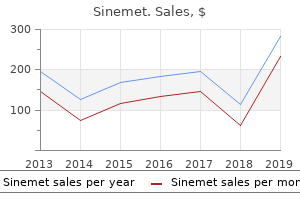
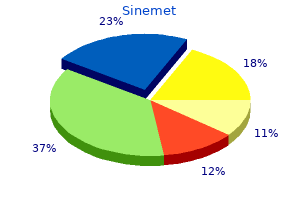
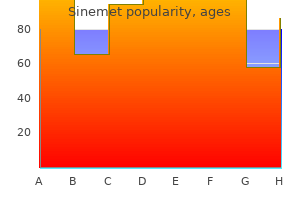
Sinemet
"Cheap sinemet 110mg on-line, medications ok during pregnancy".
By: U. Inog, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Professor, Rush Medical College
Its achievements have significantly influenced the course of scientific surgery in America and have established it as an important advocate for all surgical patients symptoms 0f ms purchase 125 mg sinemet fast delivery. The College has more than 79 606 treatment syphilis purchase sinemet 110 mg without prescription,000 members and is the largest organization of surgeons in the world. Anti-caries (anti-cavities) benefit begins with eruption of the first primary tooth. Use of recommended amounts of fluoride toothpaste minimize risks of fluorosis, a whitish discoloration of enamel. High quality evidence shows sealants are safe and effective in arresting caries progression in initial stage (incipient) non-cavitated, occlusal caries. Sealants offer a tooth-preserving treatment when compared to restorations, which may require removal of some healthy tooth structure, thereby weakening the tooth and increasing the risk that the tooth will eventually require more extensive treatment. Applying sealants as soon as initial stage caries is detected can improve outcomes by minimizing the later need for more extensive restorative care. Some children do not respond to communicative behavior guidance techniques and require treatment of dental disease. Advanced behavior guidance techniques of sedation, protective stabilization, and general anesthesia offer risks and benefits often beyond the health knowledge of parents and other caretakers. Informed consent best practice requires a thorough, understandable explanation of these techniques and alternatives including deferral of treatment with its inherent risks. Therefore, management is generally conservative and includes reversible strategies such as patient education, medications, physical therapy and/or the use of occlusal appliances that do not alter the shape or position of the teeth or the alignment of the jaws. Dental restorations (fillings) fail due to excessive wear, fracture of material or tooth, loss of retention, or recurrent decay. The larger the size of the restoration and/or the greater the number of surfaces filled increases the likelihood of failure. Restorative materials have different survival rates and fail for different reasons, but age should not be used as a failure criteria. Patients with any specific questions about the items on this list or their individual situation should consult their dentist. The Steering Committee reviewed critical issues in dentistry to identify potential recommendation topics and developed, through an evidence-based process, a list of recommendation statements with supporting scientific evidence. Via an intense consensus process, the Steering Committee prepared a list of recommendation statements which were sent to the Council on Access, Prevention and Interprofessional Relations for review. Fluoride toothpaste efficacy and safety in children younger than 6 years: a systematic review. Pit and fissure sealants for preventing dental decay in the permanent teeth of children and adolescents. Evidence-based clinical recommendations for the use of pit-and-fissure sealants: a report of the American Dental Association Council on Scientific Affairs. Update on nonsurgical, ultraconservative approaches to treat effectively non-cavitated caries lesions in permanent teeth. Sealing versus partial caries removal in primary molars: a randomized clinical trial. Systematic review of noninvasive treatments to arrest dentin non-cavitated caries lesions. Pit and fissure sealants: evidence-based guidance on the use of sealants for the prevention and management of pit and fissure caries. Guidelines for monitoring and management of pediatric patients during and after sedation for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures: an update. Guideline for Monitoring and Management of Pediatric Patients During and After Sedation for Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures Pediatr Dent. Guidelines: diagnosis & management of temporomandibular disorders & related musculoskeletal disorders. Acupuncture as a treatment for temporomandibular joint dysfunction: a systematic review of randomized trials. Application of principles of evidence-based medicine to occlusal treatment for temporomandibular disorders: are there lessons to be learned Occlusal adjustment for treating and preventing temporomandibular joint disorders. Direct composite resin fillings versus amalgam fillings for permanent or adult posterior teeth.
