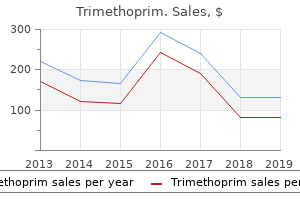
Trimethoprim
"Purchase trimethoprim without a prescription, antibiotic resistance oxford".
By: K. Diego, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Deputy Director, Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine
Landers antibiotics for acne for 6 months generic 480mg trimethoprim, ``Manipulation of Potential Punishment Parameters in the Treatment of SelfInjury infection behind eye purchase trimethoprim paypal. Reichenbach, ``Multiple Factors in the Long-Term Effectiveness of Contingent Electric Shock Treatment for Self-Injurious Behavior: A Case Example. Tough, ``Treatment of a Self-Injuring Mongoloid With ShockInduced Suppression and Avoidance. Iwata, ``A Comparison of Shock Intensity in the Treatment of Longstanding and Severe Self-Injurious Behavior. Luiselli, ``Positive Behavioral Support of Adults With Developmental Disabilities: Assessment of Long-Term Adjustment and Habilitation Following Restrictive Treatment Histories. Evans, Nonaversive Intervention for Behavior Problems: A Manual for Home and Community. Vorndran, ``On the Status of Knowledge for Using Punishment: Implications for Treating Behavior Disorders. Conti, ``Understanding Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Shocks and Storms: Medical and Psychosocial Considerations for Research and Clinical Care. Originally published in the Journal of the Association for the Severely Handicapped. Dibiasio, ``Treating Individuals With Intellectual Disabilities and Challenging Behaviors With Adapted Dialectical Behavior Therapy. Millington, ``Positive Behaviour Support for a Child With Severe Learning Disability. American Psychiatric Association, Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Borderline Personality Disorder, ed. Grey, ``An Evaluation of an Intervention Sequence Outline in Positive Behaviour Support for People With Autism and Severe EscapeMotivated Challenging Behaviour. Lovett, ``View on the Efficacy and Ethics of Punishment: Results From a National Survey. Flament, ``Adapted Dialectical Behavior Therapy for Adolescents With Self-Injurious Thoughts and Behaviors. Van Camp, ``The Effects of Competing Reinforcement Schedules on the Acquisition of Functional Communication. Wallace, ``Side Effects of Extinction: Prevalence of Bursting and Aggression During the Treatment of Self-Injurious Behavior. LoVullo, ``A Review of Behavioral Treatments for Self-Injurious Behaviors of Persons With Autism Spectrum Disorders. McCracken, ``An Evaluation of Positive Behavioural Support for People With Very Severe Challenging Behaviours in CommunityBased Settings. Levinson, ``Effects of Within-Activity Choices on the Challenging Behavior of Children With Severe Developmental Disabilities. Comments on Topics that are Beyond the Limited Scope of the Supplemental Finding V. Executive Order 12866: Regulatory Planning and Review and Executive Order 13563: Improving Regulation and Regulatory Review B. Executive Order 13175: Consultation and Coordination with Indian Tribal Governments G. Executive Order 13045: Protection of Children from Environmental Health Risks and Safety Risks H. Executive Order 13211: Actions Concerning Regulations that Significantly Affect Energy Supply, Distribution, or Use I. Executive Order 12898: Federal Actions to Address Environmental Justice in Minority Populations and Low-Income Populations K. Certain other material, such as copyrighted material, will be publicly available only in hard copy. The regulated categories and entities potentially affected by this final supplemental finding are shown below in Table 1.
