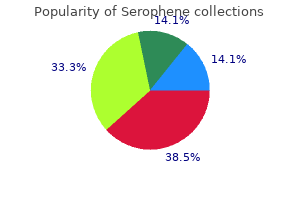
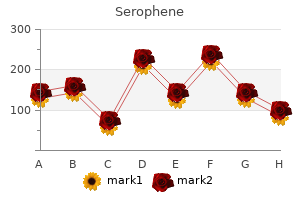
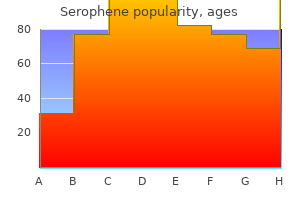
Serophene
"Order serophene 25 mg mastercard, women's health of bucks county".
By: M. Norris, M.B.A., M.B.B.S., M.H.S.
Professor, University of South Florida College of Medicine
This last term is a misnomer since they contain neither sebum nor sebaceous glands women's health issues thrombosis haemostasis safe serophene 25mg. Epidermoid cysts can occur anywhere women's health gov faq birth control methods buy generic serophene, but are most common on the face and upper trunk. They usually arise from and are lined by the stratified squamous epithelium of the follicular infundibulum. Clinically, epidermoid cysts are dermal nodules with a central punctum, representing the follicle associated with the cyst. Treatment Treatment consists of increasing the water content of the skin in the immediate external environment. Frequent soaping of the skin impairs its water-holding capacity and serves as an irritating alkali, and all soaps should therefore be avoided. Frequent use of emollients (eg, Cetaphil, Eucerin, Lubriderm) should be a major part of therapy. Treatment Epidermoid cysts can rupture, causing a foreign-body inflammatory reaction, or become infected. Keratosis Pilaris Follicular papules containing a white inspissated scale characterize keratosis pilaris. They are prominent on the extensor surfaces of the upper arms and thighs and on the buttocks and cheeks. Such lesions are seen frequently in children with dry skin and have also been associated with atopic dermatitis and ichthyosis vulgaris. Treatment Treatment is with keratolytics such as urea cream or lactic acid, followed by skin hydration. Psoriasis Pityriasis rosea Tinea corporis Lichen planus Pityriasis lichenoides (acute or chronic) Dermatomyositis Lupus erythematosus Pityriasis rubra pilaris Secondary syphilis 3. Granuloma Annulare Circles or semicircles of nontender intradermal nodules found over the lower legs and ankles, the dorsum of the hands and wrists, and the trunk, in that order of frequency, suggest granuloma annulare. Histologically, the disease appears as a central area of tissue death (necrobiosis) surrounded by macrophages and lymphocytes. In 2080% of cases the generalized eruption is preceded for up to 30 days by a solitary, larger, scaling plaque with central clearing and a scaly border (the herald patch). In whites, the lesions are primarily on the trunk; in blacks, lesions are primarily on the extremities and may be accentuated in the axillary and inguinal areas. This disease is common in school-aged children and adolescents and is presumed to be viral in origin. The role of human herpesvirus 7 in the pathogenesis of pityriasis rosea is debated. Pyogenic Granuloma these lesions appear over 12 weeks following skin trauma as a dark red papule with an ulcerated and crusted surface that may bleed easily even with minor trauma. Histologically, this represents excessive new vessel formation with or without inflammation (granulation tissue). Treatment Pulsed dye laser for very small lesions or curettage followed by electrocautery are the treatments of choice. Keloids Keloids are scars of delayed onset that continue for up to several years to progress beyond the initial wound margins. Pityriasis rosea that lasts more than 12 weeks should be referred to a dermatologist for evaluation. Treatment Treatment includes intralesional injection with triamcinolone acetonide, 20 mg/mL, or excision and injection with corticosteroids. Psoriasis Pathogenesis & Clinical Findings Psoriasis is characterized by erythematous papules covered by thick white scales. Guttate (droplike) psoriasis is a common form in children that often follows an episode of streptococcal pharyngitis by 23 weeks. The sudden onset of small papules (38 mm), seen predominantly over the trunk and quickly covered with thick white scales, is characteristic of guttate psoriasis. Chronic psoriasis is marked by thick, large scaly plaques (510 cm) over the elbows, knees, scalp, and other sites of trauma. Pinpoint pits in the nail plate are seen, as well as yellow discoloration of the nail plate resulting from ony- 1. Psoriasis occurs frequently on the scalp, elbows, knees, periumbilical area, ears, sacral area, and genitalia.
