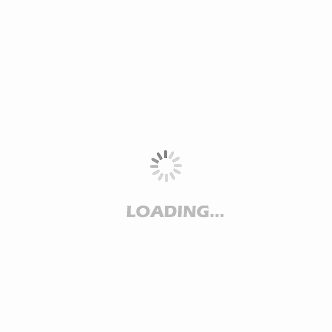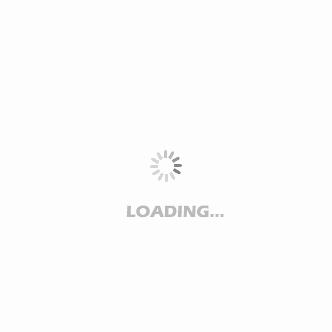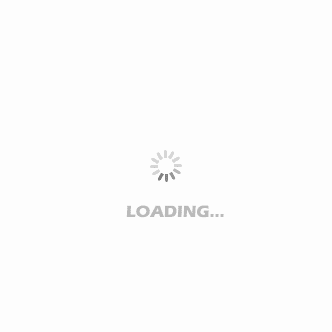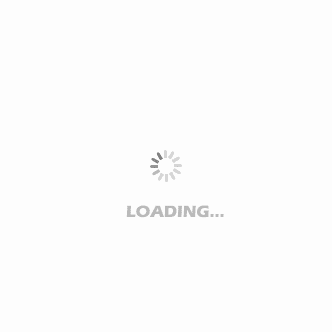
Sotalol
"Discount 40mg sotalol with amex, blood pressure 40 year old woman".
By: G. Hamlar, M.B. B.CH., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Co-Director, University of Miami Leonard M. Miller School of Medicine
Screening for colorectal cancer; a guidance statement from the American College of Physicians lipo 6 arrhythmia order sotalol 40mg on-line. Use and accuracy of diagnostic imaging by hospital type in pediatric appendicitis arteria glutea superior purchase sotalol with mastercard. Interrater reliability of clinical findings in children with possible appendicitis. About the American College of Surgeons the American College of Surgeons is a scientific and educational organization of surgeons that was founded in 1913 to raise the standards of surgical practice and to improve the quality of care for surgical patients. Its achievements have significantly influenced the course of scientific surgery in America and have established it as an important advocate for all surgical patients. The College has more than 79,000 members and is the largest organization of surgeons in the world. Anti-caries (anti-cavities) benefit begins with eruption of the first primary tooth. Use of recommended amounts of fluoride toothpaste minimize risks of fluorosis, a whitish discoloration of enamel. High quality evidence shows sealants are safe and effective in arresting caries progression in initial stage (incipient) non-cavitated, occlusal caries. Sealants offer a tooth-preserving treatment when compared to restorations, which may require removal of some healthy tooth structure, thereby weakening the tooth and increasing the risk that the tooth will eventually require more extensive treatment. Applying sealants as soon as initial stage caries is detected can improve outcomes by minimizing the later need for more extensive restorative care. Some children do not respond to communicative behavior guidance techniques and require treatment of dental disease. Advanced behavior guidance techniques of sedation, protective stabilization, and general anesthesia offer risks and benefits often beyond the health knowledge of parents and other caretakers. Informed consent best practice requires a thorough, understandable explanation of these techniques and alternatives including deferral of treatment with its inherent risks. Therefore, management is generally conservative and includes reversible strategies such as patient education, medications, physical therapy and/or the use of occlusal appliances that do not alter the shape or position of the teeth or the alignment of the jaws. Dental restorations (fillings) fail due to excessive wear, fracture of material or tooth, loss of retention, or recurrent decay. The larger the size of the restoration and/or the greater the number of surfaces filled increases the likelihood of failure. Restorative materials have different survival rates and fail for different reasons, but age should not be used as a failure criteria. Patients with any specific questions about the items on this list or their individual situation should consult their dentist. The Steering Committee reviewed critical issues in dentistry to identify potential recommendation topics and developed, through an evidence-based process, a list of recommendation statements with supporting scientific evidence. Via an intense consensus process, the Steering Committee prepared a list of recommendation statements which were sent to the Council on Access, Prevention and Interprofessional Relations for review. Fluoride toothpaste efficacy and safety in children younger than 6 years: a systematic review. Pit and fissure sealants for preventing dental decay in the permanent teeth of children and adolescents. Evidence-based clinical recommendations for the use of pit-and-fissure sealants: a report of the American Dental Association Council on Scientific Affairs. Update on nonsurgical, ultraconservative approaches to treat effectively non-cavitated caries lesions in permanent teeth. Sealing versus partial caries removal in primary molars: a randomized clinical trial. Systematic review of noninvasive treatments to arrest dentin non-cavitated caries lesions. Pit and fissure sealants: evidence-based guidance on the use of sealants for the prevention and management of pit and fissure caries. Guidelines for monitoring and management of pediatric patients during and after sedation for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures: an update.