Febrile patients in withdrawal impose an especially difficult scenario on the emergency physician because of the vast array of potential causes of the fever and their typically unreliable and uncooperative manner (Table 4) antibiotics and yogurt trimethoprim 480mg cheap. Benzodiazepines antibiotic resistance stewardship order 960mg trimethoprim amex, such as diazepam or lorazepam, should be used liberally for sedation and delirium. The diagnosis can be challenging, because many of the presenting signs and symptoms are nonspecific. For instance, a postoperative fever might be treated presumptively as infection or systemic inflammatory response syndrome when it actually is a subtle indicator of adrenal insufficiency. Primary adrenal insufficiency can result from glandular destruction or metabolic failure. Causes of glandular destruction include, but are not limited to idiopathic atrophy, hemorrhage, tuberculosis, fungal infection, and other diseases infiltrating the adrenal glands. Metabolic failure leads to insufficient hormone production, and usually results from either congenital adrenal hyperplasia, enzyme inhibitors, or autoimmune adrenal insufficiency caused by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Secondary adrenal insufficiency, more common than the primary form, can result from hypopituitarism associated with hypothalamicpituitary disease, or from suppression of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis by exogenous steroids or endogenous steroids, such as a tumor. Acute adrenal insufficiency also can be caused by adrenal hemorrhage, classically from septicemia-induced Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome (fulminant meningococcemia) and anticoagulation complications. Steroid withdrawal is the most common cause of acute adrenocortical insufficiency, and almost always leads to a glucocorticoid deficiency. Hydrocortisone, 100 mg intravenously every 6 hours, and fludrocortisone acetate (mineralocorticoid), 0. The key management principle is treatment of the underlying problem that precipitates the crisis. It occurs in susceptible individuals who have abnormal regulation of calcium in skeletal muscle. This defect allows large quantities of calcium to be released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of skeletal muscle, causing a hypermetabolic state. The hypermetabolic response leads to increased production of carbon dioxide, metabolic and respiratory acidosis, accelerated oxygen consumption, heat production, activation of the sympathetic nervous system, hyperkalemia, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and multiorgan dysfunction and failure. Unrecognized, it can lead to myoglobinuria, subsequent multiorgan failure, and death. Early diagnosis, supportive care with ventilatory and circulatory support, and treatment with dantrolene can improve the outcome. Management typically includes evaluation of the urine (analysis and culture) and appropriate antibiotics when necessary. When presenting signs and symptoms are particularly severe, a diagnosis of pyelonephritis or intra-abdominal infectious complication should be considered. Management of postprocedural pneumonia includes evaluation for leukocytosis, radiographic imaging, sputum culture, and, if appropriate, broad-spectrum antibiotics. The clinician should be mindful that, following laparotomy, radiography might reveal basilar atelectasis or pleural effusion below the diaphragm; in such cases, antibiotics are not required. Catheters become contaminated by 4 mechanisms (in decreasing order of frequency): (1) migration of organisms from the skin at the insertion site into the cutaneous catheter tract and along the surface of the catheter, with colonization of the catheter tip; (2) direct contamination of the catheter or its hub by contact with hands or contaminated fluids or devices; (3) hematogenous spread from anther focus of infection; and (4) contamination of infusate. The clinician should have a low threshold for removing presumptively infected indwelling catheters early in the course of treatment, especially when disseminated infection is suspected. Therefore, empiric therapy should include vancomycin (or other antibiotics that treat methicillin-resistant staphylococci). The emergency medicine provider must recognize the prosthetic as a potential source of infection. A thorough history and physical examination, with particular attention to past procedures, should always 1054 Narayan & Medinilla be performed, as infections associated with prosthetics can be indolent and may not emerge for weeks to years after the procedure. Sternal wound infections most often occur in the acute phase of fever (within a week after the procedure). Infection commonly occurs after the administration of an antibiotic that alters the normally protective bacterial flora of the colon. Transmission occurs via the fecal-oral route, primarily via contaminated environmental surfaces and the hands of health care workers.
