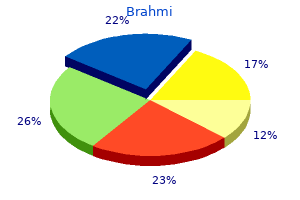
Brahmi
"Order brahmi overnight delivery, medications similar to gabapentin".
By: H. Ernesto, MD
Associate Professor, Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University
Cytochrome P450 inducers such as rifampin medicine omeprazole 20mg cheap 60caps brahmi with amex, carbamazepine medications for depression order brahmi 60 caps without prescription, and phenytoin have the potential to reduce celecoxib levels. However, no clinically significant interactions have been documented with celecoxib and methotrexate, glyburide, ketoconazole, phenytoin, or tolbutamide. Capsaicin, isolated from hot peppers, releases and ultimately depletes substance P from afferent nociceptive nerve fibers. Adverse events associated with capsaicin are primarily local, with 1 in 3 patients experiencing burning, stinging, and/or erythema that usually subsides with repeated application. Capsaicin is a nonprescription product available as a cream, gel, or lotion in concentrations ranging from 0. To be effective, capsaicin must be used regularly, and it may take up to 2 weeks to take effect. Although use is recommended four times a day, a twice-daily application may enhance long-term adherence and still provide adequate pain relief. Initial pain relief may be seen within 24 to 72 hours after injection, with peak pain relief about 1 week after injection and lasting up to 4 to 8 weeks. There is no evidence of a clinically superior corticosteroid for intraarticular use, with equipotent doses of methylprednisolone acetate and triamcinolone hexacetonide having similar efficacy. The therapy is generally limited to three or four injections per year because of the potential systemic effects of steroids, and because the need for more frequent injections indicates little response to the therapy. Adverse events associated with intraarticular injection of corticosteroids can be local or systemic in nature. Systemic adverse events are the same as with any other systemic corticosteroid and can include hyperglycemia, edema, elevated blood pressure, dyspepsia, and, rarely, adrenal suppression with continuous, repeated injections. Local adverse effects can include infection in the affected joint, osteonecrosis, tendon rupture, and skin atrophy at the injection site. It has long been thought that intraarticular corticosteroids can hasten cartilage loss, but the potential risk of cartilage destruction with steroid injections has not been substantiated. The rate of cartilage loss tends to be similar between treated and control groups. Glucosamine and Chondroitin Interest in chondroitin and glucosamine was spurred initially by anecdotal reports of benefit in animals and humans, and by the ability of these substances to stimulate proteoglycan synthesis from articular cartilage in vitro. The excellent safety profile of these agents makes them especially appealing for use in those at high risk for adverse events, such as elderly patients, and in those with multiple morbidities. Recently, enthusiasm for these agents has waned somewhat as additional efficacy data has become available. This survey showed that rates of lower limb joint replacement were twofold higher in subjects given placebo, compared with subjects given glucosamine. In addition, subjects treated with glucosamine had lower rates of pain, joint space narrowing, and limitations of physical function. The safety of the glucosamine and chondroitin therapy was similar to that of placebo. The exact role of glucosamine, chondroitin, or a combination of the two products is still unclear. Dosing should be at least 1,500 mg/day of glucosamine and 1,200 mg/day of chondroitin. The glucosamine component should be the sulfate salt rather than the hydrochloride salt, as nearly all positive efficacy studies used the better-absorbed sulfate salt. Glucosamine-related adverse events are generally mild and include gastrointestinal symptoms (gas, bloating, cramps). If made from shellfish, however, glucosamine should not be used in patients with shellfish allergies. The initial concerns regarding glucosamine-induced hyperglycemia had likely been overstated as later safety data in both healthy subjects and those with type 2 diabetes mellitus did not show significant elevations in blood glucose. Chondroitin is extremely well tolerated with the most common adverse effect being nausea. Depending on the source of chondroitin (cattle, pig, or shark), this compound could also pose risk to persons who are allergic to shark. The potential consequences related to the lack of regulatory oversight for these products can affect both efficacy and safety.
