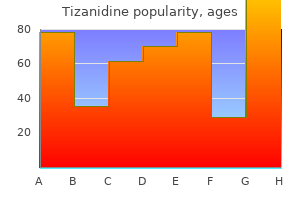
Tizanidine
"Tizanidine 4 mg line, muscle relaxant migraine".
By: Y. Sebastian, M.B.A., M.D.
Clinical Director, University of North Carolina School of Medicine
Hence spasms 2 buy tizanidine 4mg on line, the internal consistency of proxy-reports should not be taken as evidence for their accuracy spasms in 8 month old discount tizanidine amex. Accordingly, proxy-reports and self-reports of behavioral frequencies show low convergence for short and recent reference periods, periods for which the actor can actually draw on episodic information in providing a self-report. As a result, the convergence of self- and proxy-reports increases, although this increase presumably reflects reliance on the same inference strategies rather than higher accuracy (Schwarz & Wellens, 1997). The accumulating evidence highlights that every questionnaire design decision involves complex trade-offs, requiring researchers to think through the issues at hand for every particular study (for guidelines see Sudman et al. Some obvious precautions include the use of cognitive pretests (see the contributions in Schwarz & Sudman, 1996) that explore potential differences in question interpretation with a small number of respondents from all target populations. In doing so, it is important to test questions in the context in which they are to be presented in the final questionnaire otherwise contextual influences on question interpretation will be missed. Moreover, the order in which response alternatives, or substantively related questions, are presented should be varied to alert researchers to the potential influence of order effects. Theoretically, such context effects reflect the constructive nature of consumer preferences and are an integral part of consumer judgment. To the extent possible, the context created in the questionnaire should therefore resemble the context in which consumers are likely to make the respective decision in daily life, discovery of which usually requires exploratory studies. Unfortunately, it is usually impossible to optimize all features of questionnaire design at the same time and the researcher faces complex trade-offs (Schwarz & Oyserman, 2001; Sudman et al. At present, the standard training of consumer researchers does little to equip them for this task. Although they are likely to learn about the contextualized nature of human cognition and judgment in their consumer behavior courses, the material is often not linked to the question answering process that is at the heart of data collection, while methods training is frequently limited to advanced statistics. Unless the context dependency of self-reports receives more attention in consumer research, theory tests and managerial decisions may often be at the mercy of haphazard decisions at the data collection stage. The structure of autobiographical memory and the event history calendar: Potential improvements in the quality of retrospective reports in surveys. An experimental study of the effects of level of participation on proxy reports of vacation planning. Cognitive processes used by survey respondents to answer behavioral frequency questions. Asking difficult questions: Task complexity increases the impact of response alternatives. Social cognition and social reality: Information acquisition and use in the laboratory and the real world. Bureau of Transportation Statistics 10th Transportation Planning Applications Conference. Encoding, representing, and estimating event frequencies: Multiple strategy perspectives. How to make a politician more likeable and effective: Framing political judgments through the numeric values of a rating scale. The impact of age and education on response order effects in attitude measurement. An evaluation of a cognitive theory of response order effects in survey measurement. Attitude intensity, importance, and centrality, and susceptibility to response effects. The role of consciousness in priming effects on categorization: Assimilation and contrast as a function of awareness of the priming task. The effects of accessibility of information in memory on judgments of behavioral frequencies. Rethinking individualism and collectivism: Evaluation of theoretical assumptions and meta-analyses. Measuring satisfaction with organizations: Predictions from information accessibility. Assimilation and contrast effects in attitude measurement: An inclusion/exclusion model.
