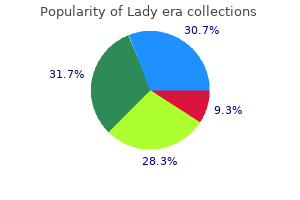
Lady era
"Order lady era 100 mg with visa, womens health 3 week workout plan".
By: W. Osmund, M.A.S., M.D.
Vice Chair, University of South Florida College of Medicine
Clinics should weigh the benefits of each screening strategy as well as their resources women's health louisville ky discount generic lady era canada, such as time and cost womens health 10k generic 100mg lady era with mastercard, in deciding on which of the three possible screening strategies to implement. Decision analytic models (1242) estimating the benefits, harms, and costs (1243) of several different strategies might be useful in making this determination (174,1244,1245). Adopting recommended screening and follow-up procedures, including screening methods, results provision, and follow-up, can lead to success in implementing cervical cancer screening in clinics (1246). National consensus guidelines are available for the management of abnormal cervical cancer screening tests (1247). These guidelines base management recommendations on case-by-case assessment of risk considering past screening history and current results (see Follow-Up). Patients with abnormal cervical cancer screening test results should be counseled about those results (see Counseling Messages). However, in most instances (even in the presence of certain severe cervical infections), cytology tests will be reported as satisfactory for evaluation, and reliable final reports can be produced without the need to repeat the cytology test after treatment. The test can be performed after removal of the discharge with a saline-soaked cotton swab. Health care facilities that train providers on cytology test collection and use simple quality assurance measures are more likely to obtain satisfactory test results (as determined by the laboratory). Both liquid-based and conventional cytology are acceptable because they have similar test-performance characteristics. Persons should be counseled on the risks, uncertainties, and benefits of screening (174,1257). Providers also should screen for tobacco use and perform cessation counseling ( Promoting Cervical Cancer Screening Clinics can use the evidence-based interventions in the Community Preventive Services Task Force guidelines to promote cervical cancer screening in their communities. Implementing interventions that increase community demand for screening (1266). These interventions are more effective if they are implemented with interventions to increase provider delivery of screening services. Patient navigators can be effective in improving both screening and follow-up after abnormal results (1267). Appropriate follow-up is essential to ensure that cervical cancer does not develop. Screening Recommendations in Special Populations Pregnancy Persons who are pregnant should be screened at the same intervals as those who are not. Clinics that serve clients who might have difficulty adhering to follow-up recommendations and for whom linkage to care is unlikely should consider offering in-house colposcopy and biopsy services. Consensus guidelines for management of abnormal cervical cancer screening tests combine patient-level risk data with clinical action thresholds to generate personalized management recommendations (Table 2). The guidelines were designed to identify persons at high risk who require colposcopy or expedited treatment and persons at low risk who might be able to safely defer invasive diagnostic procedures. The risk-based framework was designed to easily incorporate future revisions, such as the inclusion of new technologies for screening and management. Use of the guidelines can be facilitated by electronic technology that is continually updated, such as a smartphone application or the website. Colposcopy with biopsy is an acceptable option if desired by patient after shared decision-making. When considering treatment without confirmatory biopsy, shared decision-making with the patient is important. Considerations include age, concern about cancer, ability to follow up, financial concerns, and concerns about the potential effect of treatment on a future pregnancy. Ideally, cytology testing should be performed by the laboratory as a reflex test from the same specimen so the patient does not need to return to the clinic. Surveillance should continue for at least 25 years after the initial treatment, even if this extends beyond age 65 years. If a woman undergoes hysterectomy during the surveillance period, vaginal screening should continue.
