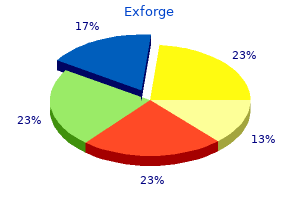
Exforge
"Buy exforge with a visa, hypertension kidney pathology".
By: S. Keldron, M.A., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Central Michigan University College of Medicine
It is used to treat painful muscle spasms attending spinal diseases and skeletal muscle disorders involving excessive release of Ca2+ (malignant hyperthermia) blood pressure medication pills order exforge in united states online. Drugs Affecting Motor Function the smallest structural unit of skeletal musculature is the striated muscle fiber blood pressure vs age purchase 80mg exforge with amex. Simple reflex contractions to sensory stimuli, conveyed via the dorsal roots to the motoneurons, occur without participation of the brain. Neural circuits that propagate afferent impulses into the spinal cord contain inhibitory interneurons. These serve to prevent a possible overexcitation of motoneurons (or excessive muscle contractions) due to the constant barrage of sensory stimuli. Neuromuscular transmission (B) of motor nerve impulses to the striated muscle fiber takes place at the motor endplate. Clinically important drugs (with the exception of dantrolene) all interfere with neural control of the muscle cell (A, B, p. Drugs Acting on Motor Systems 183 Antiepileptics Antiparkinsonian drugs Myotonolytics Dantrolene Muscle relaxants Myotonolytics Increased inhibition Inhibitory neuron Benzodiazepines. For this reason, care must be taken to eliminate consciousness by administration of an appropriate drug (general anesthesia) before using a muscle relaxant. The duration of the effect of d-tubocurarine can be shortened by administering an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, such as neostigmine (p. Unwanted effects produced by d-tubocurarine result from a nonimmunemediated release of histamine from mast cells, leading to bronchospasm, urticaria, and hypotension. More commonly, a fall in blood pressure can be attributed to ganglionic blockade by d-tubocurarine. Pancuronium is a synthetic compound now frequently used and not likely to cause histamine release or ganglionic blockade. Increased heart rate and blood pressure are attributed to blockade of cardiac M2cholinoceptors, an effect not shared by newer pancuronium congeners such as vecuronium and pipecuronium. Other nondepolarizing muscle relaxants include: alcuronium, derived from the alkaloid toxiferin; rocuronium, gallamine, mivacurium, and atracurium. The latter undergoes spontaneous cleavage and does not depend on hepatic or renal elimination. Muscle Relaxants Muscle relaxants cause a flaccid paralysis of skeletal musculature by binding to motor endplate cholinoceptors, thus blocking neuromuscular transmission (p. According to whether receptor occupancy leads to a blockade or an excitation of the endplate, one distinguishes nondepolarizing from depolarizing muscle relaxants (p. As adjuncts to general anesthetics, muscle relaxants help to ensure that surgical procedures are not disturbed by muscle contractions of the patient (p. Nondepolarizing muscle relaxants Curare is the term for plant-derived arrow poisons of South American natives. When struck by a curare-tipped arrow, an animal suffers paralysis of skeletal musculature within a short time after the poison spreads through the body; death follows because respiratory muscles fail (respiratory paralysis). Killed game can be eaten without risk because absorption of the poison from the gastrointestinal tract is virtually nil. This compound contains a quaternary nitrogen atom (N) and, at the opposite end of the molecule, a tertiary N that is protonated at physiological pH. The fixed positive charge of the quaternary N accounts for the poor enteral absorbability. It is often given at the start of anesthesia to facilitate intubation of the patient.