What is function of the efflux activity in kidney or Malpighian tubules and what happens if this is inhibited Drosophila Malpighian tubule: A model for understanding kidney development treatment for depression buy sinemet on line, function and disease medications for depression purchase 125mg sinemet otc. Development of a Drosophila melanogaster based model for the assessment of cadmium and mercury mediated renal tubular toxicity. Why then, when they have been studied so intensively, is it necessary to extend studies to another species like Drosophila rnelanogaster, and one with no obvious biomedical or agricultural significance The reasons are threefold: we know more about the genetics of Drosophila than another other insect; we can manipulate Drosophila genetically better than any insect; and Drosophila tubules are similar enough to those of other insects to allow general inferences to be drawn. The slit diaphragm forms a charge and size selective barrier that allows movement of water and solute molecules, but does not allow the large size molecules such as blood protein albumin (Weavers et al. Drosophila nephrocytes are spherical cells that remove harmful or toxic substances from the hemolymph through filtration and endocytosis. Drosophila nephrocytes are present in two clusters, namely the large garland cell nephrocytes (located near proventriculus region of the foregut) and the pericardial nephrocytes (located near the heart tube). The plasma membrane in nephrocytes forms many infoldings leading to the formation of ~30 nm wide lacunae, which are flanked by the foot processes. Therefore, nephrocytes form a nephrocyte diaphragm that provides a size and charge selective filter to take up molecules from hemolymph (Weaver et al. The waste or toxic materials taken from hemolymph by the nephrocytes are stored intracellularly in these cells through endocytosis. Failure or reduced uptake of waste or toxic materials from hemolymph by the nephrocytes suggests deformities in the nephrocyte filtration barrier. Stereo-binocular and bright-field (preferably with phase-contrast optics) microscope. Prepare the agar-sucrose food vials: heat 5 gm agar, 15 gm Sulphur-free sugar, 1 gm Nipagin and 1 mL propionic acid in 360 mL water in a conical flask until agar and sugar dissolve completely; pour 5 mL in each vial and leave them to cool and solidify before plugging. Collect first instar larvae growing on standard food and wash them with distilled water to remove remnants of food particles. Collect third instar larvae and wash them with distilled water to remove food remnants. Is it possible to use Drosophila nephrocytes to screen the environmental chemicals that can affect the function of human podocytes What would be the impact of disrupted nephrocyte diaphragm on the survival of Drosophila Accordingly, a number of anatomical structures still bear his name: Malpighian corpuscles in the circulatory and lymphatic systems, the Malpighian layer of the epidermis, and the Malpighian tube in insects. Since then, Malpighian tubules have been documented by morphologists, but it was in the twentieth century that modern physiology was brought to bear. The insect exhibits high fecundity and a short life cycle spanning over four stages: embryo, larvae, pupae and imago (adult fly). Sexual dimorphism is seen as morphological and behavioral differences between different sexes of the same species. It arises due to genetically and temporally coordinated tissue specific molecular cues during the course of development. The difference in the development and morphology of female and male reproductive organs is a prime example of sexual dimorphism. The male and female gonads can be observed in the early to late third instars larvae of Drosophila as a highly transparent cluster of cells embedded within the fat body which appears to be translucent (Maimon and Gilboa et al. The size of gonads in male is five times larger than that of female gonads during this stage (Greenspan, 2004).
These are hair-like structures projecting from the surface of the third segment of the Drosophila antenna symptoms 9f anxiety buy sinemet 300 mg with visa. Four segments of antenna: Scape treatment table buy cheapest sinemet and sinemet, attached to the head, Pedicel carrying the chordotonal/hearing organs, Funiculus housing the olfactory sensillae, and Arista. Further, the Drosophila olfactory neural circuit connectome is well deciphered to study the effects of olfactory manipulation on learning and memory. Additionally, shorter life span, modest maintenance requirements and the most extensive genetic and genomic information available for Drosophila make it a favourable model for such studies. One of the primary issues in understanding the olfactory system is figuring out whether Drosophila likes or dislikes an odour. Like other insects, Drosophila has a very keen sense of smell and can sense certain chemicals at very low concentrations. Some of the known chemical/food attractants for Drosophila melanogaster are glacial acetic acid, propionic acid, apple cider vinegar, balsamic vinegar, banana juice/powder, lemon juice, mango juice, and apple juice. This chapter describes a simple experimental procedure, the jump test (Ayyub, et al. Secondly, defects in the motor neuron circuit and muscle function, independent of the olfactory response, also affect the jump response. Nevertheless, as the first test for odour sensing ability of the fly, the assay is effective. Objective: To assay the olfactory response of Drosophila melanogaster to potentially repellent odours. Besides, stocks carrying mutant alleles for rutagaba and dunce also show altered olfactory response. Alternatively, the glassware can be heated on a flame to eliminate traces of odorants. Collect two to four days old flies of the desired genotype/s (wild-type or mutants) by anaesthetizing them on ice and place them in fresh fly food for 24 Hr. Gently put a batch of five such anaesthetized flies in the jump tube using a #1 paintbrush and close the open end of the tube with a cotton plug. Place the tubes vertically with the cotton plug at the bottom on a rack inside a humidified dark (or cardboard) box until the experiment. Leave the flies in the tube for 20-30 min to allow them to recover from cold anaesthesia. To start the Jump-Test, place the jump tube with flies in a vertical position using a stand and holder as shown in. Connect the tapered end of the jump tube to the exit/outflow end of the dispenser having the odour solution using a soft plastic/Teflon tube. To make the odour solution, prepare serial dilutions, as required, of the odour concentrate in mineral oil or liquid paraffin. Tap the tube to make flies fall on the cotton plug and then climb up the walls of the jump tube. When the flies reach an approximately two-third length of the jump tube, switch on the aquarium pump for 5 sec only. The fraction of flies jumping would increase with the repelling quality of the odour. A few flies will remain on the wall of the glass tube even after the 5-sec puff. Count the number of flies which hit the cotton plug 5 sec after turning on the airflow/pump. If some flies hit the cotton plug before turning on the pump, then wait until they climb back onto the wall. Flies also respond to light flashes and jump spontaneously in the presence of light. Keep the light source away from the table where the experiment is conducted or create a diffuse lighting condition. The jump score is calculated as an average of four such jump tests involving a total of 20 flies.