In target-setting considerations antibiotic wash cheap trimethoprim 960 mg otc, Work Group members discussed the potential for movement in each indicator bacteria 2014 discount trimethoprim 480 mg with visa, what is currently being done at community and state levels, what political will and public interest exists to create change, and whether there is funding for the work needed to create change. These considerations informed how ambitious the groups were in the targets they set. Finally, the Task Force met to set targets on the Health Outcomes they had selected and review and approved the decisions made by the Work Groups. A this indicator was added at the fourth meeting due to community interest in discussing public transportation B this indicator was added at the fourth meeting due to community interest in discussing community water safety. A this indicator was added at the fourth meeting to replace "unintentional poisoning deaths. A this indicator was added at the fifth meeting as an additional measure related to mental health. We scrupulously investigate abuses, expose facts widely, and pressure those with power to respect rights and secure justice. Human Rights Watch began in 1978 with the founding of its Europe and Central Asia division (then known as Helsinki Watch). Today it also includes divisions covering Africa, the Americas, Asia, Europe and Central Asia, the Middle East and North Africa, and the United States. Human Rights Watch is an independent, nongovernmental organization, supported by contributions from private individuals and foundations worldwide. Board of Directors members are Hassan Elmasry, Co-Chair; Robert Kissane, Co-Chair; Michael G. Kass; Marina Pinto Kaufman; Wendy Keys; Bruce Klatsky; Joanne Leedom-Ackerman; Josh Mailman; Susan Manilow; Samuel K. Murumba; Peter Osnos; Kathleen Peratis; Sigrid Rausing; Victoria Riskin; Kevin Ryan; Orville Schell; Jean-Louis Servan-Schreiber; Gary Sick; Malcolm B. David was a superb advocate, combining a piercing intellect, an extraordinary eloquence, and a deep personal commitment to the human rights cause. Colleagues around the world recall the depth and scope of his knowledge, his willingness to go the extra mile, and his determination to challenge those in power-always with unfailing courtesy. Perhaps most of all, we miss his genuine warmth, evident in his deep love for his family, and his steadfast support of colleagues and friends. It summarizes key human rights issues in more than 90 countries and territories worldwide, drawing on events from late 2017 through November 2018. Drawing on analysis of a series of human rights successes in international fora, often led by unlikely government coalitions, and of powerful activism by civic groups at national and regional levels, he shows that defense of rights worldwide is resilient and multi-faceted. Even though many once-influential governments have been missing in action on human rights or even switched sides, effective coalitions emerged to "raise the price of abuse and shift the cost-benefit calculus that convinces governments that repression pays. The rest of the volume consists of individual country entries, each of which identifies significant human rights abuses, examines the freedom of local human rights defenders to conduct their work, and surveys the response of key international actors, such as the United Nations, European Union, African Union, United States, China, and various regional and international organizations and institutions. The book reflects extensive investigative work that Human Rights Watch staff undertook in 2018, usually in close partnership with human rights activists and groups in the country in question. It also reflects the work of our advocacy team, which monitors policy developments and strives to persuade governments and international institutions to curb abuses and promote human rights. Human Rights Watch publications, issued throughout the year, contain more detailed accounts of many of the issues addressed in the brief summaries in this volume. As in past years, this report does not include a chapter on every country where Human Rights Watch works, nor does it discuss every issue of importance. The absence of a country or issue often simply reflects staffing or resource limitations and should not be taken as commentary on the significance of the problem. There are many serious human rights violations that Human Rights Watch simply lacks the capacity to address. The factors we considered in determining the focus of our work in 2018 (and hence the content of this volume) include the number of people affected and the severity of abuse, access to the country and the availability of information about it, the susceptibility of abusive forces to influence, and the importance of addressing certain thematic concerns and of reinforcing the work of local rights organizations. The World Report does not have separate chapters addressing our thematic work but instead incorporates such material directly into the country entries. The book was edited by Danielle Haas, senior editor at Human Rights Watch, with assistance from Aditi Shetty, senior coordinator, and Delphine Starr, associate.