Controversy exists as to how young the child should be when surgery is performed so that the child can obtain an optimal binocular result menstruation tent generic serophene 25 mg overnight delivery. Management of accommodative esotropia includes glasses with or without bifocals women's health center dover purchase generic serophene from india, amblyopia treatment, and in some cases surgery. Underlying neurologic disease should be referred to the appropriate specialists for further management. Exotropia Pathogenesis & Clinical Findings Exotropia is a type of strabismus in which the eyes are divergent. The patient appears wall-eyed with the visual axes of the eyes deviated in a divergent position (Figure 1527). With glasses, well-aligned at distance (B), and at near with bifocal correction (C). Cerebral visual impairment, also known as cortical blindness, is manifested as decreased visual attentiveness of varying degree. Asphyxia, trauma, intracranial hemorrhage, and periventricular leukomalacia are some of the causes of cortical visual impairment. Besides an ophthalmologic workup, electroretinogram and visual evoked response testing may be required in children with decreased vision of unexplained etiology. Devices used include magnifiers for both distance and near vision, closed-circuit television, and large-print reading materials. There are psychological consequences for the child blind from birth, as well as for the family. Although acquired blindness may give an individual time to grow as a sighted person and make preparations for life as a nonsighted person if loss of vision is slow and predicted, psychological consequences for the child and family must be addressed. The child who is blind from birth or from very early childhood has had little or no opportunity to form visual impressions of the physical world. Blind infants reach developmental landmarks on a different schedule from that of sighted children. For example, the premature child who is blind from retinopathy of prematurity may also have cerebral palsy. Leading causes of blindness in the pediatric age group differ among regions of the world and between industrialized nations and developing countries. The most common causes of blindness in the pediatric age group are thought to be cerebral visual impairment, retinopathy of prematurity, and optic nerve hypoplasia. Albinism, optic atrophy, cataract, retinitis pigmentosa, microphthalmia or anophthalmia, aniridia, and glaucoma are other diseases causing blindness. Congenital (infantile) exotropia is extremely rare in an otherwise healthy infant. Early-onset exotropia may occur in infants and children with severe neurologic problems. Treatment Treatment of exotropia is with surgery, orthoptic exercises, patching, and occasionally glasses. Occult causes of poor vision and blindness in children are those for which there are no obvious ocular defects: they Clinical Findings Children with low vision will not fixate on visual targets and often have roving eye movements. Neuroimaging or specific ocular tests such as an electroretinogram may be necessary. Treatment Blind children and their families should receive the benefit of knowledgeable therapists and support groups. Treatment A multidisciplinary approach as suggested by the American Academy of Pediatrics, the American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus, and the American Academy of Ophthalmology is recommended in evaluating children with learning disabilities. Although many therapies directed at "training the eyes" exist, scientific support for such approaches is weak. Children often have vague complaints of ocular fatigue, headaches, and difficulty reading. Learning disabilities and dyslexia result in poor reading comprehension and writing. Evaluation of the child with learning disabilities and dyslexia should include ophthalmologic examination to identify any ocular disorders that could cause or contribute to poor school performance. Most children with learning Web Resources American Academy of Ophthalmology. A dental home is established by referring a child for an oral health examination to a dentist who provides care for infants and young children (ie, pediatric dentist) 6 months after the first tooth erupts or by 12 months of age. The intent is to implement preventive dental health habits with the goal of keeping the child free from dental and oral disease.