Skin lesions present as disseminated macules or flat warts that are concentrated in areas of sun exposure and often change slowly over time spasms back muscles discount tizanidine 4 mg fast delivery. Immunologic studies in these siblings showed decreased T-cell proliferation in vitro muscle relaxant jaw pain safe 4mg tizanidine, as well as markedly decreased numbers of naive T cells. Monitoring for premalignant lesions through regular dermatologic screening is recommended. There are insufficient data to determine the safety of these vaccines for these patients. Patients presenting with a family history of asplenia or sepsis caused by encapsulated bacteria, most frequently S pneumoniae, should be evaluated for congenital asplenia. It is often a silent disease until presentation with sudden invasive disease, most frequently as pneumococcal sepsis. This contrasts with asplenia syndrome (Ivemark syndrome), which presents primarily with symptomatic congenital heart disease in early infancy. Diagnosis is made by means of ultrasound of the abdomen and examination for Howell-Jolly bodies on peripheral blood smear. Prophylaxis should be continued at least until the age of 5 years in fully vaccinated children. Some experts recommend lifelong prophylaxis, although the optimal duration of antibiotic prophylaxis is unknown. These disorders are also often referred to as periodic fever syndromes, although this designation is not entirely accurate because it is possible to have an autoinflammatory disorder without fevers and the fevers tend to be more episodic than periodic. The general approach to the evaluation and diagnosis of autoinflammatory disorders is summarized in Fig E6. Autoinflammatory disorders are very rare, and organ damage caused by these disorders typically takes some time to develop. Thus it is essential to rule out other causes of recurrent fevers or recurrent/ongoing inflammation. A careful evaluation for malignancies, recurrent infections, and autoimmunity should first be done before a workup of autoinflammatory disorders is undertaken. Careful assessment for infections is necessary, and if episodes are associated with infections, a workup for immune deficiency should be undertaken. Rash, arthritis, uveitis, serositis, nephritis, diarrhea with weight loss, or other organ involvement should point to a possible autoimmune cause. If these workups are nonrevealing, measurement of inflammatory markers can be helpful. If the clinical presentation has features strongly suggestive of an autoinflammatory component (eg, early onset), such a diagnosis should still be entertained. If the clinical presentation has features strongly suggestive of an autoinflammatory component (eg, very early onset), such a diagnosis should still be entertained. The rash can be described as nonurticarial erythematous papules or plaques that typically resolve within 24 hours. The rash lacks characteristic features of urticaria (eg, angioedema) and signs of mast cell proliferation or degranulation and is caused by neutrophilic infiltrates. Infants presenting with these symptoms should be initially evaluated for sepsis, neonatal infections, and congenital (ie, toxoplasma, rubella, cytomegalovirus, and herpes simplex virus 2) infections. Systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis can present in the first year of life with a similar rash, fevers, and arthritis, although systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis rarely presents before 6 months of age. High-dose steroids, colchicine, and androgens have been tried with mild-to-moderate success. Several other features observed include respiratory distress, aphthous ulcers, hepatomegaly, and failure to thrive. Anakinra treatment results in a rapid and sustained response, with correction of laboratory abnormalities, resolution of rash, and healing of bone lesions in all but 1 affected patient. Blau syndrome should be suspected in patients presenting with noncaseating granulomas in the skin, eyes, and joints.
