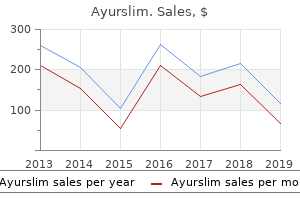
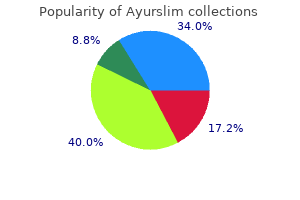
Ayurslim
"Ayurslim 60 caps for sale, aasha herbals".
By: C. Denpok, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Vice Chair, Charles R. Drew University of Medicine and Science College of Medicine
Benzodiazepines the f our benzodiazepine drugs that provide a nticonvulsant effects are: clonazepam clorazepate diazepam (parenteral f orm) lorazepam herbals in your mouth buy ayurslim 60caps with visa. Diazepam m ay be used to trea t sta tus epilepticus or zip herbals purchase ayurslim with mastercard, in rectal form, repetitive seizures. Safe and sound Sound -alikes: Diazepam and lorazepam Be careful not to confuse the sound -alike drugs dia zepam a nd lora zepam. Metabolism and excretion Benzodiazepines a re metabolized in the liver to multiple metabolites and are then excreted in urine. Pharmacodynamics Benzodiazepines a ct as: anticonvulsants antianxiety agents sedative -hypnotics muscle rela xants. Pharmacotherapeutics Each of the benzodiazepines can be used in slightly different ways. Absence, atypical, and more Clonazepam is used to trea t the following types of seizures: absence (petit mal) atypical absence (Lennox-Gastaut syndrome) atonic myoclonic. Because diazepam provides only short -term ef fects of less than 1 hour, the patient must also be given a long-acting anticonvulsant, such as phenytoin or phenobarbital, during diazepam therapy. Adverse reactions to benzodiazepines Most common Drowsiness Confusion Ataxia Weakness Dizziness Nystagmus Vertigo Fainting Dysarthria Headache Tremor Glassy-eyed appearance Less common Depression of the heart and brea thing (with high doses a nd with I. Pharmacokinetics Valproate is converted ra pidly to valproic a cid in the stomach. Valproic a cid readily crosses the placental barrier a nd a lso a ppears in brea st milk. Pharmacotherapeutics Valproic a cid is prescribed f or long-term treatment of: absence seizures myoclonic seizures tonic -clonic seizures partial seizures. Drug interactions Valproic a cid must be used ca utiously in children under 2 yea rs old, particularly those receiving m ultiple anticonvulsants and those with congenital metabolic disorders, severe seizures with mental retardation, or organic bra in disease. In these pa tients, va lproic acid carries a risk of potentia lly fatal liver toxicity (prima rily in the first 6 months of treatment). Valproic warnings these a re the most significant drug intera ctions associated with valproic acid: Cimetidine, a spirin, erythrom ycin, a nd f elbamate m ay increa se levels of va lproic acid. Carbamazepine, la motrigine, phenoba rbital, prim idone, phenytoin, and rifampin m ay decrease levels of valproic acid. Adverse reactions to valproic acid Because ra re, but deadly, liver toxicity ha s occurred with va lproic acid, it should be used with caution in patients who have a history of hepatic disease. These include: nausea a nd vomiting diarrhea constipation sedation dizziness ataxia headache muscle wea kness increased blood ammonia level. Gabapentin is approved as adjunctive thera py f or partial seizures in adults and in children ages 3 and older with epilepsy. Drug interactions Like ca rbamazepine, gabapentin ma y worsen m yoclonic seizures. Patients with rena l impairment (creatinine clearance less tha n 60 ml/minute) require a dosage reduction. Adverse reactions to gabapentin Common a dverse rea ctions to gaba pentin include: fatigue somnolence dizziness ataxia leukopenia. Less common adverse rea ctions include: edema weight gain hostility emotional lability nausea a nd vomiting bronchitis viral infection fever nystagmus rhinitis diplopia tremor. Phenyltriazines the phenyltria zine lamotrigine is chemically unrelated to other anticonvulsants. Clea rance is increa sed in the presence of other enzyme-inducing anticonvulsants. In addition, la motrigine appears to be effective f or many types of generalized seizures. Valproic a cid may decrease lamotrigine clearance and increase the stea dy -state level and effects of lamotrigine. Adverse reactions to lamotrigine Adverse rea ctions to lamotrigine com monly include: dizziness ataxia somnolence headache diplopia nausea vomiting rash. Several types of rash, including Stevens -Johnson syndrome, may occur with use of this drug. Lamotrigine now ca rries a "bla ck box" warning rega rding the rash, and the manufacturer recommends discontinuing the drug at the first sign of rash. The risk of rash may be increased by starting at high doses, by rapidly increa sing doses, or by using va lproate concurrently.
