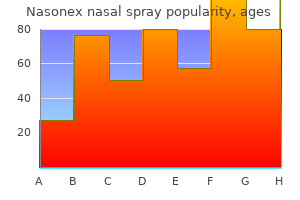
Nasonex nasal spray
"Order cheap nasonex nasal spray on line, allergy medicine that works".
By: X. Snorre, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, University of Nevada, Reno School of Medicine
The principles of prevention and treatment of these conditions are: (a) For acute mountain sickness and cerebral edema: (i) Gradual ascent to high altitude to promote acclimatisation allergy forecast flint mi buy nasonex nasal spray 18 gm cheap. Descent may be simulated by stay in a portable hyperbaric oxygen chamber (Chapter 77) allergy symptoms cough and sore throat cheap nasonex nasal spray 18 gm fast delivery. It is given in the dose of 125-250 mg 12 hourly the day before, during and for 5 days after the ascent. Acetazolamide probably helps by causing mild metabolic acidosis, which increases the respiratory drive, prevents hypoxemia and produces a pharmacological response resembling an acclimatisation response. Acetazolamide ameliorates symptoms but does not reduce the risk of cerebral edema, pulmonary edema or retinal hemorrhages. Dexamethasone, in the dose of 4 mg every 8-12 hours, begun on the day of the ascent, continued for 3 days at high altitude, and then tapered quickly may be, useful in reducing the incidence and early symptoms of acute mountain sickness. Nifedipine is the preferred drug for prevention and treatment of pulmonary manifestations of high altitude illness. It probably acts by lowering pulmonary arterial pressure, which is critical in the development of pulmonary edema. The other drugs recommended are beta adrenergic agonists which clear the fluid from the alveolar space and may lower pulmonary arterial pressure. Prophylactic nifedipine should be considered before a future ascent in a person with a history of high altitude pulmonary edema. Synthesis of thiazides stems from the original observation by Southworth (1937) that sulfanilamide, an antibacterial drug, possesses a mild diuretic activity this was later. Interestingly, chlorothiazide, synthesised as one of the carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, revealed marked diuretic activity in doses that did not significantly inhibit the carbonic anhydrase. Diazoxide, a thiazide derivative with potent hyperglycemic action, has been used in the treatment of hypoglycemia. However, during long-term therapy of hypertension, thiazides do not significantly increase the incidence of diabetes mellitus. Thiazides also decrease the reabsorption of uric acid from proximal tubule, thus raising plasma uric acid level. In addition, they compete with uric acid for urate transporter causing uric acid retention. Unlike loop diuretics (see later), thiazides reduces urinary calcium loss by acting on distal convoluted tubules and promote calcium retention; they are useful in treating idiopathic hypercalciuria. Serum cholesterol and triglycerides may increase slightly; however, this has hardly any significance as the elevation is not persistent beyond 6-12 months of treatment. Absorption, fate and excretion: Thiazides are well absorbed from the intestine and the effect starts within one hour. The slowly excreted compounds like polythiazide and bendro -flumethiazide have prolonged action. The long acting thiazides are long acting because of greater plasma protein binding and greater lipid solubility Bendroflumethiazide, polythiazide and indapamide are primarily. Plasma half life of thiazides is sufficient to permit their use once or twice daily. Adverse reactions: Apart from electrolyte disturbances such as hypokalemic and hypochloremic alkalosis, these drugs have few serious toxic effects. Hypokalemia increases the risk of fatal toxicity of certain arrhythmias (Chapter 28) and drugs like digoxin (Chapter 31). Because of structural similarity to sulfonamide, allergic reactions such as dermatitis and thrombocytopenia may occur. In the presence of renal and hepatic insufficiency these drugs may precipitate renal, failure or hepatic coma. There is no special advantage in using any particular preparation; hydrochlorthiazide is usually preffered. Excessive potassium loss can be prevented by combining thiazide drugs with spironolactone or triameterene (see later). As the maximum diuretic effect of all thiazides is similar, a patient resistant to the maximum dose of one thiazide is unlikely to respond to another. Thiazide-like diuretics: these drugs, structurally similar to thiazides, have similar mechanism but longer duration of action.