However arrhythmia game generic exforge 80mg fast delivery, the peafowl may develop respiratory sounds caused by granuloma formation within the trachea hypertension new guidelines buy generic exforge online. Specific relationships between avian hosts and individual serovars have not been defined. The presence of miliary to greater-than-pea-sized nodules in the wall of the intestinal tract and in the liver, spleen and bone marrow are characteristic of M. These typical lesions have been described in Falconiformes, Accipitriformes, Strigiformes, Phasianiformes, Charadriiformes, Ciconiiformes, Cuculiformes, Piciformes and Ralliformes. Granuloma formation can occur in any organ but is generally localized to the intestinal tract and reticuloendothelial organs. The nodules are frequently necrotic in the center and in chronic cases may be calcified. In contrast, Columbiformes, Anatiformes, Passeriformes and most of the Psittaciformes do not form typical granulomas. Acid-fast rods are found distributed throughout the parenchyma of infected organs. An infected liver or spleen may be only swollen or may show necrotic foci or even general induration. In pelicans, greasy tumor-like swellings like those seen in leukosis may be observed. The lungs, particularly of geese, weaver finches (genera Queleopsis, Quelea and Euplectes) and some Amazona spp. Paratuberculous lesions are characterized by the occurrence of clubbed villa containing acid-fast rods in the intestinal mucosa. Histopathologic identification of foci of single or confluent epithelioid cells in affected organs is suggestive of an M. Parenchymal lesions generally consist of epithelioid cells or multinucleated giant cells (mostly the foreign body type, only rarely the Langhans type) and occasionally contain lymphocytes and plasma cells. Acid-fast rods in varying quantities can be demonstrated in the affected epithelioid or multinucleated giant cells. Some infected birds will have cellfree acid-fast rods in the proventriculus or jejunal villi without an inflammatory response. In Columbiformes and some other species, atypical granulomas may form in the lungs. Mycobacterium avium was recovered from the lungs of this pigeon that was presented for severe emaciation and severe dyspnea. Clinical Disease In some bird species the clinical course is atypical, and acid-fast rods have been detected more or less accidentally. This is particularly the case with small Passeriformes, especially the Hooded Siskin. Adult birds usually develop a chronic wasting disease associated with a good appetite, recurrent diarrhea, polyuria, anemia and dull plumage. Intermittent switching lameness may occur as a result of painful lesions in the bone marrow. Arthritis, mainly of the carpometacarpal and the elbow joints or tubercle formation of the muscles of the thigh or shank can be seen occasionally. These clinical changes are particularly common in Falconiformes and Accipitriformes. Tubercle formation in the skin is rare, but when it is present, pinpoint to pigeon egg-sized nodules filled with yellow fibrinous material may be noted. Granulomas may be seen within the conjunctival sac, at the angle of the beak, around the external auditory canal and in the oropharynx. Depletion of the splenic lymphocytes and lymph follicles may induce an immunosuppression. Diagnosis the demonstration of acid-fast rods in tissues or on cytologic preparations is suggestive of mycobacteriosis. The demonstration of acid-fast rods in the feces has been suggested as a useful diagnostic tool in subclinical birds.
By the fourth bandage change arrhythmia bradycardia exforge 80mg visa, a healthy granulation bed had formed blood pressure chart to keep track of readings order generic exforge, and a primary skin closure was performed. Principles of Wound Management Impediments to Wound Healing There are many factors that can impair or prevent normal wound healing. Necrotic tissue or blood clots may harbor bacteria and physically impede epithelial cell migration. Dirt, debris, dead bone and even suture material6 may cause host reaction leading to the development of fistulous tracts. Tissue destruction resulting from desiccation, severe trauma (eg, crushing or projectile injuries) or poor surgical technique will delay healing. Wounds of the distal extremities (reduced vascular supply) and nonimmobilized injuries over joints, the axilla and the patagia tend to heal more slowly. Initial Assessment Preliminary assessment of the injured avian patient will determine if immediate life-saving treatments are necessary. It is important to avoid overlooking less obvious injuries and unrelated problems. Trau- matized birds often have multiple injuries and may be further compromised by dehydration, malnutrition and other problems, especially if there has been a delay (hours to days) between injury and presentation. Shock, fluid and nutritional therapy are critical in the early management of traumatized birds. Anesthesia may be necessary with fractious birds or in birds with extensive soft tissue or orthopedic injuries. However, if the bird is not stable, partial wound management and bandaging may have to suffice until more thorough treatment can be safely completed. When assessing a wound, one should note the location, extent and age of the injury. Associated orthopedic injuries and the vascular and nerve supply to the area should also be evaluated (Figure 16. It is common to have underlying fractures or luxations associated with soft tissue wounds of the limbs. Greenish discoloration of the skin is normal in bruised birds due to accumulation of biliverdin pigment following breakdown of hemoglobin. This discoloration develops two to three days post-injury and may persist for a week or more. The vascular integrity may be evaluated by palpating the warmth of the limb, checking the capillary refill time of the skin, clipping a toe