Late Pregnancy Bleeding Case Presentation - A 32-year-old herbals in tamilnadu order ayurslim 60caps with visa, gravida 6 herbals on demand down buy discount ayurslim 60 caps online, para 5-0-0-5 at 28 weeks of gestation presents with vaginal bleeding to the emergency room. Her vital signs show a blood pressure of 100/50, a pulse of 98, and respiratory rate of 24. The most common obstetrical and non-obstetrical causes and overall incidence of bleeding late pregnancy. If the unsuspected diagnosis is abruptio placentae, know the pathophysiology, clinical characteristics, maternal and fetal complications and management. If the suspected diagnosis is placenta previa, know the classification, incidence and probable mechanism, methods to localize the placenta clinical characteristics and management Preeclampsia and Eclampsia I. Eclampsia is the occurrence of convulsions, not caused by any coincident neurologic disease in a woman whose condition fulfills the criteria for 70 preeclampsia. Preeclampsia, can occur any time after 20 weeks of gestation but usually becomes clinically evident late in pregnancy. Incidence-Occurs in 6 to 8% of pregnancies and continues to be one of the leading causes of Maternal morbidity and mortality. Magnesium sulfate-typically administered intravenously, monitoring reflexes, respirations and urine output. Delivery is achieved by induction of labor and use of ceasarean section for fetal or obstetrical indications. The goal of management of this disease is to keep the mother healthy and prevent intrauterine fetal demise. The earlier the onset of the illness, the more severe the course with regard to mother and fetus. Definition-Place: Implantation in the lower uterine segment over or near the cervical internal os. This can result in not only a cesarean section but also a postpartum hysterectomy commonly referred to as a cesarean hysterectomy. Low-lying Placenta-placental implantation in the lower uterine segment, but the placental edge does not actually reach the internal os. Painless hemorrhage- usually occurring toward the end of the second trimester or later 2. Large placenta such as in multiple gestation and pregnancies complicated by fetal erythroblastosis. Diagnosis: the diagnosis is suspected in the setting of painless bleeding late in pregnancy, a uterus which is soft and nontender, and a presenting part which is high in the uterus. It is dangerous to do a vaginal examination on a patient with third trimester bleeding since this may precipitate uncontrollable hemorrhage. Management In the setting of a premature fetus and no active bleeding, hospitalization and close observation is standard. Delivery by cesarean section is indicated in the setting of fetal maturity or severe maternal hemorrhage. Definition the separation of the placenta from its site of implantation in the uterus before the delivery of the baby. Placental abruption can be complicated by severe maternal hemorrhage, coagulation defects, renal failure, and fetal demise. Management Treatment will vary depending on the well-being of the mother and baby. Close monitoring of fluid balance and coagulation defects is essential to optimize outcome. Marginal sinus rupture Uterine rupture Bloody show of labor Vasa Previa Non-obstetric causes-vulvovaginal trauma, cervical lesions Unknown Initial approach to a patient presenting with third-trimester bleeding A. In couples who conceive normally, 50% do so following 3 tries whereas about 92% conceive following 12 attempts. Sterility: the etiology of infertility is established and there is no possibility for conception.
Buy ayurslim discount. Пустые баночки ноябрь 2019.
