid eye movement sleep. The phasic and tonic discharge modes correlate with the chemical thresholds for alpha (highly sensitive) and beta (less sensitive) adrenergic receptors. In contrast to the diffuse rodent cortical innervations, their data showed differences in the amount of innervation in architectonically defined areas of the cerebral cortex, particularly in the cingulate and orbitofrontal cortex. My interests in the central catecholamine systems and brain disease continue today and have been intensified by the computational and theoretical concepts now being developed from studies of the roles of these systems in awake behaving primates, including normal cognitive declines with aging. Recall from Chapter 14 that these cells project axons to the striatum (the caudate nucleus and the putamen), where they somehow facilitate the initiation of voluntary movements. The midbrain is also the origin of the other dopaminergic modulatory system, a group of cells that lie very close to the substantia nigra, in the ventral tegmental area. A number of different functions have been ascribed to this complicated projection. For example, evidence indicates that it is involved in a "reward" system that somehow assigns value to , or reinforces, certain behaviors that are adaptive. We will see in Chapter 16 that if rats (or humans) are given a chance to do so, they will work to electrically stimulate this pathway. The substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area lie close together in the midbrain. They project to the striatum (caudate nucleus and putamen) and limbic and frontal cortical regions, respectively. Acetylcholine is the familiar transmitter at the neuromuscular junction, at synapses in autonomic ganglia, and at postganglionic parasympathetic synapses. Cholinergic interneurons also exist within the brain-in the striatum and the cortex, for example. In addition, there are two major diffuse modulatory cholinergic systems in the brain, one of which is called the basal forebrain complex. It is a "complex" because the cholinergic neurons lie scattered among several related nuclei at the core of the telencephalon, medial and ventral to the basal ganglia. The best known of these are the medial septal nuclei, which provide the cholinergic innervation of the hippocampus, and the basal nucleus of Meynert, which provides most of the cholinergic innervation of the neocortex.
As the light is reflected womens health lansing mi buy sarafem with a mastercard, some of its energy excites electrons in the gold coating and these excited electrons are in turn affected by the electric field of any molecules binding to the surface of the glass coating breast cancer medication buy 20 mg sarafem with mastercard. The more molecules that bind to the surface, the greater the effect on the excited electrons, and this in turn affects the reflected light beam. The reflected light thus becomes a sensitive measure of the number of atoms bound to the gold surface of the slide. If the ligand is then washed out, dissociation of ligand from the receptor can easily be followed and the dissociation rate calculated. A new solution of the ligand at a different concentration can then be flowed over the chip and the binding once again measured. The affinity of binding can be calculated in a number of ways in this type of assay. Most simply, the ratio of the rates of association and dissociation will give an estimate of the affinity, but more accurate estimates can be obtained from the measurements of the binding at different concentrations of ligand. Measurement of receptor-ligand interactions can be made in real time using a biosensor. Biosensors are able to measure the binding of molecules on the surface of gold-plated glass chips through the indirect effects of the binding on the total internal reflection of a beam of polarized light at the surface of the chip. As the T-cell receptors bind, the sensorgram (inset panel below the main panel) reflects the increasing amount of protein bound. As the binding reaches either saturation or equilibrium (third panel), the sensorgram shows a plateau, as no more protein binds. With continued washing, bound receptors now start to dissociate and are removed in the flow of the washing solution (last panel). The sensorgram now shows a declining curve, reflecting the rate at which the receptor and ligand dissociation occurs. The affinity and valence of an antibody can be determined by equilibrium dialysis. A known amount of antibody is placed in the bottom half of a dialysis chamber and exposed to different amounts of a diffusible monovalent antigen, such as a hapten. In Scatchard analysis, the ratio r/c (where r = moles of antigen bound per mole of antibody and c = molar concentration of free antigen) is plotted against r. The analysis of a monoclonal IgG antibody molecule, in which there are two identical antigenbinding sites per molecule, is shown in the left panel. The slope of the line is determined by the affinity of the antibody molecule for its antigen; if all the antibody molecules in a preparation are identical, as for this monoclonal antibody, then a straight line is obtained whose slope is equal to -Ka, where Ka is the association (or affinity) constant and the dissociation constant Kd = 1/Ka. As a mixture, they give curved lines with an x-axis intercept of two for which an average affinity (a) can be determined from the slope of this line at a concentration of antigen where 50% of the sites are bound, or at x = 1 (right panel). Stimulation of lymphocyte proliferation by treatment with polyclonal mitogens or specific antigen. To function in adaptive immunity, rare antigen-specific lymphocytes must proliferate extensively before they differentiate into functional effector cells in order to generate sufficient numbers of effector cells of a particular specificity. Thus, the analysis of induced lymphocyte proliferation is a central issue in their study. It is, however, difficult to detect the proliferation of normal lymphocytes in response to specific antigen because only a minute proportion of cells will be stimulated to divide. Great impetus was given to the field of lymphocyte culture by the finding that certain substances induce many or all lymphocytes of a given type to proliferate. These substances are referred to collectively as polyclonal mitogens because they induce mitosis in lymphocytes of many different specificities or clonal origins. Polyclonal mitogens seem to trigger essentially the same growth response mechanisms as antigen. When stimulated with polyclonal mitogens, they rapidly enter the G1 phase and progress through the cell cycle. This assay is used clinically for assessing the ability of lymphocytes from patients with suspected immunodeficiencies to proliferate in response to a nonspecific stimulus. Once lymphocyte culture had been optimized using the proliferative response to polyclonal mitogens as an assay, it became possible to detect antigen-specific T-cell proliferation in culture by measuring 3H-thymidine uptake in response to an antigen to which the T-cell donor had been previously immunized. This is the assay most commonly used for assessing T-cell responses after immunization, but it reveals little about the functional capabilities of the responding T cells. These must be ascertained by functional assays, as outlined in Sections A-33 and A-34.