There is no evidence that antibiotics given after closure of the incision have any beneficial prophylactic effect on clean or clean-contaminated surgical wounds leading women's health issues purchase 25mg serophene. Intraoperative risk factors amenable to intervention include airflow in the operating room womens health daily buy 25mg serophene with amex, sterilization of surgical instruments, attire of the surgical team, and surgical technique. Operating room air may contain vectors for microorganisms such as dust, lint, skin cells, and respiratory droplets shed from operating room personnel. The microbial density in operating room air is directly proportional to the number of people in the room. Although few studies have evaluated the efficacy of surgical attire in preventing surgical site infection, the use of scrub suits, masks, caps, gloves, and gowns minimizes exposure of the patient to the skin, mucous membranes, or hair of the surgical team and may prevent shedding of contaminated particles into the air. Optimal surgical technique such as maintaining effective hemostasis, gently handling tissues, removing devitalized tissue, eradicating dead space, using drains and sutures appropriately, and minimizing the duration of the procedure are all believed to be important in reducing the risk of surgical site infection. Adequate sterilization of surgical instruments by an approved method such as pressurized steam, dry heat, or ethylene oxide is essential. It has an attributable mortality of up to 30%, prolongs the mean duration of hospitalization by up to 9 days, and results in estimated excess costs of $1. Patients at highest risk for nosocomial pneumonia include postoperative patients (particularly after thoracoabdominal procedures) and patients with endotracheal tubes, depressed levels of consciousness, chronic underlying lung disease, and age older than 70 years. The most frequently isolated pathogens in nosocomial pneumonia are gram negative and include P. Microorganisms most often invade the lower respiratory tract through aspiration of oropharyngeal secretions or inhalation of aerosols containing bacteria. Small-volume aspiration is very common even among healthy individuals, but aspiration is even more likely in patients with depressed mental status, patients with endotracheal or upper gastrointestinal intubation or instrumentation, and postoperative patients. The predominance of gram-negative pathogens in nosocomial pneumonia probably reflects colonization of the upper respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts with gram-negative bacilli, which commonly occurs following admission to the hospital. Hospitalized patients often have an increased gastric pH because of either medication or underlying illness (achlorhydria, ileus, tube feedings, antacids, histamine antagonists). In the absence of normal acidic gastric conditions, bacteria are able to multiply freely within the stomach. Aspiration of gastric fluid in this setting may deliver high concentrations of microorganisms to the lower respiratory tract. Other potential sources of pathogens in nosocomial pneumonia include inhalation of contaminated aerosols generated by respiratory therapy or anesthesia equipment. Rarely, pathogens may reach the lung by hematogenous spread from a distant focus of infection. Strategies designed to prevent aspiration of oropharyngeal or gastric secretions are central in preventing nosocomial pneumonia. Enteral tubes, endotracheal tubes, and tracheostomy tubes should be removed promptly when no longer clinically indicated. It has been suggested that pooled secretions above the cuff of endotracheal tubes may leak into the lower respiratory tract and serve as an important source of lower respiratory tract contamination. The use of specially designed endotracheal tubes with a separate suction lumen allowing for removal of these secretions has shown benefit in one study, but this finding requires further investigation. Preventive strategies designed to decrease bacterial concentrations of gastric and oropharyngeal secretions have been attempted. In several studies, avoidance of medications that raise gastric pH seemed to prevent bacterial proliferation in gastric fluid and protect against nosocomial pneumonia in mechanically ventilated patients. Using agents that do not raise gastric pH should therefore be considered in patients requiring stress ulcer prophylaxis. Several investigators have demonstrated benefit from the use of combinations of prophylactic antimicrobial agents designed to decontaminate and prevent bacterial colonization of the gastrointestinal tract, thereby preventing pneumonia in mechanically ventilated patients. However, lack of consistent results in other studies and concern about antibiotic resistance preclude the routine use of this approach at present. Preventing contamination of instruments that come into contact with the respiratory tract is an important preventive strategy.