Applied under polyethylene occlusive dressing allergy forecast el paso tx order nasonex nasal spray online, it causes maceration of skin and acts as a keratolytic allergy testing list purchase nasonex nasal spray with visa, supplementing the action of salicylic acid. An escharotic, in addition, precipitates proteins that exude to form a scab-gets fibrosed to form a tough scar. They are used to remove moles, warts (including genital warts) condylomata, papillomas and on keratotic lesions. It causes softening and solubilization of keratin, facilitating its removal from hyperkeratinized lesions like ichthyosis, lichen planus. A causal role of the yeast Pityrosporum ovale has been shown, but various trigger factors like change in quantity and composition of sebum, increase in alkalinity of skin (due to increased sweating), external local factors, emotional stress, genetic predisposition appear to be needed to transform the yeast from a commensal to a noninvasive pathogenic organism. Dryness, folliculitis and dandruff are benefited, but > 50% patients relapse on discontinuation. Systemic absorption and toxicity can occur if it is applied to inflamed or damaged skin. Good to excellent results have been obtained with these preparations without skin irritation, contact sensitivity, phototoxicity or systemic adverse effects. They have minimal antiyeast action: may benefit seborrhoea by keratolytic and antiseptic properties. Salicylic acid It is keratolytic, has mild effect in seborrhoea, probably by removing the scales and by improving penetration of other drugs. Psoralens are furocoumarins which on photoactivation stimulate melanocytes and induce their proliferation. Methoxsalen Corticosteroids Massaged in the scalp as a lotion, topical steroids are highly effective in relieving symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis including dandruff. However, relapse rates are high on discontinuation and prolonged use can produce adverse effects like atrophy, poor healing, purpura, etc. They sensitize the skin to sunlight which then induces erythema, inflammation and pigmentation. Methoxsalen is absorbed better, undergoes less first pass metabolism and is more effective than trioxsalen. Pigmentation usually begins to appear after a few weeks; months are needed for satisfactory results. This therapy should be undertaken only under direct supervision of physician because longer exposure causes burning and blistering. Eyes, lips and other normally pigmented areas should be protected during exposure to sunlight. Topically applied emollients, keratolytics, antifungals afford variable symptomatic relief, but topical corticosteroids are the primary drugs used. They are very effective in mild-tomoderate disease, and initially even in severe cases. Most patients respond within 3 weeks, and the response may be hastened by applying the steroid under occlusion. Therapy is started with a potent steroid which is substituted after improvement by either weekly application or by a milder preparation. However, they carry their own local and systemic adverse effects, and lesions may progressively become refractory. Systemic therapy with corticosteroids and/or immunosuppressants is reserved for severe and refractory cases. Other topically used drugs are: Calcipotriol It is a synthetic nonhypercalcaemic vit D analogue effective topically in plaque type psoriasis. It binds to the intracellular vit D receptor in epidermal keratinocytes and suppresses their proliferation while enhancing differentiation. On absorption through the skin, it is inactivated rapidly by metabolism so that little systemic effect on calcium metabolism is exerted. Efficacy of calcipotriol in psoriasis is rated comparable to a moderate potency topical steroid.
Therapeutic uses: Thiamine deficiency can be prevented by improvement in the dietary intake and by preventing overmilling of cereals allergy quercetin generic 18 gm nasonex nasal spray free shipping, particularly rice allergy testing babies generic 18gm nasonex nasal spray with visa. Acute wet beriberi responds dramatically to oral or parenteral administration of thiamine. A maintenance dose of 5 to 10 mg, is given subsequently orally Most of the edema fluid is eliminated within 48 to 72 hours. In dry beriberi, it is advisable to use thiamine with other members of vitamin B complex. Physiological functions: the physiologically active form of riboflavine is formed by phosphorylation. Riboflavine deficiency in man is characterised by angular stomatitis, glossitis, a peculiar magenta pigmentation of the tongue and cheilosis (loss of epithelium at the mucocutaneous junction of lips resulting in reddened, shiny and denuded lips). Certain ocular manifestations such as conjunctivitis, blepharospasm, photophobia, burning, lacrimation and vascularisation of the cornea leading to diminution in visual acuity are observed in some cases. Absorption, fate and excretion: Riboflavine is synthesised in the large intestine, but whether it is available for absorption is uncertain. Phosphorylation of riboflavine to the active form occurs in the intestinal wall, liver and erythrocytes. Only 9% of the orally administered dose appears in urine; the metabolic fate of the remainder is not known. Excess of riboflavine is readily excreted in the urine to which it imparts yellow colour and fluorescence. Therapeutic uses: In the treatment of ariboflavinosis, 5 to 10 mg of the vitamin is given daily in combination with other members of vitamin B group. Nicotinic acid is present in large quantities in rice polishings, liver, milk, eggs and lean meat, and to a smaller extent in potatoes and in vegetables. Non-endemic pellagra occurs in chronic alcoholism, malabsorption syndrome, carcinoid syndrome, cirrhosis, poorly controlled diabetes mellitus, and in cachexia secondary to malignancy. Associated folic acid deficiency is responsible for the megaloblastic anemia while deficiency of riboflavine, which is necessary for the conversion of tryptophan into nicotinic acid, and of pyridoxine; may account for the cheilosis, stomatitis, dermatitis, vaginitis and proctitis. Inactivation occurs mainly by N-methylation and to some extent by conjugation; the products are eliminated in the urine. The vitamin may appear in urine in the active form if large doses are given orally. Therapeutic uses: Pellagra: Nicotinic acid or its amide is used in the treatment of pellagra in the daily dose of 50 to 500 mg. The neuropathy and the lesions of face and lips, however, may need adjuvant treatment with riboflavine. All the three forms are converted in the body to pyridoxal phosphate which is the physiologically active form. Physiological functions: Pyridoxal phosphate acts as a coenzyme for amino acid decarboxylases and transaminases. A syndrome in infants secondary to ingestion of proprietary milk preparation deficient in pyridoxine has been described. The characteristic features include irritability abdominal, distension, twitching, failure to gain weight, hypochromic microcytic anemia and convulsions. Pyridoxine deficiency in adults may lead to lesions of the skin and mouth resembling those seen in ariboflavinosis and pellagra, to peripheral neuritis and to mental changes. Adverse reactions: Pyridoxine, administered in physiological doses, does not produce any adverse effects. Administration of large doses has been reported to cause peripheral sensory neuropathy and ataxia. There is no evidence to suggest that supplementation of vitamin B6 with or without folate and B12 reduces the risk of stroke or cancer. Yeast, wheat, peanuts, cereals, milk, vegetables and liver contain large amounts of pantothenic acid. Physiological actions: Coenzyme A is involved in several fundamental biological reactions such as fatty acid metabolism, synthesis of cholesterol and steroid hormones and acetylation reactions. Pantothenic acid deficiency in human beings under normal circumstances is not known.
Purchase genuine nasonex nasal spray on-line. Urticaria Treatment How To Cure - Full Urticaria Cure Review - Chronic Urticaria Treatment Natural.