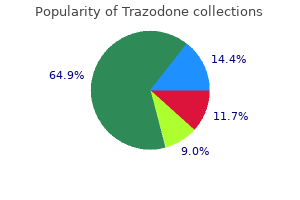
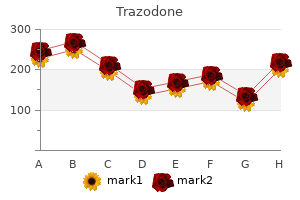
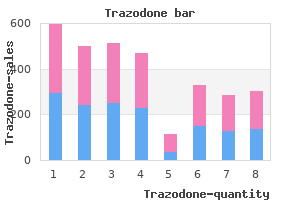
Trazodone
"Generic 100 mg trazodone fast delivery, medicine 44291".
By: Y. Milok, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Associate Professor, University of Alaska at Fairbanks
After a 30 min break treatment zinc deficiency order genuine trazodone, the participants were presented with 153 signal pair combinations (all unique combinations of 18 signals taken two at a time) in random order and asked to indicate which signal from each pair was more urgent medicine kim leoni order generic trazodone on-line. The workload task was assessed to be sufficiently demanding on the attention of the participants for the purposes of this experiment. The results showed that perceived urgency increased strongly with increasing pulse level. Signals with shorter interpulse intervals were perceived as significantly more urgent, with signals with no interpulse interval (zero ms) considered the most urgent. For each signal type, urgency was rated highest when the 81 this publication is available free of charge from: doi. Finally, sequential signals were rated as significantly less urgent than simultaneous and frequency modulated signals. Response time was significantly shorter for the highest pulse level than for the lowest, with a difference of 60 ms. Although this is a very short delay, it can make a difference in a job requiring immediate response, such as piloting a fighter jet. The mean response time for sequential signals was significantly greater (up to 40 ms) than for simultaneous and frequency modulated signals. The correlation between results for perceived urgency and response time indicates that response time is fastest when perceived urgency is greatest. Through variation of parameters, proper design of pulsebased signals can assist listeners in deciding how urgently they need to respond. Certain signal characteristics can be modified to match the urgency perceived by the listener with the urgency required by the situation. For operators engaged in a task in a noisy environment, response time was shorter by 60 ms for a higher pulse sound level compared to that for a lower pulse level. Discipline: Acoustics/Audiology Rating: 7B Auditory signals are often used to monitor high risk situations, such as patients at a hospital, or gauges in an airplane cockpit. However, it has been shown that the urgency of these signals do not always match the urgency of the situation at hand. This results in people either ignoring the signals, or turning them off due to their annoying and distracting nature. This study aimed to test how the fundamental frequency, the inter-pulse interval, and the pulse level of an auditory signal affected response time and perceived urgency. This could be used to better match signals to the warning they are meant to convey. The three main variables in this study were pulse fundamental frequency, inter-pulse interval and pulse level. In order to determine perceived urgency, participants were randomly exposed to each signal twice, and asked to rate the urgency as a number greater than 0. Next, response time was tested, and each participant was again exposed to the 27 signals twice. The results showed that there was a lower perception of urgency for signals with a fundamental frequency of 200 Hz, compared with those with fundamentals of 500 Hz and 800 Hz. Additionally, shorter inter-pulse intervals resulted in higher perceived urgency with the 0 ms interval being rated as the most urgent. The pulse level also affected perceived urgency with increased sound pressure above ambient resulting in increased perceived urgency. Pulses with the combination of higher fundamental frequency, shorter inter-pulse interval, and higher sound pressure levels above ambient were judged as more urgent than other signals. However, the response time task showed that only higher pulse level and fundamental frequency corresponded with decreased response time.
Syndromes
- Swollen spleen
- Hematoma (blood accumulating under the skin)
- Nervousness
- What other symptoms do you have? For example, do you have diarrhea, wheezing, hives, or difficulty breathing?