A qualitative analysis of the adoption and use of social communication technologies by older adults hypertension numbers proven 40mg sotalol. Risk factors for onset of osteoarthritis of the knee in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis blood pressure medication that does not cause joint pain order sotalol visa. Living arrangements of older adults in the developing world: An analysis of demographic and health survey household surveys. Life satisfaction and associations with social network and support variables in three samples of elderly people. Loneliness as a specific risk factor for depressive symptoms: Cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses. The relationship of psychosocial factors to total mortality among older Japanese-American men: the Honolulu Heart Program. Network size, social support and happiness in later life: A comparative study of Beijing and Hong Kong. Vision impairment and hearing loss among community-dwelling older Americans: Implications for health and functioning. Psychosocial risk factors and mortality: A prospective study with special focus on social support, social participation, and locus of control in Norway. Happy people live longer: Subjective well-being contributes to health and longevity. Social ties and change in social ties in relation to subsequent total and cause-specific mortality and coronary heart disease incidence in men. Designing for older adults: Principles and creative human factors approaches (2nd ed. Structural and cognitive social capital and depression among older adults in two Nordic regions. Influence of social network on occurrence of dementia: A community-based longitudinal study. Duration and severity of depression predict mortality in older adults in the community. Effect of social networks on 10 year survival in very old Australians: the Australian longitudinal study of aging. Social support network structure in older people: Underlying dimensions and association with psychological and physical health. The loss of independence in activities of daily living: the role of low normal cognitive function in elderly nuns. Executive cognitive abilities and functional status among community-dwelling older persons in the San Luis Valley Health and Aging Study. Social support and oxytocin interact to suppress cortisol and subjective responses to psychosocial stress. Social isolation dysregulates endocrine and behavioral stress while increasing malignant burden of spontaneous mammary tumors. Social and environmental factors and life expectancy, infant mortality, and maternal mortality rates: Results of a cross-national comparison. Loneliness and social isolation as risk factors for mortality: A meta-analytic review. The dynamic interplay of social network characteristics, subjective well-being, and health: the costs and benefits of socioemotional selectivity. Does social network site use buffer against well-being loss when older adults face reduced functional ability Developing online community accessibility guidelines for persons with disabilities and older adults. Living arrangements of older adults in the Netherlands and Italy: Coresidence values and behavior and their consequences for loneliness. The differential impact of subjective and objective aspects of social engagement on cardiovascular risk factors.
Many adults prehypertension levels purchase sotalol master card, including most with type 2 diabetes hypertension 34 weeks pregnant order sotalol 40mg mastercard, would be unable or unwilling to participate in such intense exercise and should engage in moderate exercise for the recommended duration. Although heavier resistance training with free weights and weight machines may improve glycemic control and strength (164), resistance training of any intensity is recommended to improve strength, balance, and the ability to engage in activities of daily living throughout the life span. Providers and staff should help patients set stepwise goals toward meeting the recommended exercise targets. As persons intensify their exercise program, medical monitoring may be indicated to ensure safety and evaluate the effects on glucose management. Avoiding extended sedentary periods may help prevent type 2 diabetes for those at risk and may also aid in glycemic control for those with diabetes. A wide range of activities, including yoga, tai chi, and other types, can have significant impacts on A1C, flexibility, muscle strength, and balance (147, 167,168). Flexibility and balance exercises may be particularly important in older adults with diabetes to maintain range of motion, strength, and balance (156). If not contraindicated, patients with type 2 diabetes should be encouraged to do at least two weekly sessions of resistance exercise (exercise with free weights or weight machines), with each session consisting of at least one set (group of consecutive repetitive exercise motions) of five or more different resistance exercises involving the large muscle groups (169). For type 1 diabetes, although exercise in general is associated with improvement in disease status, care needs to be taken in titrating exercise with respect to glycemic management. Each individual with type 1 diabetes has a variable glycemic response to exercise. This variability should be taken into consideration when recommending the type and duration of exercise for a given individual (171). Women with preexisting diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes, and those at risk for or presenting with gestational diabetes mellitus should be advised to engage in regular moderate physical activity prior to and during their pregnancies as tolerated (156). However, providers should perform a careful history, assess cardiovascular risk factors, and be aware of the atypical presentation of coronary artery disease in patients with diabetes. Certainly, highrisk patients should be encouraged to start with short periods of low-intensity exercise and slowly increase the intensity and duration as tolerated. Providers should assess patients for conditions that might contraindicate certain types of exercise or predispose to injury, such as uncontrolled hypertension, untreated proliferative retinopathy, autonomic neuropathy, peripheral neuropathy, and a history of foot ulcers or Charcot foot. Those with complications may require a more thorough evaluation prior to beginning an exercise program (171). Hypoglycemia an ophthalmologist prior to engaging in an intense exercise regimen may be appropriate. Individuals on these therapies may need to ingest some added carbohydrate if pre-exercise glucose levels are,90 mg/dL (5. In some patients, hypoglycemia after exercise may occur and last for several hours due to increased insulin sensitivity. Hypoglycemia is less common in patients with diabetes who are not treated with insulin or insulin secretagogues, and no routine preventive measures for hypoglycemia are usually advised in these cases. Intense activities may actually raise blood glucose levels instead of lowering them, especially if pre-exercise glucose levels are elevated (152). Therefore, a thorough assessment should be done to ensure that neuropathy does not alter kinesthetic or proprioceptive sensation during physical activity, particularly in those with more severe neuropathy. Studies have shown that moderate-intensity walking may not lead to an increased risk of foot ulcers or reulceration in those with peripheral neuropathy who use proper footwear (174). In addition, 150 min/week of moderate exercise was reported to improve outcomes in patients with prediabetic neuropathy (175). All individuals with peripheral neuropathy should wear proper footwear and examine their feet daily to detect lesions early. Exercise in the Presence of Microvascular Complications See Section 11 "Microvascular Complications and Foot Care" doi. Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy is also an independent risk factor for cardiovascular death and silent myocardial ischemia (177).
