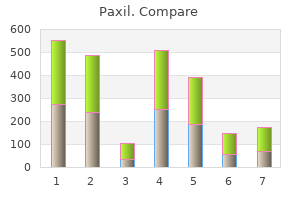
Paxil
"Buy paxil 20 mg mastercard, treatment skin cancer".
By: U. Ateras, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Vice Chair, A.T. Still University School of Osteopathic Medicine in Arizona
Although such measures can be expensive medicine 018 buy cheap paxil 30mg on line, the costs are likely to be economically justifiable based on the medical expenses associated with treating human cases of rodent-related diseases and the property damage caused by some of these animals symptoms 7 days after iui buy paxil in united states online. The following rules should be followed to reduce the risk of people acquiring a rodentor lagomorph-related illness in areas undergoing urbanization. Implement strict planning and regulatory processes intended to reduce the risk that urban sprawl will lead to increased exposures of people to non-commensal rodent- or lagomorph-related diseases. Educate the public and government officials about the risks of rodent- or lagomorphrelated diseases in sites undergoing urbanization, and provide these people with information about the steps that can be taken to protect individuals who are likely to be exposed to these diseases. Minimize contact between people and disease-bearing non-commensal rodents or lagomorphs through implementation of effective and sustainable environmental-management programmes. Appropriate management strategies should include habitat modifi458 459 Non-commensal rodents and lagomorphs Public Health Significance of Urban Pests References2 Alderton D (1996). Pneumonic pasteurellosis associated with Pasteurella haemolytica in chipmunks (Tamias sibiricus). The encyclopedia of arthropod-transmitted infections of man and domesticated animals. Susceptibility of the hispid cotton rat (Sigmodon hispidus) to the Lyme disease spirochete (Borrelia burgdorferi). Susceptibility of various species of rodents to the relapsing fever spirochete, Borrelia hermsii. The encyclopedia of arthropodtransmitted infections of man and domesticated animals. Older citations that are not readily accessible via electronic search engines were discussed and listed in the literature cited when available and appropriate. Methods for assessing the burden of parasitic zoonoses: echinococcosis and cysticercosis. Serologic and genetic identification of Peromyscus maniculatus as the primary rodent reservoir for a new hantavirus in the southwestern United States. A household based, case control study of environmental factors associated with hantavirus pulmonary syndrome in the southwestern United States. London, British Museum (Natural History); Ithaca, New York, Cornell University Press. Role of grey squirrels and pheasants in the transmission of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, the Lyme disease spirochete, in the U. A serological survey and isolation of leptospires from small rodents and wild boars in the Republic of Croatia. Removing deer mice from buildings and the risk for human exposure to Sin Nombre virus. Giardia in beaver (Castor canadensis) and nutria (Myocastor coypus) from east Texas. Biological, epidemiological and clinical aspects of echinococcosis, a zoonosis of increasing concern. The mammalian radiations: an analysis of trends in evolution, adaption, and behavior. Climatic and environmental patterns associated with hantavirus pulmonary syndrome, Four Corners region, United States. Isolation and characterization of Whitewater Arroyo virus, a novel North American arenavirus.