The pharmacokinetics of fluoxetine and fluvoxamine were similar in patients with renal failure and in healthy subjects; however treatment 3rd stage breast cancer generic brahmi 60caps with mastercard, the manufacturer recommends starting with a lower dose in patients with renal impairment symptoms 7 safe 60 caps brahmi. The pharmacokinetics of sertraline are not altered in patients with significant renal dysfunction, and dosage adjustment is not necessary in these patients. Case reports and anecdotal information suggest that the anti-obsessional drugs are likely to be equally effective in the elderly and in younger adults. Treatment should be initiated with low doses in elderly patients, and doses should be increased slowly, with vigilance for emergence of side effects. Some elderly patients can ultimately require doses similar to those used in younger adults, but doses must be individualized according to response and tolerance of side effects. The use of clonazepam should be avoided because of the potential for excess sedation, particularly in frail elderly patients and those with gait disturbances. Dosage should be reduced and titrated slowly during initiation of fluvoxamine therapy in elderly patients. Sertraline plasma clearance in elderly patients was approximately 40% lower than in a group of younger individuals. Clearance of desmethylsertraline was also decreased in elderly men but not in elderly women. The manufacturer recommends that the initial dose be reduced in the elderly (10 mg/day), and total daily doses should not exceed 40 mg. Symptoms often improve during the second trimester and worsen during the third trimester. If drug therapy during pregnancy is required, fluoxetine appears to be the safest choice. However, the neurobehavioral effects of prenatal exposure on the neonate and the child have not been fully elucidated. It is highly protein-bound (greater than 90%) in the blood and has a half-life of 15 hours. Wellconducted trials comparing these medications with placebo, headto-head comparative trials, and meta-analyses have established that fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline, and citalopram are equally effective and that clomipramine may be somewhat more effective. Side effects can be more severe when larger doses are used and with faster dose escalation. Tolerance to adverse effects often develops over 6 to 8 weeks of treatment, and tolerance is more likely to develop to nausea, diarrhea, sedation, diminished 1187 libido and/or orgasm, anxiety, restlessness, insomnia, and anticholinergic side effects than to akathisia. Typical antipsychotics are generally not recommended because of an increased likelihood of extrapyramidal symptoms. Data from Expert Consensus Panel for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder 55and Ellingrod. If there is inadequate response to an average dose, then it should be incrementally increased to the maximum dose within 4 to 9 weeks from the start of treatment. Eight to thirteen weeks is considered an adequate trial before changing to another drug or augmenting with another agent. After patients have responded to the acute phase of treatment, treatment gains are maintained with maintenance-phase strategies. Monthly followup visits are recommended for at least 3 to 6 months, and a medication taper can be considered after 1 to 2 years of treatment. The drug dosage can be decreased by 25%, and then 2 months should lapse before again decreasing the dose, depending on response. Long-term or lifelong prophylaxis with pharmacotherapy is recommended after two to four severe relapses or three to four mild relapses. Mundo and colleagues studied patients successfully treated with clomipramine or fluvoxamine and reduced their doses by 33% to 66% for maintenance therapy, with clear advantages for tolerability and compliance. The degree of response can indicate a need to modify dosage, change drug, or augment therapy. The clinician should inquire about and address problematic adverse effects (including the emergence of suicidal ideation) reported by the patient. Patients older than 40 years of age should receive a pretreatment electrocardiogram before starting clomipramine. In patients with liver disease, baseline and periodic liver function tests are recommended when clomipramine is used. If clomipramine is given concurrently with sympatholytic antihypertensive agents, blood pressure should be regularly monitored. Patients receiving clomipramine who develop fever and sore throat should have leukocyte and differential white blood cell counts assessed to evaluate for agranulocytosis.