Differential diagnosis of miliary or disseminated tuberculosis includes histoplasmosis rm herbals discount ayurslim 60 caps on line, as well as Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia herbals shoppes 60caps ayurslim free shipping, disseminated Mycobacterium avium complex infection, and neoplastic syndrome. Histoplasmosis tends to exhibit the same clinical manifestations as miliary or disseminated tuberculosis, with fever, weight loss, and hepatosplenomegaly, identical laboratory results showing anemia or pancytopenia, and identical diagnostic imaging with diffuse micronodular infiltrate. In addition to hematological alterations, systemic histoplasmosis often involves elevated alkaline phosphatase levels and, above all, marked elevations in lactic dehydrogenase. The fungus can sometimes be seen in a peripheral blood smear; however, given the unavailability of other diagnostic studies such as hemocultures, and the length of time they take, a definitive differential diagnosis can be made only through bone marrow aspiration and biopsy or identification of the fungus in a smear from oral or mucous lesions. It is fully automated and contained, poses a low biological risk, is appropriate for any laboratory level, and yields results in less > 23 than two hours. In comparison with culture, its sensitivity in patients with a positive sputum-smear is 98. It detects rifampicin and isoniazid resistance, and its results are available in less than two days. It is recommended for reference laboratories, since it requires a high biosafety level. The best sputum is the first of the morning, and a practical way of collecting two or three samples is the following: Day 1 (sample 1) After receiving instructions, the patient gives a sputum sample on the day of his visit to the health facility (the sample should be collected in very-well-ventilated settings, and health workers should ideally use N-95 respirators or collect the sample outdoors). That day, the patient will be given a receptacle for a second sample to bring the next day. In suspected cases with a dry cough, sputum induction can be used, provided that infection control measures can be guaranteed to prevent the risk of nosocomial transmission (No. The sputum induction technique involves safe, noninvasive collection of sputum through nebulizations that facilitate expectoration. The procedure should be performed in the morning in a fasting state after cleansing the upper respiratory tract to minimize contamination from nasal secretions or saliva. Ten minutes before starting, an inhaled beta-adrenergic should be administered to the patient to prevent bronchoconstriction, followed by nebulization for 10 to 15 minutes with a 3-5% hypertonic solution; the patient should then be instructed to cough and spit. The procedure can be repeated once, half an hour later, if the sample is inadequate. While more expensive and less accessible because it requires greater training and technological capacity, its contribution to diagnosis is important, though slower (2-8 weeks, depending on the method). Lowenstein-Jensen medium: the most common medium worldwide, it is a traditional method that uses a solid, coagulated-egg-based medium with a close-to-neutral pH. Its advantages are its simplicity, the possibility of doing a colony count, and its affordability. The procedure requires an equipped laboratory with adequate biosafety and skilled personnel. Ogawa Kudoh: this is an inexpensive procedure with a low level of complexity and biohazard. Laboratories that perform it must have the same level of biosafety as for smear microscopy. It is also useful for transporting a sputum sample from an outlying area to a reference laboratory. The reading is automated, using sensors that detect changes in the pressure of these gases. Use of these cultures cuts the average diagnosis time to 10 days; however, they are more expensive than traditional media and require laboratories with a high biosafety level and sufficient numbers of trained personnel. The intensity of any visible band on the strip is compared with a reference standard. It can be done using an indirect technique (by seeding several 26 < centesimal dilutions of bacilli recovered from the culture) or a direct technique (by seeding samples with a high bacillary load). Simple to perform with no need for sophisticated equipment, it may be appropriate in resource-constrained laboratories. In cases of severe immunodeficiency, the radiological findings tend to be atypical, with a predominance of lymphatic involvement and signs of hematogenous dissemination (diffuse interstitial infiltrates or miliary pattern). It will be necessary to reassess the patient, looking for conditions that could be confused with tuberculosis.
