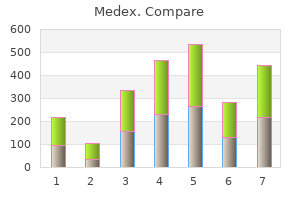
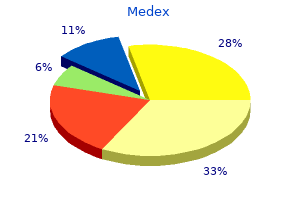
Medex
"Order genuine medex, hiv aids infection rate zimbabwe".
By: I. Murat, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Program Director, University of Nebraska College of Medicine
The most common organisms isolated in chronic rhinosinusitis subjects include Staphylococcus aureus hiv zero infection discount medex 5 mg, anaerobes anti viral hand foam buy medex in united states online, and gram-negative enterics such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The presence or absence of nasal polyps may represent different pathophysiologic mechanisms. Nasal polyps are smooth, edematous lobulated masses that usually arise from the middle meatus or sphenoethmoid recess and represent a noninfectious and most often eosinophilic inflammatory reaction. Rhinosensitivity: establishing definitions for clinical research and patient care. A pathologic examination of the black necrotic debris that is often seen intranasally demonstrates arterial and venous thrombosis due to direct fungal invasion. The treatment consists of (1) debriding all involved structures, including the orbital contents, if necessary; (2) aggressive intravenous antifungal therapy; (3) normalizing the underlying immunocompromised state (usually neutropenia); and (4) stabilizing the diabetes. Fungal ball-Fungal ball is the development of a noninvasive conglomeration of fungal hyphae into a mass. Aspergillus is the most common pathogen, and chronic rhinosinusitis results from paranasal sinus obstruction. Typically, polypoid tissue is seen anterior to a mass consisting of mucin, fungal elements, CharcotLeyden crystals, and eosinophils. Even though this is not an invasive, infectious process, the treatment is primarily surgical with postoperative topical nasal steroids. Adult chronic rhinosinusitis: definitions, diagnosis, epidemiology, and pathophysiology. Radiologic correlates of symptom-based diagnostic criteria for chronic rhinosinusitis. Findings to be noted include mucopurulence at the ostiomeatal complex and sphenoethmoid recess, edema, erythema, polyps/polypoid tissue, and crusting. In acute bacterial rhinosinusitis, endoscopy is useful to confirm the diagnosis and to obtain cultures at the middle meatus. Because symptoms do not correlate well with findings in chronic rhinosinusitis, endoscopy and/or imaging is essential to make the appropriate diagnosis and to obtain cultures from the middle meatus. When performed carefully to avoid contamination from the nose, middle meatus cultures correlate well with maxillary sinus aspiration, which is the gold standard. The symptoms of facial pressure and pain, purulent nasal discharge, nasal congestion, hyposmia, tooth pain, and a poor response to nasal decongestants can help differentiate these entities. On the other hand, symptoms of chronic rhinosinusitis do not correlate well with findings. In addition to providing excellent visualization of mucosal thickening, air fluid levels, and bony structures, coronal scans give optimal visualization of the osteomeatal complex and are conveniently oriented for the surgeon in terms of surgical planning. The presence of purulence on examination of the nasal cavity can assist in the diagnosis. Sinus infection is more likely if symptoms become worse after 5 days or last longer than 10 days. Allergic rhinitis may also cause rhinorrhea and postnasal drip, as seen in sinusitis. With recent antibiotic use or in moderate disease, initial drug selection should include a respiratory quinolone, amoxicillin/clavulanate, ceftriaxone, or a combination to provide broad-spectrum coverage in adults and amoxicillin/clavulanate or ceftriaxone in children. Failure to respond to treatment within 72 hours should lead to a reevaluation and change of therapies to provide broader coverage. Chronic sinusitis is associated with a different set of pathogens and therefore demands an antibiotic with a spectrum that includes gram-negative organisms, S aureus, and anaerobes. Migraine headaches are characterized by throbbing head pain, frequently unilateral, that lasts from 4 to 72 hours. Migraines can occur with or without neurologic symptoms such as visual disturbances or numbness. Noting the presence of an aura, the relatively short duration of symptoms, and the response to migraine medicines such as ergot alkaloids can help differentiate migraine headaches from sinusitis. The bandlike frontal pressure associated with tension headache typically worsens as the day goes on, whereas sinus pain remains relatively constant.