- Nausea and vomiting
- Excessive bleeding following circumcision
- Platelet count
- Rapid heart beat
Recognition symptoms 3 weeks pregnant buy trazodone pills in toronto, as on multiple-choice test treatment for 6mm kidney stone order trazodone 100 mg online, only involves determining which item from a list seems most correct (Haist, Shimamura, & Squire, 1992). Students who do better on a multiple-choice exam will also, by and large, do better on an essay exam (Bridgeman & Morgan, 1996). Measures of relearning (or savings) assess how much more quickly information is processed or learned when it is studied again after it has already been learned but then forgotten. If you have taken some French courses in the past, for instance, you might have forgotten most of the vocabulary you learned. Relearning can be a more sensitive measure of memory than either recall or recognition because it allows assessing memory in terms of "how much" or "how fast" rather than simply "correct" versus "incorrect" responses. Relearning also allows us to measure memory for procedures like driving a car or playing a piano piece, as well as memory for facts and figures. Implicit Memory While explicit memory consists of the things that we can consciously report that we know, implicit memory refers to knowledge that we cannot consciously access. However, implicit memory is nevertheless exceedingly important to us because it has a direct effect on our behavior. Implicit memory refers to the influence of experience on behavior, even if the individual is not aware of those influences. There are three general types of implicit memory: procedural memory, classical conditioning effects, and priming. Procedural memory refers to our often unexplainable knowledge of how to do things. When we walk from one place to another, speak to another person in English, dial a cell phone, or play a video game, we are using procedural memory. Procedural memory allows us to perform complex tasks, even though we may not be able to explain to others how we do them. There is no way to tell someone how to ride a bicycle; a person has to learn by doing it. The ability to crawl, walk, and talk are procedures, and these skills are easily and efficiently developed while we are children despite the fact that as adults we have no conscious memory of having learned them. A second type of implicit memory is classical conditioning effects, in which we learn, often without effort or awareness, to associate neutral stimuli (such as a sound or a light) with another stimulus (such as food), which creates a naturally occurring response, such as enjoyment or salivation. The memory for the association is demonstrated when the conditioned stimulus (the sound) begins to create the same response as the unconditioned stimulus (the food) did before the learning. The final type of implicit memory is known as priming, or changes in behavior as a result of experiences that have happened frequently or recently. One measure of the influence of priming on implicit memory is the word fragment test, in which a person is asked to fill in missing letters to make words. You can try this yourself: First, try to complete the following word fragments, but work on each one for only three or four seconds. I think you might find that it is easier to complete fragments 1 and 3 as "library" and "book," respectively, after you read the sentence than it was before you read it. Once a concept is primed it influences our behaviors, for instance, on word fragment tests. Seeing an advertisement for cigarettes may make us start smoking, seeing the flag of our home country may arouse our patriotism, and seeing a student from a rival school may arouse our competitive spirit. Research Focus: Priming Outside Awareness Influences Behavior One of the most important characteristics of implicit memories is that they are frequently formed and used automatically, without much effort or awareness on our part. In one demonstration of the automaticity and influence of priming effects, John Bargh and his colleagues (Bargh, Chen, & Burrows, 1996) conducted a study in which they showed college students lists of five scrambled words, each of which they were to make into a sentence. Furthermore, for half of the research participants, the words were related to stereotypes of the elderly. The purpose of this task was to prime stereotypes of elderly people in memory for some of the participants but not for others. When the research participant had gathered all of his or her belongings, thinking that the experiment was over, the experimenter thanked him or her for participating and gave directions to the closest elevator. Then, without the participants knowing it, the experimenters recorded the amount of time that the participant spent walking from the doorway of the experimental room toward the elevator.
Palytoxin poisoning should be suspected in patients who present with rapid onset of respiratory distress and tonic muscle contractions soon after eating grazing fish species (especially sardines symptoms 9dpo bfp discount trazodone 100 mg visa, but also other fish such as herring 4 medications at target cheapest generic trazodone uk, anchovies, etc), and especially during warm summer months. Cases have been described only in Caribbean, African coastal, and Indo-Pacific waters. The complication of rhabdomyolysis, with creatine kinase levels peaking at about 24 to 36 hours after symptom onset, would also be an important later clue if the diagnosis has not yet been made. Other palytoxin intoxication syndromes differ from fish poisoning in varying degrees according to the route of exposure: dermal exposure, as with marine aquarium hobbyists, can be expected to produce local and systemic skin manifestations as described above; inhalational exposure near an algal bloom is known to produce respiratory distress and a