Buy sotalol line. Have Your Blood Pressure Medications Been Recalled.
The studies do not report characteristics of the providers or the environments and information that would allow assessment of whether the patients changed before and after telehealth or were different at the intervention and comparison hospital was not provided hypertension in african americans cheap sotalol 40 mg free shipping. Given that research on emergency care often faces time constraints and challenging environments arrhythmia breathing best purchase sotalol, less data may be collected, producing less information about the context, and restricting synthesis to the major outcomes and limiting subgroup analysis. The studies we identified reflected this and included a range of specialties such as trauma, pediatrics, neurology, psychiatry, cardiology, burns, orthopedics and plastic surgery. In the case of emergency care, consultations are often executed under time pressure or chaotic conditions. The majority of these studies (13) were conducted in the United States47,49,51,53,83,89,90,93,95,97,111,117,133 while two (in three articles) were conducted in Hong Kong239,245,247 and one each in Japan,241 Italy,191 South Korea,235 Brazil,253 and Turkey. All of the studies used either video so the specialist could see the patients or transmitted images such as scans or x-rays. Emergency Care Telehealth Specialist Consultations: Effectiveness in Improving Clinical and Economic Outcomes the 13 studies reporting clinical outcomes all reported improvements. Most of these reported lower mortality that was not statistically significantly different. Four reported some savings with telehealth, though not always significantly different, while one study reported higher costs. One studies reported a dollar estimate for potential savings per case when transfers were avoided, but did not test this difference. Having both inpatient and total charges suggests that costs are not just being shifted from one site of care to another, though details about what specific costs were included was not provided. The most frequently included were rate of transfer and time to treatment or decision. The impact of telehealth consultations appears greater on these intermediate outcomes, and the effect is generally positive. For example, pediatric video consultations compared with phone only or no consultation increased quality of care in one study49 and reduced medication error in pediatric emergency care in another;51 burn consultations reduced emergency air transports from 100 to 44. The study using video for neurology consultations reported time from referral to decision was longer with both telephone and video consultation when compared with no consultation, but it is unclear if this is a problem or a reflection of more complete assessments. The non-United States studies appear to have similar goals though increasing access to care in rural areas was not explicitly stated as one of the goals of these studies. The combination of the similarity in objectives and technology, the wide range of types of specialties and patients, and the lack of detailed information on the environment or specifics of telehealth implementation make identifying subgroups of patients or programs with different outcomes problematic. In these studies, telehealth was used to allow an emergency medicine physician or specialist to contribute to patient assessments and decisions about prehospital treatment and transport. More than half of these studies (11 of 21) involved transmitting information, frequently including electrocardiograms, about patients experiencing heart attack symptoms. This is important because outcomes are better if patients are treated quickly after symptom onset and diagnosis. One study of prehospital cardiac care in Brazil reported the mean cost of admissions was higher for patients treated with telehealth. In the studies of prehospital cardiac assessment, nine113,143,162,171-173,179,189,218 included a measure of time to treatment. Other outcomes included no difference in guideline adherence141 and a statistically significant increase in admissions to tertiary hospitals in a study conducted in Brazil. Additionally, different uses of telehealth in this category are evaluated using very different outcomes. This makes it difficult to identify any subgroups or characteristics that could be used to differentiate successful telehealth interventions within the categories provided. Additionally, the categories are fundamentally different, making comparisons across categories inappropriate. We identified 106 articles that evaluated telehealth consultations used to inform diagnosis, treatment, or management of patients receiving care in the outpatient setting. These studies span several specialties and use several different technologies to facilitate consultations. To capture and organize this diverse group of studies, we presented the results in three ways. First, we provided an overview of the results summarized by clinical topic in Table 11.