Although conventional adjuvant radiation treatment consisted of radiation alone hiv infection in south africa buy medex cheap, two recent randomized trials have shown improved local control with concurrent radiation and cisplatin for certain risk factors hiv infection rate in botswana order medex 5mg free shipping. As noted previously, newer protocols are using various combinations of radiation with systemic therapies for tumor sensitization and eradication of micrometastatic disease. Altered radiation schedules are also being studied-both with and without systemic agents. When the field will encompass the oral cavity, carious teeth are extracted before starting radiation owing to the radiation-induced dental decay and increased risk of osteoradionecrosis. Short-term side effects of radiation, lasting up to 6 weeks after the conclusion of therapy, include mucositis, odynophagia, dysphagia, skin and erythema, altered taste, and edema. Common long-term side effects include varying degrees of xerostomia, fibrosis, and edema. Uncommon side effects include hypothyroidism, chondroradionecrosis, and osteoradionecrosis. As noted previously, an exceedingly rare complication is radiationinduced sarcoma. Chemotherapy for larynx cancer-Chemotherapy had not traditionally been part of larynx cancer primary treatment protocols. Starting in the 1980s, organ-preserving protocols using chemotherapy in conjunction with radiation for advanced-stage laryngeal cancer have been compared with standard surgery and radiation treatment. In general, lowered rates of distant metastasis are seen, although questionably higher rates of local recurrence are also cited in comparison with surgery and locoregional radiation protocols. Cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil are the two agents found to be the most effective against larynx cancer. Recently, paclitaxel (Taxol) and docetaxel (Taxotere) have demonstrated activity without the side effects of cisplatin, which include neurotoxicity, ototoxicity, and renal toxicity. Chemotherapy has been given in the neoadjuvant (induction) setting concurrent with radiation and also in the adjuvant setting. Even though successes have been reported for all three approaches, concurrent chemoradiation has generally been deemed the most successful. Trials with neoadjuvant and concurrent intra-arterial chemotherapy have shown excellent local tumor response in selected cases, but with enhanced local toxicity. Agents, such as amifostine, are being used to mitigate side effects and preserve salivary function in the setting of radiation. Once again, cisplatin is the preferred agent, but methotrexate was historically used with some benefit. Vocal problems-Hoarseness may complicate any treatment of larynx cancer, even the smallest larynx cancer. Voice changes can be as subtle as the loss of vocal range, vocal fatigue, and lowered threshold for bouts of laryngitis. Swallowing problems-After partial laryngectomy procedures, aspiration risk is significant. This can be due to surgical removal or to denervation, in whole or in part, of the protective mechanisms of the larynx. Acute side effects of radiation include mucositis, thick secretions, odynophagia, and edema, which all contribute to swallowing difficulties in the immediate peri-radiation period. Xerostomia is a long-term side effect of radiation that also contributes to dysphagia. Stricture, stenosis, or fibrosis of the pharyngoesophageal segment as a result of surgical scarring or as a residual effect of radiation can lead to intolerance of solid foods or an inability to take adequate nutrition by mouth. Loss of taste and smell-Radiation can permanently damage taste buds, although this side effect is often transient. After total laryngectomy, anatomic changes result in a lack of airflow through the nose and mouth. Fistula development-A fistula, or connection between the pharynx and skin of the neck, reflects the failure of the pharyngeal surgical closure to seal after laryngectomy. This results in the leakage of saliva and pharyngeal contents (including food) into the neck.
Purchase medex 5mg with amex. HIV AIDS and Helper T-Cells.
The Necrosauridae hiv infection rate japan cheap medex online mastercard, occurring from the Early Cretaceous to the Oligocene hiv infection via saliva purchase genuine medex online, also have some uniquely varanoid traits and have been proposed as a sister group of the helodermatids. Aside from the preceding fossil representatives, the extant squamate families lack a fossil presence until the Middle Cretaceous or later. History of Extant Reptiles Crocodylians the Crocodylia, as now defined, is a clade consisting of the ancestor of extant crocodylians and all its descendants. Members of this clade, vernacularly the crocodylians, appeared first in the Cretaceous, although no members of the extant families occur in the fossil record until the Tertiary. The older and broader definition of Crocodylia included protosuchians, eusuchians, and other groups and extends the history into the Lower Jurassic. A few members of these older clades survived into the mid-Tertiary; however, the Tertiary belongs to the crocodylians. The higher clades (gavialoids, alligatoroids, and crocodyloids) include many fossil taxa, and these reveal a Cretaceous divergence of gaviaoloids from the other crocodylians (Table 3. Extinct gharial or gavialoid fossils occur in the Late Cretaceous and were geographically widespread. Taxa occurred in North America (Cretaceous to Pliocene), South America (Oligocene to Pliocene), Europe (Cretaceous to Eocene), Australia (Pliocene), Africa (Late Cretaceous), and southern Asia (Eocene to Recent). It appeared at the end of the Cretaceous and survived into the Paleocene of North America and Europe. The pristichampsines must also have arisen in the Cretaceous; however, they appeared Chapter 3 Evolution of Ancient and Modern Amphibians and Reptiles 105 only briefly in the Middle Eocene of Europe. They were peculiar crocodylians with heavy dorsal and lateral armor and hoof-like terminal phalanges. The alligatorines appeared first in the Early Oligocene, although the group certainly arose much earlier because the caimans were present in the Early Tertiary, represented by Eocaiman from the Middle Paleocene to Middle Miocene and the nettosuchids from the mid-Eocene to the Pliocene of South America. The nettosuchids had a unique jaw articulation and typically a broad, elongate snout. Melanosuchus and Caiman appear only in the Neotropic Late Miocene and Pleistocene, respectively. In contrast, Alligator ranges from the Early Oligocene to the present in North America and Asia. Crocodyloids similarly had a moderate diversity in the Late Cretaceous and Early Tertiary. The tomostomines occurred in the Middle Eocene of Egypt and China, then intermittently in northern Africa and Europe from the Oligocene to the Middle Miocene and then not again until the Late Pliocene in Asia. The crocodylines include a variety of lineages of which the "true" Crocodylus is of only recent origin from the Pliocene to the present. The mekosuchines had a variety of body and head forms, ranging from narrow elongate skulls like gharials to short, broad-headed species. Mekosuchus survived into the Recent era in New Caledonia and apparently was hunted to extinction by the first humans to arrive there. The ribs and vertebrae were fused to dermal bones to form a carapace, and some pectoral girdle elements and dermal bones fused to form a plastron. A pleurodire, Proterochersis, was contemporaneous and sympatric in Europe with Proganochelys. The pelvic girdle was fused to the plastron, indicating that it was the earliest pleurodire and confirming that the divergence of cryptodires and pleurodires had occurred. After Proterochersis, the pleurodire Platychelys occurred through much of the Jurassic and into the Early Cretaceous. By the mid-Cretaceous, pleurodire are represented in many fossil faunas, particularly those of the Southern Hemisphere.