Cytochrome P4501A1 and glutathione S transferase gene polymorphisms in patients with aplastic anemia in India medications j tube purchase cheapest brahmi and brahmi. Standardization of definitions and criteria of assessment of adverse drug reactions: Drug-induced cytopenia medicine in balance discount 60 caps brahmi with amex. A first report of their relation to drug use with special reference to analgesics. A prospective study of androgens and bone marrow transplantation for treatment of severe aplastic anemia. Chloramphenicolinduced bone marrow injury: possible role of bacterial metabolites of chloramphenicol. Anticonvulsant-induced aplastic anemia: increased susceptibility to toxic drug metabolites in vitro. Aplastic anemia: Presence in human bone marrow of cells that suppress myelopoiesis. Interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha suppress both early and late stages of hematopoiesis and induce programmed cell death. Lymphocyte phenotype and lymphokines following anti-thymocyte globulin therapy in patients with aplastic anaemia. Treatment of aplastic anemia with antilymphocyte globulin and methylprednisolone with or without cyclosporine. Study of the association between cytochromes P450 2D6 and 2E1 genotypes and the risk of drug and chemical induced idiosyncratic aplastic anaemia. Current status of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in acquired aplastic anemia. Bone marrow transplants from mismatched related and unrelated donors for severe aplastic anemia. Treatment of acquired severe aplastic anemia: bone marrow transplantation compared with immunosuppressive therapy-The European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Experience. Review: Drug-induced neutropenia-pathophysiology, clinical features, and management. Modern management of nonchemotherapy drug-induced agranulocytosis: a monocentric cohort study of 90 cases and review of the literature. Risk of clozapine-associated agranulocytosis and mandatory white blood cell monitoring. Possible role of free radical formation in clozapine (Clozaril)-induced agranulocytosis. Positive direct antiglobulin tests and immune hemolytic anemia in patients receiving procainamide. Possible contribution of acetylamrinone and its enhancing effects on platelet aggregation under shear stress conditions in the onset of thrombocytopenia in patients treated with amrinone. Acute profound thrombocytopenia associated with anaphylactic reaction after abciximab therapy during percutaneous coronary angioplasty. Acute profound thrombocytopenia following C7E3 Fab (Abciximab) therapy: Case reports, review of the literature and implications for therapy. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: clinical manifestations and management strategies. The incidence of heparininduced thrombocytopenia in hospitalized medical patients treated with subcutaneous unfractionated heparin: a prospective cohort study. Thrombocytopenia associated with heparin-coated catheters in patients with heparin-associated antiplatelet antibodies. Risk factors and long-term follow-up of patients with the immune type of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Drug-induced thrombocytopenia: clinical data on 309 cases and the effect of corticosteroid therapy. Direct examination of tissue and body fluids by Gram stain provides simple and rapid information about the potential pathogen. Isolation of the offending organism by culture assists in the diagnosis of infection and allows for more definitive directed treatment.
Overexpression of oncogenes responsible for apoptosis may produce an "immortal" cell medicine zantac discount brahmi american express, which has increased potential for malignancy treatment eczema purchase 60caps brahmi otc. The most common chromosomal abnormality found in lymphoid malignancies is the t(14;18) translocation. Translocation of this protooncogene to chromosome 14 in proximity to the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene leads to overexpression of bcl2, which decreases apoptosis and confers a survival advantage to the cell. Loss of p53 disrupts normal apoptotic pathways, imparting a survival advantage to the cell. Recent evidence also has revealed an important role for apoptosis as a mechanism of inherent resistance to chemotherapy. In cancer cells, the function of telomeres is overcome by overexpression of an enzyme known as telomerase. Telomerase replaces the portion of the telomeres that is lost with each cell division, thereby avoiding senescence and permitting an infinite number of cell doublings. As information regarding the role of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes accumulated, it became evident that a single mutation is probably insufficient to initiate cancer. Thus, several detectable genetic mutations may be present in an established tumor. Early mutations are found in both premalignant lesions and in established tumors, whereas later mutations are found only in the established tumor. This theory of sequential genetic mutations resulting in cancer has been demonstrated in colon cancer. In colon cancer, the initial genetic mutation is believed to be loss of the adenomatous polyposis coli gene, which results in formation of a small benign polyp. Oncogenic mutation of the ras gene is often the next step, leading to enlargement of the polyp. Loss of the p53 gene and another gene, believed to be the "deleted in colorectal cancer" gene, complete the transformation into a malignant lesion. Loss of p53 is thought to be a late event in the development and progression of the malignancy. Identification of genes and other proteins involved in carcinogenesis has several important clinical implications. They may be used in cancer screening to identify individuals at increased risk for cancer and are being used to design new anticancer agents and gene therapies, several of which have recently been approved for use. Specific genetic abnormalities are so commonly associated with some types of cancers that the presence of that abnormality aids in the diagnosis of that cancer. Hence, adenomas are benign growths of glandular origin, or growths that exhibit a glandular pattern. Correction of these early changes could potentially prevent the occurrence of a cancer. Precancerous lesions may be described as consisting of either hyperplastic or dysplastic cells. Hyperplasia is an increase in the number of cells in a particular tissue or organ, which results in an increased size of the organ. It should not be confused with hypertrophy, which is an increase in the size of the individual cells. Hyperplasia occurs in response to a stimulus and reverses when the stimulus is removed. Dysplasia is defined as an abnormal change in the size, shape, or organization of cells or tissues. Hyperplasia and dysplasia may precede the appearance of a cancer by several months or years. Malignant cells are divided into those of epithelial origin or the other tissue types. Another term used frequently in the description of malignancy is carcinoma in situ.
