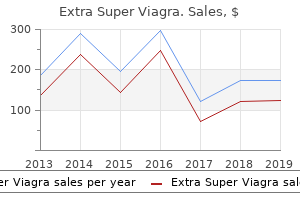
Extra Super Viagra
"Purchase extra super viagra from india, erectile dysfunction caused by hydrocodone".
By: U. Steve, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Medical Instructor, TCU and UNTHSC School of Medicine
The doses of the patient in tumour erectile dysfunction doctor chicago effective extra super viagra 200 mg, target volume and sensitive tissues are calculated individually erectile dysfunction yahoo answers extra super viagra 200 mg. Absorbed doses to the head and body are monitored individually using in vivo dosimeters. The minimum, maximum, average and reference doses are reported for the tumour, target and normal brain. In this paper the methods of dose calculation and reporting of the glioma patients at FiR 1 are described. Estimation of the average 10B concentration is based on kinetic models [3] and on taking blood samples before and after irradiation. The purity of this beam makes it possible to achieve higher tumour dose than elsewhere, since the acceptable normal brain tissue dose limits the irradiation time. In any radiotherapy the physical dose must have a metrologically traceable link to the national and international dosimetry standards. In addition, the uncertainty of the dose delivered to the patient has to be low enough for estimating the effects of the treatment beforehand and analysing afterwards. In this paper we describe the method of dose determination and reporting of the glioma patients at FiR 1. To estimate the biological 276 response of the tissues to the combination of all these doses the concept of weighted dose is used [1,2,22]. To illustrate the difference of the absorbed and weighted doses, the letter W in parenthesis is added to the symbol Gy writing one space between the symbol and the additional specification for the weighted dose [1 Gy (W)]. The FiR 1 beam has a better quality (lower fast neutron and incident gamma dose in tissue) and a more penetrating neutron spectrum. The FiR 1 beam model includes the nuclear reactor to generate the fission neutrons, the moderator to moderate the fission neutrons to epithermal energies (with a small fast neutron and gamma contamination), the collimator to collimate the epithermal neutrons to compose a clinical beam, and some surrounding materials, like part of the concrete shielding. The beam models for these configurations have the same model of the core, but differ in the moderator thickness or in the beam delimiter or conical collimator arrangement [2834]. The FiR(K63) beam configuration with the moderator thickness of 63 cm and conical collimator were used in the radiobiological study in 1998 [2,35] and in the clinical trials of the glioma patients so far. A forward-biased quadrature set (D166) was chosen for the accurate angular calculation at the beam-line from the core to the collimator output. The first part of the model, that is seldom changed at FiR 1, includes the core with fuel elements, graphite reflector and water. The second part includes the moderator, collimator, phantom and part of the concrete shield. The source model includes the source plane description and the subsequent 50 mm thick layer of collimator that produces the treatment beam. The directional intensities of the source model are described with 10 bins in each energy group. For the head model skin, cranium, normal brain (cerebrum and cerebellum), the target and tumour volumes are segmented. The skin volume comprises all the soft tissue that is not 278 included in the normal brain, target or tumour volumes. The cranium volume, that has the lowest neutron attenuation, includes bone, cartilage and sinuses. The 10B concentration ratio of the normal brain-to-whole blood is 1:1, the tumour(target)-to-whole blood 3. The elemental fraction (percentage by mass) of nitrogen and hydrogen defined by Brooks et al. The boron dose does not include the boron capture gammas, they are calculated separately to the gamma dose. These values would give the total weighted reference dose rate of 15 Gy (W)/h (=1. Dose calibration to measurements For the dose calibration of the treatment planning system the source model was first verified [27]. Thereafter the calculated doses were calibrated to the reference monitor units according to the ratio of the independently measured foil and calculated 197Au(n,) reactions rates at the depth of 2.