nail or pricking the skin. Other diagnostic tests used to assess an injured bird include microbiological cultures, hematology, radiology and ophthalmologic examination. Surface Preparation and Wound Treatment the initial goal in treating contaminants or infected wounds is the removal of devitalized tissue, foreign material and bacteria. The feathers surrounding the wound should be gently plucked or trimmed to allow more thorough cleansing and to prevent feather matting during the healing phases. Plucking feathers will allow for earlier regrowth of feathers, but caution should be used to prevent additional trauma to friable skin while plucking. Wound lavage using a curved tip irrigating syringe will remove foreign material, reduce bacterial numbers and rehydrate soft tissues. Hydrogen peroxide has been shown to be ineffective for bacterial infections, but may be effective as a sporicide in cases of suspected clostridial infections, or for initial cleansing of dirty wounds. Wound debridement following lavage involves removal of as much of the devitalized and necrotic tissue as possible until viable, vascularized tissue is recognized. In complicated or older wounds, the debridement process may have to be repeated over a period of a few days. Topical medications in certain wounds may be beneficial; however, use of non-water-soluble medications should be avoided due to loss of insulation with soiled feathers. Bacitracin, neomycin and polymyxin are effective against a wide spectrum of bacteria. After lavage and debridement, the wound should either be sutured, managed by second intention healing or managed as an open wound with delayed closure. Older, infected or more complicated wounds should be managed as open wounds and allowed to heal by second intention. Fracture repair was uneventful, but when the bandage was removed, a severe wing droop was still evident and muscle atrophy had occurred to the wing musculature. The functions of bandages32 are to: Apply pressure to reduce dead space, swelling, edema and hemorrhage Protect the wound from pathologic microorganisms Immobilize the wound and underlying fractures, if present Protect the wound from desiccation and additional trauma from abrasions or self-mutilation Absorb exudate and help debride the wound surface Provide comfort for the patient.
The liver (l) arteria peronea order exforge 80mg online, spleen (s) blood pressure ideal purchase exforge in india, proventriculus (p), ventriculus (v), duodenal loop (d) and pancreas (arrow) are visible. The patient became depressed, anorectic and began to regurgitate two weeks postsurgery. Radiographs indicated dilated bowel loops suggestive of an intestinal obstruction. Shown are the pancreas (p), inflamed serosal surface of the duodenum (d) and mesenteric hemorrhage (arrow) of the anastomosis. The heart (h), proventriculus (p), ventriculus (v) and right liver lobe (l) can also be visualized. Note the position of the reflection of the caudal thoracic air sac from the surface of the liver lobe (see Color 14. In some species the pancreas is divided into three lobes: the dorsal lobe (arrow), the ventral lobe (open arrow) and the splenic lobe (see Color 14. In species that do not have gall bladders, bile may accumulate in the right bile duct and appear as though a gall bladder is present. From this dorsal view, the splenic head (arrow) of the pancreas and lateral edge of the liver (l) can also be identified. In this case, the enlarged mottled spleen (s) was from a neonatal Blue and Gold Macaw that died from avian polyomavirus. The right lung (lu), both liver lobes (l), proventriculus (p), ventriculus (v), descending duodenum (dd), ascending duodenum (ad), pancreas (arrow) and colon (c) can be visualized from this view. In health, the kidneys appear dark red-brown and are embedded within the renal fossae. The adrenal glands are small, round, yellow structures at the cranial divisions of the kidneys. The quiescent ovary of this bird is granular and pigmented (melanin pigment) (courtesy of Ken Latimer). The lung is attached to the dorsal body wall and interdigitates with the spinal processes and ribs. Cranial division of left kidney (k1), middle division of left kidney (k2), caudal division of left kidney (k3), lung (lu), common iliac vein (arrow), caudal renal vein (open arrow) and ureters (u). Infected birds frequently die of exsanguination secondary to the tears in the liver (l) (courtesy of Brett Hopkins). Abdominocentesis indicated the presence of a septic exudate containing numerous gram-negative bacteria. At necropsy, a perforating lesion was noted in the proventriculus (arrow), and the liver was enlarged, pale and mottled. Histopathology indicated a gram-negative septicemia with hepatitis and peritonitis. The accumulation of bile was detected radiographically as a fluid-filled mass slightly dorsal to the hepatic shadow. Lung (lu), heart with thickened, opaque pericardium (h), liver (l), proventriculus (p) and ventriculus (v). Note the plaques (arrows) and thickening of the dorsal wall of the intestinal peritoneal cavity. The bird was housed indoors but the food was kept in an open container and was contaminated with roach feces. Note the hemorrhage and ulceration (arrows) at the isthmus, which is common in birds with Clostridium perfringen infections. This bacteria secretes an exotoxin that causes generalized vasculitis and is associated with atony of the proventriculus. At necropsy, multiple masses were identified in association with the pancreas and dorsal body wall. Histopathology indicated a pancreatic adenocarcinoma with carcinomatosis (arrows) of the abdominal cavity (courtesy of Cheryl Greenacre). Amyloidosis commonly occurs in waterfowl with chronic inflammatory diseases (courtesy of R. The proximal cervical musculature (cm), crop (c), pectoral musculature (pm) and abdominal musculature (am) have been exposed.