Because of the much higher propensity for infections medications janumet generic paxil 10mg online, catheter malfunction and inadequate blood flow through these catheters medicine 852 purchase paxil us, and the risk of developing vein stenosis along the path of the catheter, it is critical that a permanent access plan be developed and implemented as soon as it is determined that the patient has chronic (and not acute) kidney failure. Finally, if the age and medical condition of the patient permit, living-related transplantation should be pursued. This section briefly discusses different dialysis techniques, including short daily hemodialysis and nocturnal hemodialysis, with a focus on conventional, thrice weekly, in-center dialysis, as this remains the most common hemodialysis strategy. The dialysis dose, the time needed to optimize kidney replacement therapy, and strategies for accomplishing this are reviewed. To place common hemodialysis strategies into context, current in-center hemodialysis regimens average less than 3. Considering that this level is below the level at which hemodialysis is initiated, it is clear that the delivery Because kidney disease is often "silent," it is inevitable that some patients will present with clear indications for initiation of dialysis but without a permanent access. Several factors should be considered in the prescription of dialysis to optimize outcomes. For the hypothetical 70-kg person, the first step is to calculate the volume of urea distribution, which is total body water. For men, this is assumed to be 60% of body weight (42 L), whereas in women it is assumed to be 55% of body weight (38. The next step is to determine the clearance of the dialyzer at specific "blood" and dialysate flow rates. An in vitro evaluation of urea clearance is usually included in the package insert of the dialyzer, accounting for the surface area of the dialyzer, the solution flow rate, and other dialyzer factors. However, since this is an in vitro assessment based on an aqueous solution, it is reasonable to assume that the in vivo urea clearance is approximately 80% of the reported in vitro clearance. Blood-pressure medications also complicate the achievement of the target weight, because these medications may predispose patients to hypotension during fluid removal. Accordingly, achievement of target weight based on clinical assessment is often a process of trial and error that subjects patients to frequent episodes of hypotension. The first (Bioimpedance) can be used on the patient during dialysis by applying electrodes to the skin and measuring the electrical impedance of tissue as fluid is removed during dialysis via ultrafiltration. The second device, called the "crit-line," provides a continuous measure of online hematocrit. Recently, retrospective analyses of large data sets from the United States and other countries have highlighted the impressive survival benefit of patients dialyzed for 4 or more hours. Possible explanations include theoretical benefits of an increase in the dose of dialysis as well as a decrease in the rate of ultrafiltration to below 10 mL/kg/h, which has been found to be associated with better cardiovascular stability. A final important reason for starting patients at 4 hours is psychological; after a patient is initiated on dialysis for less than 4 hours, there is a strong reluctance on the part of many patients to increase the dialysis duration, regardless of the reason. Substantial declines in hematocrit indicate the need to lower the postdialysis target weight. Recent literature suggests that rates of ultrafiltration that exceed 10 mL/kg/h (approximately 700 mL/h for the 70 kg person) are often associated with cardiovascular instability, hypotension, and cramps. Although urea is no longer considered the principal "uremic toxin," urea concentration in the blood and subsequent urea clearance with dialytic therapy correlate reasonably well with the changes observed clinically. Furthermore, urea is easily measured in the blood and dialysate, is evenly distributed in total body water, and rapidly diffuses from intracellular to extracellular and vascular spaces. Therefore, it is reasonable to assume that changes in urea concentration during dialysis reflect the dose of dialysis. On the basis of limited long-term studies and no clinical trial data, the best patient outcomes appear associated with Kt/V values of 1. It is therefore important to be aware of the potential errors that could be introduced in determining each of these measures. Potential Errors in Predialysis Urea Measurement 2 minutes after dialysis is terminated (preferred) or toward the end of dialysis after the dialysate flow is stopped and the blood pump has been slowed to 50 mL/min for at least 5 minutes to avoid recirculation. Recirculation of blood at the end of dialysis not only refers to the possibility of mixing the blood from the inlet (arterial) and outlet (venous) blood that occurs commonly when the needle tips are close to each other (less than 1 inch apart), particularly when blood flow is high, but also refers to a phenomenon called cardiopulmonary recirculation. Cardiopulmonary recirculation occurs throughout a dialysis session and can be illustrated by the following observation: when tested, the urea concentration of the blood entering the dialyzer is often different from the urea concentration of the blood in distant peripheral tissues, because the dialyzed blood (which has low urea) concentration dilutes the blood entering the right atrium from the tissues, and it takes several minutes for this blood in the right atrium to be "pumped" or distributed to the peripheral tissues. This cardiopulmonary recirculation is more pronounced in patients dialyzed with high urea clearance dialysis (large dialyzer surface area or rapid blood flow) and in patients with low cardiac output.