In cases of acute sportsrelated trauma in nonambulatory female athletes herbalstarcandlescom quality ayurslim 60caps, sports medicine professionals must maintain a high index of suspicion for fracture herbals wikipedia buy 60 caps ayurslim. Further complicating the picture, these athletes will frequently have decreased lower extremity sensation and thus a lower likelihood of reporting acute pain secondary to fracture. In these circumstances, a thorough physical exam of the lower extremities should be accompanied by radiologic imaging of any area deemed particularly concerning, with followup to monitor for the development of swelling, ecchymosis, or limb deformity. These recommendations are most pertinent in sports that incur the risk of highspeed trauma, such as alpine skiing, wheelchair racing, and handcycling, although low velocity trauma may also lead to fracture. Nondisplaced fractures of osteoporotic bone can easily be missed on plain radiographs; therefore clinicians should have a low threshold for proceeding with advanced imaging if a fracture is suspected. Longitudinally, care should be taken to optimize bone health in female athletes with a disability as a focus of sports injury prevention. Vitamin D levels may be monitored to ensure these remain in the normal range, with appropriate repletion as necessary for athletes with levels <30 ng/mL. In athletes for whom dietary availability of calcium may be low, supplementation is advised. For the population of female athletes with a disability who are less than 50 years of age, calculation of a Zscore is the most appropriate measure of bone mineral density. Scores less than two standard deviations below agematched normal values constitute osteoporosis that may increase the risk of fracture (Figure 13. Female athletes with a disability must be educated regarding the importance of bone health and fracture risk with lowvelocity trauma, while ensuring a safe competition environment to minimize injury. Bowel and bladder considerations Among female athletes with a disability, bowel and bladder management remains of great importance in promoting athlete health and optimal sports performance. In addition to the potential effects of stress incontinence and pelvic floor dysfunction, many female athletes with a disability may also experience increased difficulty in maintaining optimal genitourinary and gastrointestinal health. Neurogenic bowel and bladder dysfunction occur secondary to a loss of central neurologic control of bowel and bladder emptying. An awareness of this phenomenon is essential for medical personnel working with female athletes with a disability at all sport participation levels from developmental to elite. Voluntary bowel and bladder function are controlled by a complex interplay between central and peripheral neurologic control centers, which in optimal circumstances enable continence at socially appropriate times. As related to genitourinary function, neurogenic bladder may result from injury to the cerebral cortex or pontine micturition center. Dysfunction in various regions of this complex neurologic pathway will result in different subtypes of neurogenic bladder, a discussion of which is beyond the scope of this chapter. In sum, athletes will typically experience either an overactive, spastic bladder, or a flaccid bladder with difficulty emptying. For both conditions, female athletes will typically employ an intermittent selfcatheterization protocol for predictable emptying in appropriate settings. Alternatively, for female athletes with upper extremity impairments resulting in difficulty with toilet transfers and/or decreased hand dexterity, bladder emptying may be accomplished by the use of an indwelling suprapubic or urethral catheter. This option enables female athletes to void in a hygienic fashion without having to transfer into or out of a wheelchair. For the treatment of overactive, spastic bladder, anticholinergic agents such as oxybutynin are frequently prescribed to inhibit spastic activity of the detrusor muscle, thus improving bladder storage capacity. For female athletes with a flaccid, underactive bladder, selfcatheterization remains the mainstay of treatment to ensure complete bladder emptying. Of note, for antidoping purposes, female athletes should be educated regarding the importance of having a sterile urinary catheter available for sample collection and to avoid potential contamination. Additionally, many female athletes will purposefully become dehydrated during longhaul international travel due to concern for difficulty accessing the lavatory or inaccessible restroom facilities. In this circumstance, it is advised that female athletes take care to stay well hydrated for several days prior and several days after the travel period in order to ensure adequate hydration at the time of training and competition. Symptoms may include dysuria, urinary frequency, cloudy urine, or foulsmelling urine. If infection is suspected, appropriate antibiotic treatment should be initiated immediately to prevent more significant illness and thus a detrimental impact on sports performance. For purposes of promoting optimal bowel management, many female athletes will employ what is termed a "bowel program" in order to achieve a bowel movement at a time that is convenient for daily life activities and optimal sports performance. Similar to what has been noted for the bladder, colonic neurologic pathways are controlled via both central and peripheral mechanisms. Neurogenic bowel may result from injury to the cerebral cortex, the ascending/descending spinal cord tracts, the spinal cord sacral control center, or the sacral nerve roots.