A kidney prehypertension remedies buy exforge now, ureter heart attack jaw pain right side generic exforge 80 mg with amex, and bladder film is taken to ensure that no stool, gas, or barium will obscure visualization of the uterus and fallopian tubes. A speculum is inserted into the vagina, and contrast medium is introduced into the uterus through the cervix via a cannula, after which both fluoroscopic and radiographic images are taken. Inform the patient that a vaginal discharge is common and that it may be bloody, lasting 1 to 2 days after the test. Inform the patient that dizziness and cramping may follow this procedure, and that analgesia may be given if there is persistent cramping. Normal placement and intensity of staining provide information about the immunoglobulin bands. Abnormalities are revealed by changes produced in the individual bands, such as displacement, color, or absence of color. Inform the patient that the test is used to assess the immune system with respect to the type and quantity of immunoglobulins in blood and urine. Assess whether the patient received any vaccinations or immunizations within the last 6 mo or any blood or blood components within the last 6 wk. Alternatively the specimen can be left in the collection device for a health care staff member to add to the laboratory collection container. Positively identify the patient, and label the appropriate specimen containers with the corresponding patient demographics, date, and time of collection. Urine: Clean-Catch Specimen: Instruct the male patient to (1) thoroughly wash his hands, (2) cleanse the meatus, (3) void a small amount into the toilet, and (4) void directly into the specimen container. IgE binds to the membrane of special granulocytes called basophils in the circulating blood and mast cells in the tissues. Mast cells are abundant in the skin and the tissues lining the respiratory and alimentary tracts. When IgE antibody becomes cross-linked with antigen/allergen, the release of histamine, heparin, and other chemicals from the granules in the cells is triggered. A sequence of events follows activation of IgE that affects smooth muscle contraction, vascular permeability, and inflammatory reactions. The inflammatory response allows proteins from the bloodstream to enter the tissues. Helminths (worm parasites) are especially susceptible to immunoglobulinmediated cytotoxic chemicals. Inform the patient that the test is used to assess IgE levels in order to identify the presence of an allergic or inflammatory immune system response. Immunoglobulins neutralize toxic substances, support phagocytosis, and destroy invading microorganisms. Immunoglobulins produced by the proliferation of a single plasma cell (clone) are called monoclonal. IgM is the largest immunoglobulin, and it is the first antibody to react to an antigenic stimulus. Inform the patient that the test is used to assess the immune system with respect to the quantity of immunoglobulin levels present in the blood. Refer to the Gastrointestinal, Hematopoietic, Immune, and Musculoskeletal System tables at the back of the book for related tests by body system. Route of Recommended Collection Administration Time Oral Oral Intramuscular 12 hr after dose Varies according to dosing protocol Varies according to dosing protocol Immunosuppressant Cyclosporine Methotrexate Important note: this information must be clearly and accurately communicated to avoid misunderstanding of the dose time in relation to the collection time. Miscommunication between the individual administering the medication and the individual collecting the specimen is the most frequent cause of subtherapeutic levels, toxic levels, and misleading information used in calculation of future doses. Many factors must be considered in effective dosing and monitoring of therapeutic drugs, including patient age, weight, interacting medications, electrolyte balance, protein levels, water balance, and conditions that affect absorption and excretion, as well as foods, herbals, vitamins, and minerals that can either potentiate or inhibit the intended target concentration. Cyclosporine: Greater than 400 ng/mL Signs and symptoms of cyclosporine toxicity include increased severity of expected side effects, which include nausea, stomatitis, vomiting, anorexia, hypertension, infection, fluid retention, hypercalcemic metabolic acidosis, tremor, seizures, headache, and flushing. Possible interventions include close monitoring of blood levels to make dosing adjustments, inducing emesis (if orally ingested), performing gastric lavage (if orally ingested), withholding the drug, and initiating alternative therapy for a short time until the patient is stabilized. The effect of methotrexate on normal cells can be reversed by administration of 5formyltetrahydrofolate (citrovorum or leucovorin).
Generic exforge 80mg with mastercard. Live Experiment to cure Diabetes high Blood Pressure & Heart Disease.