Some states have legally recognized that many adolescents age 14 and older can meet the cognitive criteria and emotional maturity for competence and may decide independently medications known to cause hair loss purchase 20 mg paxil amex. The Supreme Court has decided that pregnant symptoms vitamin b12 deficiency discount paxil 30mg with amex, mature minors have the constitutional right to make decisions about abortion without parental consent. Although many state legislatures require parental notification, pregnant adolescents wishing to have an abortion do not have to seek parental consent. The state must provide a judicial procedure to facilitate this decision making for adolescents. Children who are legally emancipated from parental control may seek medical treatment without parental consent. The definition varies from state to state but generally includes children who have graduated from high school, are members of the armed forces, married, pregnant, runaways, are parents, live apart from their parents, and are financially independent or declared emancipated by a court. State legislatures have concluded that minors with certain medical conditions, such as sexually transmitted infections and other contagious diseases, pregnancy (including prevention with the use of birth control), certain mental illnesses, and drug and alcohol abuse, may seek treatment for these conditions autonomously. States have an interest in limiting the spread of disease that may endanger the public health and in eliminating barriers to access for the treatment of certain conditions. Ethical Issues in Genetic Testing and Screening in Children the goal of screening is to identify diseases when there is no clinically identifiable risk factor for disease. Screening should take place only when there is a treatment available or when a diagnosis would benefit the child. Testing usually is performed when there is some clinically identifiable risk factor. Genetic testing and screening present special problems because test results have important implications. Some genetic screening (sickle cell anemia or cystic fibrosis) may reveal a carrier state, which may lead to choices about reproduction or create financial, psychosocial, and interpersonal problems. Collaboration with, or referral to , a clinical geneticist is appropriate in helping the family with the complex issues of genetic counseling when a genetic disorder is detected or likely to be detected. Examples of diseases that can be diagnosed by genetic screening, even though the manifestations of the disease process do not appear until later in life, are polycystic kidney disease; Huntington disease; certain cancers, such as breast cancer in some ethnic populations; and hemochromatosis. Testing for these disorders should be delayed until the child has the capacity for informed consent or assent and is competent to make decisions, unless there is a direct benefit to the child at the time of testing. The pediatrician is required to act in the best interests of the child, even when religious tenets may interfere with the health and well-being of the child. When an infant or child whose parents have a religious prohibition against a blood transfusion needs a transfusion to save his or her life, the courts always have intervened to allow a transfusion. In contrast, parents with strong religious beliefs under some state laws may refuse immunizations for their children. However, state governments can mandate immunizations for all children during disease outbreaks or epidemics. By requiring immunization of all, including individuals who object on religious grounds, the state government is using the principle of distributive justice, which states that all members of society must share in the burdens and the benefits to have a just society. Children as Human Subjects in Research Confidentiality Confidentiality is crucial to the provision of medical care and is an important part of the basis for a trusting the goal of research is to develop new and generalized knowledge. Parents may give informed permission for children to participate in research under certain conditions. Special federal regulations have been developed to protect child and adolescent participants in human investigation. Chapter 4 these regulations provide additional safeguards beyond the safeguards provided for adult participants in research, while still providing the opportunity for children to benefit from the scientific advances of research. Many parents with seriously ill children hope that the research protocol will have a direct benefit for their particular child. The greatest challenge for researchers is to be clear with parents that research is not treatment. Families who have not had time to prepare for the tragedy of an unexpected death require considerable support. Palliative care can make important contributions to the endof-life and bereavement issues that families face in these circumstances. This may become complicated in circumstances where the cause of the death must be fully explored. The need to investigate the possibility of child abuse or neglect subjects the family to intense scrutiny and may create guilt and anger directed at the medical team.
Order generic paxil line. My heart attack symptoms.