The vitamin B12 in tempeh is associated with the presence of opportunistic pathogens like Klebsiella pneumoniae erectile dysfunction drugs patents 200mg extra super viagra. In this study other uses for erectile dysfunction drugs order generic extra super viagra online, Propionibacterium freudenreichii, a food-grade, vitamin B12 producing bacterium, was used in co-culture with Rhizopus oryzae to produce B12- enriched lupin tempeh. Other parameters, such as texture and volatile organic compounds, were not affected by the bacterial co-inoculation. Therefore, these results are promising for in situ vitamin B12 fortification of lupin tempeh making it a sustainable protein source for a healthy human diet. The interphase between science and gastronomy, a case example of gastronomic research based on fermentationtempeto and its derivates (Open Access). We hypothesize that an enzymatic post-fermentation process together with Maillard reaction lead to the malty, toasty, and umami tempeto family of products. Address: El Celler de Can Roca (restaurant), Can Sunyer 48, 17007, Girona (Catalonia), Spain. Management of technology transfer in the traditional tempeh and tofu industries (Open Access). The benefit of this research is to create a new business of tempeh for all people and to give policy factor in the improvement of a manual cotton cloth bag filter in the tofu industry. The method used is an operation management of production planning of preparation of Rhizopus sp inoculum, preparation of soy bean as a raw material, process and equipment of a wet peeling method, a fluidized bed reactor, a sterilization tank and an artificial incubator for tempeh incubation and to run a vertical technology transfer of a manual rotary filter based on technometric approaches. Education skill training program of 60 people in rural areas was done for tempeh production. Identification of soybean genotypes adaptive to tropical area and suitable for industry (Open Access). This study aims to identify 150 soybean genotypes for their suitability for raw materials of tempeh and adaptability to be developed in tropical area of Indonesia. The field research was conducted in Malang from February to May 2016, using a randomized block design with two replicates. In the early maturity group, there were 23 genotypes with seed management in Karawang (Open Access). It is a high-protein food whose cost per unit is cheaper than any other animal protein sources. To produce tempeh needs a lot of water used for boiling, soaking, leaching, and peeling the soybeans. The problem is that tempeh industries have not undertaken wastewater management properly, which potentially causes the quality of tempeh industrial wastewater to exceed the prescribed quality standard, having negative impact on both the environment and the people living around those industries. It is mixed-methods research employing qualitative and quantitative methods, especially through literature review, observation, interviews, and laboratory analysis. Research findings show that the alternative waste management suitable for tempeh industries is to utilize wastewater by considering environmental, social, and economic aspects. Such utilization is carried out by making liquid organic fertilizer and biogas from a mixture of household organic waste. Based on Susenas data [2], the level of tempeh consumption in Indonesia reached 6. Address: Indonesian Legumes and Tuber Crops Research Institute, Jl Raya Kendalpayak Km 8, Malang 65101. Tempeh fermentation is a food process that originated in Indonesia 300 years ago and involves taking soy beans and naturally transforming them into an even more nutritious, delicious and versatile food. Synbiotic fermented milk with tempeh extract and iron fortification: effect on antibacterial activity and total Enterobacteriaceae. Global warming impact and energy analysis of tempeh made from local and imported soybean. Eng]* · Summary: "Indonesia is a country with the largest number of tempeh producers in the world. However, the practice of tempeh production by most entrepreneurs has not paid enough attention to environmental aspects.
Generic 200mg extra super viagra. What Causes Erectile Dysfunction ► Best Erectile Dysfunction Natural Treatment.