Constipation spasms near anus order online tizanidine, which may be ameliorated with stool softeners spasms just below ribs discount tizanidine express, can progress to obstipation and, rarely, acute bowel obstruction. Many patients become unhappy and demoralized about resulting changes in body shape. Management strategies for dealing with these milder adverse effects include careful refeeding, frequent physical examinations, and forewarnings to patients about mild refeeding edema. A severe refeeding syndrome may occur when severely malnourished patients (generally those weighing <70% of their healthy body weight) are re-fed too rapidly, particularly in the context of enteral or parenteral feedings but also with vigorous oral refeeding regimens. This syndrome consists of hypophosphatemia, hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia, and fluid retention. In some case series, the refeeding syndrome has been reported to occur in roughly 6% of hospitalized adolescents (118). Excessively rapid refeeding and nasogastric or parenteral feeding may be particularly dangerous because of their potential for inducing severe fluid retention, cardiac arrhythmias, cardiac failure, respiratory insufficiency, delirium, seizures, rhabdomyolysis, red cell dysfunction, and even sudden death, especially in the lowest-weight patients (118, 119). In such cases, phosphorus, magnesium, and/or potassium supplementation will be necessary (118, 120). In one series of hospitalized adolescents, moderate hypophosphatemia occurred in 5. Besides monitoring of mineral and electrolyte levels, general medical monitoring during refeeding should include assessment of vital signs, monitoring of food and fluid intake and output (if indicated), and observation for edema, rapid weight gain (associated primarily with fluid overload), congestive heart failure, and gastrointestinal symptoms. For children and adolescents who are severely malnourished (weigh <70% of their standard body weight), cardiac monitoring, especially at night, may be advisable (120). Some patients are completely unable to recognize their illness, accept the need for treatment, or tolerate the guilt that would accompany eating, even when performed to sustain their lives. On the rare occasions when staff have to take over the responsibilities for providing lifepreserving care, nasogastric feedings are preferable to intravenous feedings. In some programs, supplemental overnight pediatric nasogastric tube feedings have been used to facilitate weight gain in cooperative patients. This practice is not routinely recommended at present, although it appears to be well tolerated, may slightly decrease hospital stays in children, and may be experienced positively by some patients, particularly younger patients, who may feel relieved to Treatment of Patients With Eating Disorders 43 Copyright 2010, American Psychiatric Association. If used, such interventions should never supplant expectations that the patient will resume normal eating patterns on his or her own. Total parenteral feeding is required only rarely and for brief periods in life-threatening situations. Forced nasogastric or parenteral feeding can each be accompanied by substantial dangers. When nasogastric feeding is necessary, clinical experience suggests that continuous feeding. As an alternative to nasogastric feedings, in very difficult situations where patients physically resist and constantly remove their nasogastric tubes, gastrostomy or jejunostomy tubes may be surgically inserted. As described above, rapid refeeding can be associated with the severe refeeding syndrome, and infection is always a risk with parenteral feedings in emaciated and potentially immunocompromised patients with anorexia nervosa. If using interventions that patients with anorexia nervosa may experience as coercive, the clinician should consider the potential impact on the therapeutic relationship, especially since maintaining a sense of control is often a key dynamic in these patients. During the last few years, there has been considerable debate about the ethics of involuntarily feeding patients with anorexia nervosa (122, 123). There is general agreement that children and adolescents who are severely malnourished and in grave medical danger should be refed, involuntarily if necessary, but that every effort should be made to gain their cooperation as cognitive function improves. Ethical as well as clinical dilemmas often confront clinicians dealing with adult patients with chronic anorexia nervosa and their families. The general principles to be followed are those directing good, humane care; respecting the wishes of competent patients; and intervening respectfully with patients whose judgment is severely impaired by their psychiatric disorders when such interventions are likely to have beneficial results (124, 125). For patients who initially lack motivation, their awareness and desire for recovery may be increased by psychotherapeutic techniques based on motivational enhancement, although solid evidence for this contention is lacking. At the same time, clinical consensus suggests that psychotherapy alone is generally not sufficient to treat severely malnourished patients with anorexia nervosa. Although the value of establishing and maintaining a psychotherapeutically informed relationship is clearly beneficial and psychotherapeutic sessions to enhance patient motivation and further patient weight gain are likely to be helpful, the value of formal psychotherapy during the acute refeeding stage is uncertain (127). Attempts to conduct formal psychotherapy may be ineffective with starving patients, who are often negativistic, obsessional, or mildly cognitively impaired, presumably in relation to the known cortical atrophy seen in nutritionally compromised patients. One study documented the difficulty researchers have had in initiating and sustaining cognitive-behavioral therapies for patients with anorexia nervosa (128). Most nutritional rehabilitation programs incorporate emotional nurturance and one of a variety of behavioral interventions that link exercise, bed rest, and privileges with target weights, desired behaviors, and informational feedback.