In an effort to improve outcomes abro oil treatment buy brahmi online now, several other agents have also been investigated in the treatment of aplastic anemia symptoms 4 days before period purchase brahmi cheap online. The additive benefits of other immunosuppressive agents such as mycophenolate, cyclophosphamide, and sirolimus have been evaluated. Some patients have had a faster neutrophil recovery, whereas others showed no difference in hematopoietic recovery. These symptoms can appear rapidly, within days to weeks after the initiation of the offending drug. The median duration of exposure prior to the development of agranulocytosis ranges from 19 to 60 days for most drugs associated with this adverse event, but the time to onset is greater than 1 month for most of these agents. Time to neutrophil recovery typically has been reported to range from 4 to 24 days. The cause of drug-induced agranulocytosis is not fully understood, and several mechanisms have been proposed. Initially, it was thought that drugs affected only the mature granulocytes, causing a maturation arrest. However, more recent studies have demonstrated that drugs may have either a direct toxic effect or an antibodymediated effect on the bone marrow, neutrophils, or stem cells. This hapten-type reaction is often seen when drugs, such as the penicillin derivatives, are given in large doses. Continuous presence of the drug is required for the destruction of neutrophils in this type of reaction. The second mechanism of immune-mediated agranulocytosis is called the innocent bystander phenomenon. The complex is nonspecifically adsorbed to the neutrophil membrane, resulting in complement activation. Functioning in a manner somewhat similar to that of the second mechanism, the third mechanism of immune response involves a protein carrier that combines with the drug and then attaches to the cell membrane. In addition, there are several other immune-mediated mechanisms that have been identified. The production of autoantibodies to a spoiled membrane is a mechanism in which the offending drug alters the neutrophil membrane. This alteration induces the formation of autoantibodies (antibodies that attach directly to the neutrophil), which causes cellular destruction by the phagocytic system. High concentrations of -lactam antibiotics, carbamazepine, and valproic acid have been associated with inhibition of colony-forming units of granulocytes and macrophages. Finally, drug-induced apoptosis and direct toxicity for pluripotent or bipotent hematopoietic progenitor stem cells have also been associated with clozapine and ticlopidine respectively. More recently, immunosuppressive regimens combining antithymocyte globulin, glucocorticoids, and cyclosporine are gaining favor. Clinical data suggest that there is no difference in survival achieved with the two treatments among patients followed for 6 years. Parity between the treatments will necessitate that clinicians individualize treatment decisions, while considering risk factors, economics, and quality of life. The antibodies and drug form a complex in the serum, and the complex nonspecifically binds to the cell membrane. Researchers have shown with in-vitro cell cultures that penicillin derivatives in high concentrations inhibit the growth of myeloid colony-forming units in patients recovering from drug-induced agranulocytosis. Antithyroid medications, such as propylthiouracil and methimazole, have been reported to cause agranulocytosis. The current incidence of this adverse effect is unknown, but early publications report agranulocytosis in approximately 0. The investigators also reported a possible dose-response relationship with methimazole.
Purchase brahmi 60caps with mastercard. 141110 DJ 종현 Jonghyun - 하루의 끝 (The End of a Day) 푸른밤종현입니다.