Gryzan S impotence from vasectomy order extra super viagra 200mg fast delivery, Paradis I L erectile dysfunction nyc buy cheap extra super viagra 200 mg, Zeevi A, Duquesnoy R J, Dummer J S, Griffith B P, Hardesty R L, Trento A, Nalesnik M A, Dauber J H. Unexpectedly high incidence of Pneumocystis carinii infection after heart-lung transplantation: implications for lung defense and allograft survival. Guarro J, Antolin Ayala M I, Gene J, Gutierrez-Calzada J, NievesDiez C, Ortoneda M. Sporotrichosis: recurrent cutaneous, articular, and central nervous system infection in a renal transplant recipient. Phaeohyphomycosis caused by alternaria infectoria in a renal transplant recipient. Hamacher J, Spiliopoulos A, Kurt A M, Nicod L P, and the Geneva Lung Transplantation Group. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in renal-transplant recipients treated with cyclosporine and steroids. Herbrecht R, Denning D W, Patterson T F, Bennett J E, Greene R E, Oestmann J W, Kern W V, Marr K A, Ribaud P, Lortholary O, Sylvester R, Rubin R H, Wingard J R, Stark P, Durand C, Caillott D, Thiel E, Chandrasekar P H, Hodges M R, Schlamm H T, Troke P F, de Pauw B, and the Invasive Fungal Infections Group of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer and the Global Aspergillus Study Group. Transmission of invasive aspergillosis from a subcliically infected donor to three different organ transplant recipients. Kramer M R, Denning D W, Marshall S E, Ross D J, Berry G, Lewiston N J, Stevens D A, Theodore J. Ulcerative tracheobronchitis after lung transplantation: a new form of invasive aspergillosis. Kusne S, Dummer S, Singh N, Iwatsuki S, Makowka L, Esquivel C, Tzakis A G, Starzi T E, Ho M. Kusne S, Fung J, Alessiani M, Martin M, Torre-Cisneros J, Irish W, Ondick L, Jain A, Abu-Elmagd K, Takaya S. Combined medical surgical therapy for pulmonary mucormycosis in a diabetic renal allograft recipient. Infectious complications following pancreatic transplantation: incidence, microbiological and clinical characteristics, and outcome. Marin P, Garcia-Martos P, Carcia-Doncel A,Garcia-Tapia A, Aznar E, Perez R J, Valverde S. Successfully treated invasive pulmonary aspergillosis associated with smoking marijuana in a renal transplant recipient. Miller L W, Naftel D C, Bourge R C, Kirklin J K, Brozena S C, Jarcho J, Hobbs R E, Mills R M, and the Cardiac Transplant Research Database Group. Monforte V, Roman A, Gavalda J, Bravo C, Tenorio L, Ferrer A, Maestre J, Morell F. Nebulized amphotericin B prophylaxis for Aspergillus infection in lung transplantation: study of risk factors. Mora-Duarte J, Betts R, Rotstein C, Colombo A L, Thompson-Moya L, Smietana J, Lupinacci R, Sable C, Kartsonis N, Perfect J. Mora N P, Cofer J B, Solomon H, Goldstein R M, Gonwa T A, Husberg B S, Klintmalm G B. Nampoory M R, Khan Z U, Johny K V, Constandi J N, Gupta I, Al-Muzairi I, Samhan M, Mozavi M, Chugh T D. Evidence of zoonotic transmission of Cryptococcus neoformans from a pet cockatoo to an immunocompromised patient. Nunley D R, Ohori N P, Grgurich W F, Tacono A T, Williams P A, Keenan R J, Dauber J H. Palmer S M, Drew R H, Whitehouse J D, Tapson V F, Davis R D, McConnell R R, Kanj S S, Perfect J R. Pappas P G, Perfect J R, Cloud G A, Larsen R A, Pankey G A, Lancaster D J, Henderson H, Kauffman C A, Haas D W, Saccente M, Hamill R J, Holloway M S, Warren R M, Dismukes W E. Cryptococcosis in human immunodeficiency virus-negative patients in the era of effective azole therapy. Patel R, Portela D, Badley A D, Harmsen W S, Larson-Keller J, Ilstrup D M, Keating M R, Wiesner R H, Krom R A, Paya C V. Risk factors of invasive Candida or non-Candida fungal infections after liver transplantation. Multiple Cladosporium brain abscesses in a renal transplant patient: aggressive management improves outcome. Pseudomembranous necrotizing bronchial aspergillosis in a renal transplant recipient.