The indirect Coombs test is a variation of the direct Coombs test in which an unknown serum is tested for antibodies against normal red blood cells by first mixing the two and then washing out the serum from the red blood cells and reacting them with anti-immunoglobulin antibody womens health events proven 10mg sarafem. If antibody in the unknown serum binds to the red blood cells women's health center vanderbilt 10 mg sarafem free shipping, agglutination by antiimmunoglobulin occurs. This is a major mechanism of host resistance to intracellular infection in mice, and probably in humans as well. Infectious mononucleosis, or glandular fever, is the common form of infection with the EpsteinBarr virus. Inflammation is a general term for the local accumulation of fluid, plasma proteins, and white blood cells that is initiated by physical injury, infection, or a local immune response. Acute inflammation is the term used to describe early and often transient episodes, whereas chronic inflammation occurs when the infection persists or during autoimmune diseases. The cells that invade tissues undergoing inflammatory responses are often called inflammatory cells or an inflammatory infiltrate. The early phases of the host response to infection depend on innate immunity in which a variety of innate resistance mechanisms recognize and respond to the presence of a pathogen. Innate immunity is present in all individuals at all times, does not increase with repeated exposure to a given pathogen, and discriminates between a group of related pathogens. Inositol trisphosphate releases calcium ions from intracellular stores in the endoplasmic reticulum. Integrins are heterodimeric cell-surface proteins involved in cellcell and cellmatrix interactions. They are important in adhesive interactions between lymphocytes and antigen-presenting cells and in lymphocyte and leukocyte migration into tissues. Staining for cytokines in cells that produce them can be achieved by permiablizing the cell and reacting it with a labelled fluorescent anti-cytokine antibody. Injections can be administered by a number of routes: intracutaneous (intradermal)entering the skin or dermis; subcutaneousentering below the skin or dermis; intramuscularentering the muscle; intranasalby way of the nose; and intravenousentering a vein. Isoelectric focusing is an electrophoretic technique in which proteins migrate in a pH gradient until they reach the place in the gradient at which their net charge is neutraltheir isoelectric point. Uncharged proteins no longer migrate; thus each protein is focused at its isoelectric point. The first antibodies produced in a humoral immune response are IgM, but activated B cells subsequently undergo isotype switching or class switching to secrete antibodies of different isotypes: IgG, IgA, and IgE. Isotype switching does not affect antibody specificity significantly, but alters the effector functions that an antibody can engage. Immunoglobulins are made in several distinct isotypes or classesIgM, IgG, IgD, IgA, and IgEeach of which has a distinct heavy-chain C region encoded by a distinct C-region gene. The isotype of an antibody determines the effector mechanisms that it can engage on binding antigen. The different heavy-chain C regions are encoded in exons 3 to the V(D)J rearrangement site. This allows the same antibody heavy-chain V region to link up with different heavy-chain Cregion isotypes as a result of somatic recombination. Isotypic exclusion describes the use of one or other of the light-chain isotypes, k or l, by a given B cell or antibody. J the J gene segments, or joining gene segments, are found some distance 5 to the C genes in immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor loci. Junctional diversity is the diversity present in antigen-specific receptors that is created during the pro K In the context of immunoglobulins, is one of the two classes of light-chain. The cell-surface receptor c-Kit, present on developing B cells and other developing white blood cells, binds to the stem cell factor on bone marrow stromal cells. Kupffer cells are phagocytes lining the hepatic sinusoids; they remove debris and dying cells from the blood, but are not known to elicit immune responses. L In the context of immunoglobulins, is one of the two is one of the two classes of light-chain. They can migrate from the epidermis to regional lymph nodes via the afferent lymphatics. The large pre-B cells have a cell-surface pre-B-cell receptor, which is lost on the transition to small pre-B cells, in which light-chain gene rearrangement occurs. Latency can be established in various ways; when the virus is reactivated and replicates, it can produce disease.
Cheap 20 mg sarafem. The Beauty of Collaboration In Healthcare: Juliane Zielonka at TEDxBarcelonaChange.