Apparently most of the translocations have been successful symptoms hiv infection after 4 years medex 5 mg without prescription, although a few populations were destroyed when fires destroyed translocation sites hiv infection steps order 5 mg medex. A similar success story applies to the Majorcan midwife toad Alytes muletensis. This toad was discovered first as a fossil and considered extinct on the Balearic Islands off the east coast of Spain. A few isolated populations were later discovered in the deep mountain gorges of Majorca. Apparently, many populations of this species were heavily preyed upon and driven extinct by the European water snake Natrix maura, which was introduced into the Balearics by the Romans for religious use. Once rediscovered in 1980, the toads were given legal protection, some nature reserves were established, and two zoos established breeding colonies, each from a few individuals. These breeding colonies have been used for repatriation; of eight repatriations, three populations now have begun to reproduce, one translocation failed, and the status of the other four is indeterminate. The endangered Houston toad (Anaxyrus houstonensis) is a resident of southeastern Texas in pine flat woods with sandy soils. Agriculture and other development have eliminated many populations and reduced this species to a few isolated populations. This toad is adaptable to captive breeding, and a breeding program at the local Houston zoo has provided adults and thousands of eggs and metamorphs for translocation. In spite of massive efforts to reestablish the toad at extirpated and new sites, no new populations have become established. A similar lack of success is common in "mitigation," or relocation, projects that move animals from sites that are scheduled for destruction because of development. Thousands of gopher tortoises (Gopherus polyphemus) have been relocated in central Florida because of development projects. Of the hundreds of relocations, only a few include short-term monitoring of the relocated individuals, showing that usually 50% or more of the relocated individuals disappear from the new site within 2 years. A site in southeast England scheduled for development had a large population of slowworms (Anguis fragilis). Slowworms were captured and relocated at a natural site that lacked slowworms but was otherwise ecologically similar. The translocation failed; the slowworms at the relocation sites were clearly less robust than those from nearby populations and did not become established and reproduce. Further, they mislead the public, developers, and government officials by suggesting that natural populations are conserved. Although these efforts result from good intentions, they lead to poor conservation and should be eliminated as a development tradeoff strategy. Relocation and augmentation programs have real and potential dangers built into them. For example, a disease of the upper respiratory tract has decimated populations of the desert tortoise (Gopherus agassizii) in the Mojave Desert of southern California and now appears to be spreading through the gopher tortoise populations of Florida. Small isolated populations are often closely adapted to their local environment, and while subtle to the human eye, microenvironments can be quite different among nearby populations. Connecting with the Public and Policy Makers Ecological Research Populations Communities Ecosystems Landscapes Conservation Practice Protected areas and species Zoological and botanical parks Aquaria Ecological Ethics Professional Codes. Over time the new genetic pool can adapt to the specific local environment, but the initial response of the local population is likely lower survivorship. The essential message of translocation conservation is to anticipate failure and proceed cautiously with intense scrutiny to avoid causing further injury to the species or population in need of intervention. For any kind of conservation strategy to be successful, it must result in attitude changes both in the public at large and the people who set regional, national, and global policy. This challenge is daunting, considering how overwhelmed people are by complexity of their daily lives and how focused politicians are on securing funding for their next political race. Ecological research related to conservation tends to end once scientific papers are published, because scientists must continually seek new funding or initiate new studies in order to advance in their profession. Scientists need to play an active role in setting conservation strategy, but our current university system does not adequately reward those kinds of activities. Scientists should also be involved in educating policy makers, which is not what they are trained to do. In addition, because ecological research and conservation practices often raise difficult ethical questions, setting standards for ecological research and conservation practices needs to be high priority.