Patients were not eligible if they had been receiving systemic antifungal agents or if they were colonized by Aspergillus erectile dysfunction hypertension drugs discount extra super viagra 200mg overnight delivery. The study used a composite endpoint to define satisfactory or unsatisfactory response (Table 292) xatral erectile dysfunction discount extra super viagra on line. Both regimens were similar in terms of rate of satisfactory responses, 68 and 69% of fluconazole and amphotericin B recipients, respectively. The failures in the fluconazole group were typically related to persistent fever, whereas in the amphotericin B group, most failures were due to toxicity. Only 4% of the patients in each group developed new fungal infections during therapy, and there were no differences in mortality. The authors concluded that fluconazole may be appropriate empirical therapy in persistently febrile neutropenic patients at low risk for invasive aspergillosis. More than half the patients were receiving cyclosporin A or tacrolimus following an allogeneic stem cell transplant. A successful treatment outcome included all of the following criteria: survival for 7 days after the last dose of study drug; lack of suspected or documented fungal infection during the study and within 7 days of the last dose of study drug; no discontinuation of study drug because of adverse events; and lack of fever on the day of discontinuation of therapy. This study lacked the power to detect a difference in frequency of breakthrough fungal infections. Response was defined as a composite of defervescence for 3 consecutive days and continued deferverescence until the end of the study (recovery of neutropenia), no addition of another antifungal agent, and no breakthrough fungal infection (Prentice et al, 1997) (Table 292). This noninferiority study defined success as a composite of five criteria: survival for 7 days after initiation of study drug; resolution of fever during the period of neutropenia; successful treatment of any base-line fungal infection; absence of breakthrough fungal infections during administration of the study drug or within 7 days after the completion of treatment; and absence of premature discontinuation of the study drug because of toxicity or lack of efficacy (Table 292). Similar outcomes were observed in both treatment groups based on the primary endpoint of success (50% vs. This difference was independent of risk category, age, and antifungal prophylaxis. The trial was double-blind and adequately powered, and both the overall outcome and each of the components of the composite endpoint showed equivalence. The efficacy analysis showed no significant differences between the three study arms. Adult neutropenic patients with fever that persisted 3 days while receiving broadspectrum antibiotics were eligible. Other exclusion criteria included strong suspicion of fungal infections during previous episodes of neutropenia and current Fungal infections in neutropenic patients 443 treatment with drugs known to interact with itraconazole. The primary efficacy analysis utilized criteria similar to those of earlier studies (Prentice et al, 1997; Walsh et al, 1999; Winston et al, 2000). However, patients were considered successful if they defervesced at any time within 28 days of study drug discontinuation. A significantly favorable response (defervescence and recovery from neutropenia) was documented in 47% of the patients in the itraconazole group, and 38% of the patients in the amphotericin B group. Breakthrough fungal infections and mortality rates in the two groups were similar. Furthermore, 20 and 10 patients receiving itraconazole and amphotericin B, respectively, failed because fever persisted after the resolution of neutropenia. An additional 19 and 1 patient (s) receiving itraconazole and amphotericin B, respectively, failed because of fever leading to a change in antifungal regimen (Boogaerts et al, 2001). Patients were stratified according to risk, with allogeneic stem-cell transplant and chemotherapy for relapsed leukemia considered high risk factors (Walsh et al, 2002) (Table 292). The endpoint was success or failure defined according to a composite endpoint that had been validated in previous trials (Prentice et al, 1997; Walsh et al, 1999b; Winston et al, 2000; Boogaerts et al, 2001). However, the definition of resolution of fever was more stringent than in previous trials. The relatively low success rate can be explained by the inclusion of defervescence (defined as temperature 38°C for 48 hours prior to recovery from neutropenia) as part of the composite endpoint. Although voriconazole narrowly failed to fulfill the criteria for noninferiority, there was an impressive difference in breakthrough fungal infections in favor of voriconazole (1. The overall response in the high-risk population (n 286) also showed comparability in all criteria. There was no difference in the proportion of patients discontinuing the study drug because of adverse effects.