Individual chromosomes often can be identified by the length of their arms and the location of the centromere symptoms of high blood pressure purchase 300 mg sinemet otc. If the centromere is in the middle of the chromosome and the arms (telomeres) are of equal length medications 142 sinemet 125 mg online, the chromosome is said to be metacentric. If the centromere is close to one end, the chromosome is acrocentric, and if the centromere is between the midpoint and the end, the chromosome is submetacentric. Chromosomes are permanent entities of the cell and are present at every stage of the cell cycle, but their appearance depends on the physiologic state of the cell. At interphase the chromosomes form delicate, tortuous threads, and it is only during cell the nuclear envelope consists of two concentric unit membranes, each 7. The inner membrane is smooth, whereas the outer membrane often contains numerous ribosomes on its cytoplasmic surface and is continuous with the surrounding endoplasmic reticulum. The pores measure about 10 nm in diameter and are closed by a nuclear pore complex that consists of two rings, one of which faces the cytoplasm. The number and distribution of nuclear pores depend on the type of cell and its activity. The nuclear envelope aids in organization of the chromatin and controls the two-way traffic of ions and molecules moving between the nucleus and cytoplasm. Molecules less than 10 nm in diameter pass through the nuclear pore complex by passive diffusion, whereas large molecules (entering newly synthesized proteins, exiting ribonucleoproteins) require an energy-dependent transport mechanism. It is thought that a signal sequence of amino acids directs them to the nuclear envelope, and after binding of a signal sequence to a receptor in the nuclear pore complex, the nuclear pore opens much like an iris diaphragm of a camera to permit passage of the larger molecules. A thin meshwork of filaments called lamins is made up of three polypeptides and lies along the inner surface of the nuclear membrane to form the nuclear lamina. The lamins are structurally similar to intermediate filaments and are classified as types A, B, and C according to their location and chemical properties. Type B lamins lie nearer the outer surface of the nuclear lamina and binds to specific integral (receptor) proteins of the inner nuclear membrane. Types A and C lamins lie along the inner surface of the nuclear lamina and link the membrane-bound lamin B to chromatin. The three lamins are thought to function in the formation and maintenance of the nuclear envelope of interphase cells. Since these sites (nucleolusorganizing regions) are located on five different chromosomes, any one cell may contain several nucleoli. As seen in electron micrographs, nucleoli lie free in the nucleus, not limited by a membrane. They show two regions, each associated with a particular form of ribonucleoprotein. The second region, the pars fibrosa, tends to be centrally placed and consists of dense masses of filaments 5 nm in diameter. Deoxyribonucleoprotein also is associated with the nucleolus and is present in filaments of chromatin that surround or extend into the nucleolus. With the addition of the small ribosomal subunit, ribosomes are then transported to the cytoplasm through nuclear pores. Nucleoli are found only in interphase nuclei and are especially prominent in cells that are actively synthesizing proteins. They are dispersed during cell division but reform at the nucleolus-organizing regions during reconstruction of the daughter nuclei after cell division. They carry out energy transformations and biosynthetic activities and are able to replicate themselves. In addition to forming the interface between the cell and its external environment, they also are important in transportation of materials, organization of different energy transfer systems, transmission of stimuli, provision of selectively permeable barriers, and separating various intracellular compartments. All materials that pass into or out of a cell must cross the plasmalemma; this structure is instrumental in selecting what enters and leaves the cell. Large molecules are taken in by pinocytosis, particulate matter can be incorporated into the cell by phagocytosis, and small molecules enter the cell by diffusion. The rate at which material diffuses into the cell depends on whether the material is soluble in lipid or water.
Purchase 125 mg sinemet with amex. Useless ID - Deny It (Live at The Schwaben Club).