In one study menstruation youngest age buy 100mg lady era amex, maternal treatment with metronidazole (400 mg 3 times/day for 7 days) produced a lower concentration in breast milk and was considered compatible with breastfeeding over longer periods (1052) women's health loddon mallee bendigo effective 100 mg lady era. Data from studies involving human subjects are limited regarding tinidazole use during pregnancy; however, animal data indicate this drug poses moderate risk. Thus, tinidazole should be avoided for pregnant women, and breastfeeding should be deferred for 72 hours after a single 2-g oral dose of tinidazole. Uncomplicated Vulvovaginal Candidiasis Diagnostic Considerations A diagnosis of Candida vaginitis is clinically indicated by the presence of external dysuria and vulvar pruritus, pain, swelling, and redness. Signs include vulvar edema, fissures, excoriations, and thick curdy vaginal discharge. For those with negative wet mounts but existing signs or symptoms, vaginal cultures for Candida should be considered. If Candida cultures cannot be performed for these women, empiric treatment can be considered. Yeast culture, which can identify a broad group of pathogenic yeasts, remains the reference standard for diagnosis. Vulvovaginal candidiasis: epidemiologic, diagnostic, and therapeutic considerations. The creams and suppositories in these regimens are oil based and might weaken latex condoms and diaphragms. Unnecessary or unapproved use of over-the-counter preparations is common and can lead to a delay in treatment of other vulvovaginitis etiologies, which can result in adverse outcomes. However, women with persistent or recurrent symptoms after treatment should be instructed to return for follow-up visits. A minority of male sex partners have balanitis, characterized by erythematous areas on the glans of the penis in conjunction with pruritus or irritation. These men benefit from treatment with topical antifungal agents to relieve symptoms. Special Considerations Drug Allergy, Intolerance, and Adverse Reactions Topical agents usually cause no systemic side effects, although local burning or irritation might occur. Therapy with the oral azoles has rarely been associated with abnormal elevations of liver enzymes. Clinically important interactions can occur when oral azoles are administered with other drugs (1141). However, to maintain clinical and mycologic control, a longer duration of initial therapy. If this regimen is not feasible, topical treatments used intermittently can also be considered. If recurrence occurs, 600 mg of boric acid in a gelatin capsule administered vaginally once daily for 3 weeks is indicated. This regimen has clinical and mycologic eradication rates of approximately 70% (1149). Candida glabrata does not form pseudohyphae or hyphae and is not easily recognized on microscopy. Micro-organisms that comprise the vaginal flora, such as strict and facultative anaerobes (1160) and G. Special Considerations Compromised Host Women with underlying immunodeficiency, those with poorly controlled diabetes or other immunocompromising conditions. Only topical azole therapies, applied for 7 days, are recommended for use among pregnant women.
Aggressive case management breast cancer zip up sweatshirt buy 100mg lady era fast delivery, referral networks womens health jackson ca discount lady era 100mg overnight delivery, and treatment linkages are needed to prevent women from disengaging from treatment. From initial contact with the client, the ability to follow up, to coordinate care, and to provide comprehensive services (such as transportation and child care), is essential to effective treatment. Considerations for women who are parents with dependent children the safety of children often is a chief concern and one of the principal barriers to treatment engagement and retention for parents- especially women-entering detoxification programs. Even if women do not have custody of their children, they often are the ones who continue to care for them. Thus, ensuring that children have a safe place to stay while their mothers are in detoxification is of vital importance. Working with parents to identify supportive family or friends may help identify available temporary child care resources. Detoxification and methadone treatment during pregnancy Some detoxification programs will not treat a pregnant woman because they lack the necessary obstetrical support and are concerned about liability. Detoxification presents critical risks to a fetus, and withdrawal of a pregnant woman from addictive drugs or alcohol should always Treatment Engagement, Placement, and Planning 97 be accompanied by close medical supervision and monitoring. Risks of detoxification depend on the drug being abused, but the primary drugs of concern are typically opioids and, potentially, sedative-hypnotics. Sudden withdrawal of these drugs results in withdrawal by a fetus and sometimes leads to fetal distress or death. Withdrawal should be done under supervised conditions and with proper substitutes, such as methadone for opioids. In general, it is neither recommended nor necessary for pregnant women to cease methadone treatment. In situations where withdrawal is being contemplated, a thorough assessment should be conducted to determine whether the woman is an appropriate candidate for medical withdrawal. It is important to note that relapse rates among women who use heroin are high, thus placing their fetuses at risk for adverse consequences (Jones et al. If withdrawal is elected, it should be conducted under the supervision of physicians experienced in perinatal addiction and under the guidance of a protocol using fetal monitoring. Medical withdrawal usually is conducted in the second trimester because of the danger of miscarriage in the first trimester and because withdrawalinduced stress may cause premature delivery or fetal death in the third trimester (Donaldson 2000; Kaltenbach et al. While pharmaceutical agents other than methadone have been introduced to treat symptoms of opioid withdrawal, the research is still preliminary (Anderson et al. Outpatient treatment settings are the most common, are widely available, and are the setting in which most women receive treatment. In general, outpatient treatment is most appropriate for women with less severe substance use problems and with greater social support and resources. While outpatient services are used for less severe symptoms of substance use disorders, this level of treatment can be employed at various points across the continuum of care. Specifically, continuing care services use outpatient treatment to provide support for ongoing recovery and treatment in a less restrictive environment as recovery evolves. Effective outpatient treatment programs for women should be more comprehensive than traditional programs and should provide a constellation of services (refer to Figure 5-3). The development of interagency relationships is essential, yet referral alone will not guarantee utilization of these services. Beyond staff support, it is often necessary to 98 Treatment Engagement, Placement, and Planning initiate the first contact with the agency referral, to assist the client in developing or making the necessary arrangements to access the community service or referral, and to provide followup to obtain the outcome of the referral. Throughout the last two decades, substance abuse programs have acknowledged the necessity of establishing formalized relationships among community agencies to streamline services and to effectively address and manage the diverse needs of women seeking treatment for substance use disorders. Professional staff are available 24 hours a day, and the facility is clinically managed. Clinical experience has shown that women in residential care frequently require some or all of the services listed in Figure 5-3 in addition to specific substance abuse treatment services.