There is a dramatic decline in daytime sleep (scheduled napping) by 5 yr medicine for yeast infection generic paxil 10mg overnight delivery, with a less marked and more gradual continued decrease in nocturnal sleep amounts into late adolescence medications drugs prescription drugs discount paxil 10 mg with mastercard. Less common causes of sleep disturbance in childhood involve inappropriate timing of the sleep period (as occurs in circadian rhythm disturbances), or primary disorders of excessive daytime sleepiness (central hypersomnias such as narcolepsy). Insufficient sleep is usually the result of difficulty initiating (delayed sleep onset) and/or maintaining sleep (prolonged night wakings), but, especially in older children and adolescents, may also represent a conscious lifestyle decision to sacrifice sleep in favor of competing priorities, such as homework and social activities. The underlying causes of sleep onset delay/prolonged night wakings or sleep fragmentation may in turn be related to primarily behavioral factors (bedtime resistance resulting in shortened sleep duration) and/or medical causes (obstructive sleep apnea causing frequent, brief arousals). It should be noted that certain pediatric populations are relatively more vulnerable to acute or chronic sleep problems. These include children with medical problems, including chronic illnesses, such as cystic fibrosis, asthma, and rheumatoid arthritis, and acute illnesses, such as otitis media; children taking medications or ingesting substances with stimulant. No established nocturnal/diurnal pattern in the 1st few wk; sleep is evenly distributed throughout the day and night, averaging 8. Safe sleep practices for infants: Place the baby on his or her back to sleep at night and during nap times. Place the baby on a firm mattress with a well-fitting sheet in a safety-approved crib. Do not use pillows or comforters Cribs should not have corner posts over 116 in high or decorative cut-outs. The capacity to self-soothe begins to develop in the 1st 12 wk of life, and is a reflection of both neurodevelopmental maturation and learning. Sleep consolidation, or "sleeping through the night," is usually defined by parents as a continuous sleep episode without the need for parental intervention. Infants develop the ability to consolidate sleep between 6 wk to 3 mo Cognitive, motor, social, language developmental issues impact on sleep Nighttime fears develop; transitional objects, bedtime routines important Persistent co-sleeping tends to be highly associated with sleep problems in this age group Sleep problems may become chronic Most sleep issues that are perceived as problematic at this stage represent a discrepancy between parental expectations and developmentally appropriate sleep behaviors. Newborns who are noted by parents to be extremely fussy and persistently difficult to console are more likely to have underlying medical issues, such as colic, gastroesophageal reflux, and formula intolerance. Behavioral insomnia of childhood; sleep onset association type Sleep-related rhythmic movements (head banging, body rocking) Behavioral insomnia of childhood, sleep onset association type Behavioral insomnia of childhood, limit setting type Behavioral insomnia of childhood, limit setting type Sleepwalking Sleep terrors Nighttime fears/nightmares Obstructive sleep apnea Nightmares Obstructive sleep apnea Insufficient sleep Insufficient sleep Delayed sleep phase disorder Narcolepsy Restless legs syndrome/periodic limb movement disorder Middle childhood (6-12 hr) Adolescence (>12 yr) Average sleep duration 7-7. Insomnia of Childhood Insomnia may be broadly defined as repeated difficulty initiating and/or maintaining sleep that occurs despite age-appropriate time and opportunity for sleep. These sleep complaints must also result in some degree of impairment in daytime functioning for the child and/or family, which may range from fatigue, irritability, lack of energy, and mild cognitive impairment to effects on mood, school performance, and quality of life. Insomnia complaints may be of a short-term and transient nature (usually related to an acute event), or may be characterized as long-term and chronic. Insomnia, like many behavioral issues in children, is often primarily defined by parental concerns rather than by objective criteria, and therefore should be viewed in the context of family. One of the most common sleep disorders found in infants and toddlers is behavioral insomnia of childhood, sleep onset association type. In this disorder, the child learns to fall asleep only under certain conditions or associations which typically require parental presence, such as being rocked or fed, and does not develop the ability to self-soothe. During the night, when the child experiences the type of brief arousal that normally occurs at the end of a sleep cycle (every 60-90 minutes in infants) or awakens for other reasons, he or she is not able to get back to sleep without those same conditions being present. Bedtime and wake-up time should be about the same time on school nights and non-school nights. Avoid high-energy activities, such as rough play, and stimulating activities, such as watching television or playing computer games, just before bed. Make sure your child spends time outside every day whenever possible and is involved in regular exercise. A low-level night light is acceptable for children who find completely dark rooms frightening. Children can easily develop the bad habit of "needing" the television to fall asleep. The problem is one of prolonged night waking resulting in insufficient sleep (for both child and parent). Management of night wakings should include establishment of a set sleep schedule and bedtime routine, and implementation of a behavioral program. The treatment approach typically involves a program of rapid withdrawal (extinction) or more gradual withdrawal (graduated extinction) of parental assistance at sleep onset and during the night.