Studies of national samples of girls and boys exposed to physical and sexual abuse have shown that although binge and purge behaviors were nearly twice as prevalent among girls (13%) as boys (7%) muscle relaxant back pain purchase tizanidine now, boys who had experienced both physical and sexual abuse were nearly twice as likely as girls to report these behaviors (odds ratios 8 back spasms 40 weeks pregnant discount tizanidine 4mg line. Especially in the bulimia nervosa and binge eating disorder subgroups, males with eating disorders who present to tertiary care cenTreatment of Patients With Eating Disorders 61 Copyright 2010, American Psychiatric Association. As in women, there is a higher risk of osteoporosis in men with eating disorders (398, 399). Although many similarities exist between males and females with different types of eating disorders, notable differences have been reported. Females with anorexia or bulimia nervosa score higher on the Drive for Thinness subscale than do males, and this appears to be a real difference; females also score higher on the body dissatisfaction subscale than do males, but this may result from a failure of these scales to address the specific ways in which males are dissatisfied with their bodies. Studies of binge eating disorder patients demonstrate that women have greater body image dissatisfaction and are more likely to cope with negative affect by binge eating, whereas men have higher rates of drug and alcohol use disorder histories (400). For example, with regard to personality traits, males with eating disorders have somewhat less perfectionism, harm avoidance and reward dependence behaviors, and cooperativeness than females (405). Openblind studies suggest that bringing testosterone levels to within normal ranges in males during nutritional rehabilitation for anorexia nervosa may be helpful in increasing lean muscle mass, but definitive studies on this have not been completed. Although studies in clinical samples have suggested that a higher prevalence of homosexuality may exist among males with eating disorders (390), this finding has not yet been confirmed epidemiologically. Nevertheless, because issues concerning sexual orientation are not uncommon among males with eating disorders seen in clinical settings, these issues should be considered in treatment (390). Further, because they are generally taller and larger framed to begin with, males with anorexia nervosa often require much larger weight gains to return to a healthy weight (391, 399). Age Although most eating disorders start while patients are in their teens and 20s, earlier and later onsets have been observed as well. Children often present with physical symptoms such as having nausea, experiencing abdominal pain, feeling full, or being unable to swallow (all conditions requiring evaluation to investigate a variety of potential etiologies) (407). These young patients know that they are underweight, would like to be heavier, may not know why this goal is hard to achieve, and usually show more generalized anxiety unrelated to food. Other syndromes to be considered are selective eating disorder, functional dysphasia, and pervasive refusal syndrome (407). With respect to middle-aged patients, case reports and clinical consensus now suggest that as the baby boomer generation grows older, body image concerns and eating disorders are becoming more prevalent. At the other end of the age spectrum, incidence rates for anorexia nervosa among women over age 50 years are low, accounting for <1% of patients with newly diagnosed anorexia nervosa (421). Anorexia nervosa has been reported in elderly patients in their 70s and 80s; these are generally women in whom the illness has been present for 40 or 50 years. In some case reports, adverse life events such as deaths, a marital crisis, or a divorce have been found to trigger these older-onset syndromes. The fear of aging has also been described as a major precipitating factor in some patients (142, 422). Rates of co-occurring depression have been reported to be higher among these patients in some studies but not in others (423). Regardless of the age at onset, concerns about comorbid medical conditions, especially osteopenia and osteoporosis, take on greater significance with older patients. Cultural factors Specific pressures and values concerning weight and shape vary among different cultures. The quest for beauty and acceptance in accordance with the stereotypes women perceive in contemporary media is leading increasing numbers of women around the world to develop attitudes and eating behaviors associated with eating disorders. Popkin and Gordon-Larsen (428) have described a phenomenon called the "nutritional transition" in economically emerging countries.
Generic 2 mg tizanidine otc. This Is Everything: Gigi Gorgeous.