Syndromes
- Retinal detachment
- Chromosome
- Tumors
- Body stiffness
- Is the weakness worse in the morning or at night?
- What drugs, vitamins, herbs, and other supplements you are taking, even ones you bought without a prescription
Water is an important therapeutic agent menopause systems order serophene on line, and optimally hydrated skin is soft and smooth women's health lebanon pa buy cheap serophene 100 mg. Because water evaporates readily from the cutaneous surface, skin hydration (stratum corneum of the epidermis) is dependent on the water concentration in the air, and sweating contributes little. However, if sweat is prevented from evaporating (eg, in the axilla, groin), local humidity and hydration of the skin are increased. As humidity falls below 1520%, the stratum corneum shrinks and cracks; the epidermal barrier is lost and allows irritants to enter the skin and induce an inflammatory response. Therefore, dry and scaly skin is treated by soaking the skin in water for 5 minutes and then adding a barrier to evaporation (Table 142). Oils and ointments prevent evaporation for 812 hours, so they must Wet Dressings By placing the skin in an environment where the humidity is 100% and allowing the moisture to evaporate to 60%, pruritus is relieved. Evaporation of water stimulates colddependent nerve fibers in the skin, and this may prevent the transmission of the itching sensation via pain fibers to the central nervous system. It also is vasoconstrictive, thereby helping to reduce the erythema and also decreasing the inflammatory cellular response. The simplest form of wet dressing consists of one set of wet underwear (eg, long johns) worn under dry pajamas. The underwear should be soaked in warm (not hot) water and wrung out until no more drops come out. Topical Glucocorticoids Twice-daily application of topical corticosteroids is the mainstay of treatment for all forms of dermatitis (Table 143). After wet dressings are discontinued, topical steroids should be applied only to areas of active disease. Clinical Appearance Primary lesions (first to appear) Macule Papule Plaque Vesicle Bulla Pustule Nodule Wheal Secondary changes Scales Lichenification Erosion and oozing Crusts Fissures Scars Atrophy Color the lesion should be described as red, yellow, brown, tan, or blue. Configuration of lesions Annular (circular) Linear (straight lines) Grouped Discrete Distribution Note whether the eruption is generalized, acral (hands, feet, buttocks, face), or localized to a specific skin region. Annular nodules represent granuloma annulare; annular scaly papules are more apt to be caused by dermatophyte infections. Linear papules represent lichen striatus; linear vesicles, incontinentia pigmenti; linear papules with burrows, scabies. Induration of skin with exaggerated skin lines and a shiny surface resulting from chronic rubbing of the skin. A moist, circumscribed, slightly depressed area representing a blister base with the roof of the blister removed. A flat, raised, or depressed area of fibrotic replacement of dermis or subcutaneous tissue. A solid, elevated area < 1 cm in diameter whose top may be pointed, rounded, or flat. A circumscribed, elevated lesion < 1 cm in diameter and containing clear serous fluid. A circumscribed, elevated lesion > 1 cm in diameter and containing clear serous fluid. If it moves with the skin on palpation, it is intradermal; if the skin moves over the nodule, it is subcutaneous. A circumscribed, flat-topped, firm elevation of skin resulting from tense edema of the papillary dermis. Description and Examples potency steroids (see Table 143) are applied to the face or intertriginous areas. These 1- to 2-mm white papules occur predominantly on the face in 40% of newborns. Their intraoral counterparts are called Epstein pearls and occur in up to 6085% of neonates. Base Foam Liquids Powder Grease and emulsifier; oil in water Excess grease and emulsifier; water in oil Grease Combined With Uses Cosmetically eloquent; increasing number of products available.
Purchase serophene 50mg free shipping. Do You Know Vastu Tips can bring Good Health? Vastu Tips for Better Health.