Foreign experts may command a legitimacy denied prophets in their own country derived from their presentation of technology and experience bacteria 5 kingdoms purchase trimethoprim online now, but this expertise may be less valuable than it at first appears bacterial yeast infection symptoms trimethoprim 960 mg online. Thus Winid (1981) argued that the French consultants called in to plan development in the Awash Valley of Ethiopia lacked political, ecological, social, cultural, scientific and technical knowledge of the region, and in the field they had contact only with the local elite, lacked supervision and failed to transfer technology. There is a risk of foreign experts glibly repeating dominant preconceptions and myths about tropical ecosystems (for example, about overgrazing or desertification; see Chapter 8), which have misdirected development so often in the past (Leach and Mearns 1996). Most project feasibility studies are undertaken by teams dominated by these disciplines, or by consortia typically dominated by engineering companies. Sociology, anthropology and ecology are typically slotted in with perhaps a one- or two-person-month input on a project where the total planning input is several person-years. None of these will necessarily lead to development projects with smaller environmental and social impacts, but they do represent attempts to diversify and strengthen the range of tools available. Arguably, unless the environment is taken fully into account at the strategic level of planning, it will not be surprising if individual projects generate unforeseen and unwelcome impacts. A key issue is the involvement of stakeholder groups in assessment and decision-making, something rarely achieved. It is holistic, involving the analysis, monitoring and management of intended and unintended social consequences (both positive and negative), of planned interventions and any social change processes they bring about. Thus people forced to resettle as a result of dam construction may be affected by a complex chain of social and environmental impacts associated with loss of resources, changed disease incidence, conditions in a resettlement location and social change resulting from translocation (loss of social cohesion, respect for elders, traditions or religious belief). The ability of improved project and programme appraisal methodologies to contribute to sustainability depends crucially on institutional capacity and governance. Provisions for assessing environmental impacts had become almost universal by the mid-1990s (Barrow 1997), although in many countries capacity to implement them still remained weak. Aid agencies and environmental policy In the absence of effective governance and environmental regulation, the effectiveness with which proper account is taken of sustainability depends to a considerable extent on the capacity of the aid donor organizations that fund so much development. The performance of both multilateral and bilateral aid agencies began to receive attention in the 1970s and 1980s (Stein and Johnson 1979; Johnson and Blake 1980; V. The key to the actual level of consideration of environmental aspects of project development in any aid bureaucracy is the attitude and perception of particular individuals within the normal planning structure. In the 1970s and early 1980s this was a problem for the World Bank, despite its surprising record of employing staff popularly identified with the environmentalist cause such as Robert Goodland and the economist Herman Daly (Holden 1988). The World Bank (or more properly the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development and the Delivering mainstream sustainable development 165 International Development Association, which are separate arms of the Bretton Woods family of organizations) is the largest multilateral aid donor. The sheer size of its lending makes its environmental policy of considerable importance, and of consuming interest to environmentalists (Fox and Brown 1998b). By that time it was usually too late to redesign projects, and difficult to build in environmental safeguards. As an ecologist working for the Bank, Watson found her ideas rejected as unrealistic and impractical every time they contained implications for practice. With the World Environment Centre, the Bank organized a series of seminars for major consulting firms in the early 1980s to raise awareness of the need for proper environmental appraisal of projects (Goodland 1990). In 1987 the Bank created an Environment Department with forty new staff, and new scientific and technical staff in regional offices (Holden 1987). Behind these organizational changes lay some softening of the rigid doctrines of Bank economics, with the appointment to the Latin American office of the zero-growth economist Herman Daly. New systems of national accounting were developed to reflect the depletion of non-renewable resources and unsustainable exploitation of renewable resources, and to revise the discount rate, which biased appraisals in favour of projects with short-term pay-offs against longer-term cost/benefit considerations (Holden 1988). The Bank also produced a series of policy papers in the 1980s addressing issues central to sustainability, including an overall environmental policy statement and papers on involuntary resettlement, wildlands conservation, pollution control and pesticides, and tribal people. These codified existing best practice, and had already existed in draft for several years. By the early 1990s, environmental critique of the Bank had developed from specific issues (often concerning rainforests, roads or dams) into a broader attempt to make the Bank accountable to civil societies in donor and borrowing countries (Fox and Brown 1998b). However, practice was publicly shown to be behind policy, particularly in the case of the Sardar Sarovar Dam on the Narmada River in India (discussed above).
Discount generic trimethoprim uk. ABST test Microbiology/Antibiotic Sensitivity Test/Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing/STAR LABORATORY.