Syndromes
- Your medical history
- Heart rhythm problems (arrhythmia)
- Collapse
- Blindness, decreased vision
- A fever (temperature greater than 101 °F)
- Urinalysis
To avoid reinfection women health clinic buy lady era mastercard, sex partners should be instructed to abstain from condomless sexual intercourse until they and their sex partners have been treated womens health 30 day meal plan purchase lady era without a prescription. Human data reveal that levofloxacin presents a low risk to the fetus during pregnancy but has potential for toxicity during breastfeeding; however, data from animal studies increase concerns regarding cartilage damage to neonates (431). In addition, all pregnant women who have chlamydial infection diagnosed should be retested 3 months after treatment. Recommended Regimen for Chlamydial Infection During Pregnancy Azithromycin 1 g orally in a single dose Alternative Regimen Amoxicillin 500 mg orally 3 times/day for 7 days Because of concerns regarding chlamydia persistence after exposure to penicillin-class antibiotics that has been demonstrated in animal and in vitro studies, amoxicillin is listed as an alternative therapy for C. Erythromycin is no longer recommended because of the frequency of gastrointestinal side effects that can result in therapy nonadherence. Neonates born to mothers at high risk for chlamydial infection, with untreated chlamydia, or with no or unconfirmed prenatal care, are at high risk for infection. However, presumptive treatment of the neonate is not indicated because the efficacy of such treatment is unknown. Infants should be monitored to ensure prompt and age-appropriate treatment if symptoms develop. Processes should be in place to ensure communication between physicians and others caring for the mother and the newborn to ensure thorough monitoring of the newborn after birth. Neonates born to mothers for whom prenatal chlamydia screening has been confirmed and the results are negative are not at high risk for infection. Diagnostic Considerations Sensitive and specific methods for diagnosing chlamydial ophthalmia in the neonate include both tissue culture and nonculture tests. Ocular specimens from neonates being evaluated for chlamydial conjunctivitis also should be tested for N. Topical antibiotic therapy alone is inadequate for treating ophthalmia neonatorum caused by chlamydia and is unnecessary when systemic treatment is administered. Data regarding the efficacy of azithromycin for ophthalmia neonatorum are limited. Therefore, follow-up of infants is recommended to determine whether the initial treatment was effective. The possibility of concomitant chlamydial pneumonia should be considered (see Infant Pneumonia Caused by C. Management of Mothers and Their Sex Partners Mothers of infants who have ophthalmia caused by chlamydia and the sex partners of these women should be evaluated and presumptively treated for chlamydia (see Chlamydial Infection Among Adolescents and Adults). In the absence of laboratory results in a situation with a high degree of suspicion of chlamydial infection and the mother is unlikely to return with the infant for follow-up, exposed infants can be presumptively treated with the shortercourse regimen of azithromycin 20 mg/kg body weight/day orally, 1 dose daily for 3 days. Recommended Regimen for Chlamydial Pneumonia Among Infants Erythromycin base or ethyl succinate 50 mg/kg body weight/day orally divided into 4 doses daily for 14 days Infant Pneumonia Caused by C. Characteristic signs of chlamydial pneumonia among infants include a repetitive staccato cough with tachypnea and hyperinflation and bilateral diffuse infiltrates on a chest radiograph. Diagnostic Considerations Specimens for chlamydial testing should be collected from the nasopharynx. Tissue culture is the definitive standard diagnostic test for chlamydial pneumonia. Tracheal aspirates and lung biopsy specimens, if collected, should be tested for C. Treatment Because test results for chlamydia often are unavailable at the time initial treatment decisions are being made, treatment for C. Data regarding effectiveness of azithromycin in treating chlamydial pneumonia are limited.
Order 100 mg lady era. How to Answer Common Admission Interview Question - Why this university? II Interview tips.