This guideline is broadly applicable to many media treatment renal cell carcinoma discount paxil 40 mg, but is tailored to microbial hazards to humans medications 10325 purchase cheap paxil on line. These two sets of frameworks were not the only sources consulted for development of this guideline. Microbial Risk Assessment Guideline Page 10 While there are differences between chemicals and microbes (as detailed in section 1. If quantitative data are not available, a qualitative approach can be used to address the current risk issue(s). Information on the identities of these experts, their individual expertise, and their professional experience should be publicly available, subject to national considerations. These experts should be selected in a transparent manner based on their expertise and their independence with regard to the interests involved, including disclosure of conflicts of interest in connection with risk assessment. Microbial Risk Assessment Guideline Page 12 Although risk assessments conducted by different agencies are not used for the same purposes, agencies usually perform risk assessments with one or more of the following goals in mind (adapted from U. The goals could shape the planning and scoping discussion (see Chapter 2) and ultimately the risk assessment. Risk assessors often conduct screenings when a time critical decision is needed. A risk assessor may resort to default assumptions to bridge data gaps that cannot wait for research to fill. In addition, screening assessments may actually provide the needed information that can address a risk management issue without having to initiate a more data or model intensive risk assessment. For example, this type of assessment might involve a single pathogen associated with multiple foods, a single food that has multiple pathogens, or multiple pathogens and multiple foods. Risk ranking assessments can help establish regulatory program priorities and identify critical research needs. This type of assessment technique helps identify the key factors that affect exposure including the impact Microbial Risk Assessment Guideline Page 13 of potential mitigation or intervention strategies on the predicted risk. As an example, an assessment could determine how treating drinking water with a chemical (risk to disinfection by-product exposure) would impact public health versus the impact of exposure to pathogenic organisms in water that is not treated. The assessment examines risk of introduction of disease agents through water, air, food animals, or animal products in the United States. Although not strictly speaking a "risk assessment," the results can be similar where they identify threats and characterize the nature, probability, and magnitude of adverse effects, and the results can help to inform risk management decisions. For example, it may be necessary to assess the risks associated with intentional contamination of the food or water supply with biological agents or release of biological agents as an aerosol into highly populated indoor or outdoor public areas. These assessments can identify corrective actions that can reduce the risk or lessen the severity of potential consequences. Science-policy Microbial Risk Assessment Guideline Page 14 positions and choices are by necessity utilized during the risk assessment process in two major ways. First, there are some basic, fundamental science-policy positions that frame the risk assessment process to ensure that the risk assessments are appropriate for a particular decision. These scoping "boundaries" for the risk assessment are articulated during the planning and scoping process and ultimately explained clearly in the risk characterization. These science-policy positions not only shape the risk assessment process, but are usually factors in the risk management process outside the risk assessment. Second, the use of default assumptions in a risk assessment is a science-policy choice often invoked when there is a lack of data. These choices are more specific than the framing science policies mentioned above. Given the nature of uncertainty and data gaps, default assumptions (sometimes simply called defaults) address these uncertainties when data are unavailable or otherwise not suitable for use. The report also stated that agencies should have principles for choosing default options. This is a science-policy choice, generally agreed upon during the planning and scoping discussions, when data gaps are identified (see section 2. During the risk assessment itself, a default is used only when essential data are lacking. Point estimates also can be considered defaults when the distribution of the parameter adds unnecessary complexity given the needs of the risk assessment. The consumption value of 2 liters per day per person is often used for chemicals and represents the 90th percentile of the 1994 to 1996 and 1998 Continuing Survey of Food Intake by Individuals community drinking water consumption data.