mild dermatitis, but also fever (in a majority of cases) and conjunctivitis (in a minority). Gastrointestinal symptoms were also reported in a significant minority of inhalational cases, and low-grade fever was reported in most of the aquarium hobbyists. Definitive laboratory identification of palytoxins in seafood can be accomplished with rapid and sensitive hemolysis neutralization assays,82 but the relative rarity of these syndromes does not make the licensing or widespread commercial availability of these tests likely in the foreseeable future. A number of other investiga- tional methods of detection (including immunoassays and a fluorescence polarization) have been described in the literature. For exposures restricted to contact with intact skin/mucosa only (eg, beachgoers exposed to algal blooms), experience indicates that nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs are effective and that the condition is self-limited. Supportive care and the amelioration of symptoms are then the basis of treatment, with aggressive hydration via infusion of intravenous fluids being the primacy focus in significant intoxications where avoidance of rhabdomyolysis-induced renal failure is the goal. Palytoxin(s) have been implicated in a number of human fatalities involving ingestion of tropical fishes, with one author estimating a case fatality rate-based on an admittedly limited number of cases-of 45%. Given the apparent potency of exposures to aerosols, as well as the lethality associated with ingestions, palytoxins seem to have potential as bioterrorism agents. The large numbers sickened (more than 200 individuals) in the 2005 Genoa event (20% of whom were hospitalized) indicate these possibilities. Although the toxins may be highly lethal, extracting and weaponizing them is relatively difficult because of the relatively small amounts of toxins typically produced by the source organ472 isms. Such toxins may be more suitable for causing incapacitation or death among small groups or for assassinations. Brevetoxins inhibit sodium channel inactivation, leading to depolarization of membranes. Although naturally acquired cases typically resolve spontaneously in 1 to 3 days, patients should be carefully observed and may require aggressive airway management. Domoic acid is a neuroexcitatory amino acid that kills cells within the central nervous system, particularly in the hippocampus, which is associated with learning and memory. Patients with domoic acid intoxication develop gastrointestinal symptoms and neurological symptoms, including anterograde memory loss and myoclonus. Medical management of domoic acid intoxications includes monitoring of hemodynamic status and pharmacological treatment of seizures. Palytoxins derive from both dinoflagellate blooms or from the polyps of soft corals of the genus Palythoa. Oral intoxication can lead to malaise, vomiting and diarrhea, a bitter or metallic taste in the mouth, muscle aches and cramps, numbness or tingling in the extremities, bradycardia, and dyspnea. Inhalation exposure can lead to respiratory symptoms such as fever, sore throat, cough, dyspnea, headache, nausea/ vomiting, rhinorrhea, lacrimation, and dermatitis. An underappreciated exposure mechanism is through the home aquarium trade, whereby several incidences of inhalational or dermal intoxication have occurred through the handling or disinfection of Palythoa polyps. Treatment of palytoxin intoxication, which is nonspecific, is based on the route of exposure. The apparent extreme aerosol toxicity of palytoxins, as suggested by several incidences of beachgoers being intoxicated during near-shore blooms of O ovata, makes it critical for further investigation of the aerosol toxicology of these compounds. A procedure for isolation and purification of the poison from toxic clams and mussels. Paralytic shellfish poisoning: post-mortem analysis of tissue and body fluid samples from human victims in the Patagonia fjords. Hypertension and identification of toxin in human urine and serum following a cluster of mussel-associated paralytic shellfish poisoning outbreaks. Post-mortem analysis of samples from a human victim of a fatal poisoning caused by the xanthid crab, Zosimus aeneus. Lack of an effect of saxitoxin on the contractility of isolated guinea-pig trachea, lung parenchyma and aorta. Liquid chromatographic determination of paralytic shellfish poisons in shellfish after prechromatographic oxidation.
This point is reinforced by the fact that although a sustained hegemony has not formed in Europe for at least 1 treatment 1860 neurological buy trazodone 100 mg,500 years symptoms 7 days after ovulation buy trazodone 100mg lowest price, hegemonies have been more common in 54 System-Level Theories non-Western historical systems (Hui, 2004; Kaufman, Little, and Wohlforth, 2007). Long-cycle theory also emphasizes the rise and fall of states, and we discuss it below. For more liberal conceptions of hegemonic order, see Ikenberry (2000) and Lake (2009). One could imagine a power transition theory that gave primary emphasis to military power, but theorists associated with the power transition research program have chosen not to do so. For analyses of the dynamics of the contemporary unipolar system under American primacy, see Ikenberry, Mastanduno, and Wohlforth (2009) and other articles in the January 2009 issue of World Politics. Note that prevention as defined here differs from strategies designed to avert war or humanitarian disasters, such as "preventive diplomacy," "preventive deployment," and "preventive intervention. Any future Israeli strike against Iran to interrupt its apparent development of a nuclear program would reflect a strategy of preventive war. The Bush Administration probably referred to its actions as "preemptive" because preemptive attacks in response to imminent threats are easier to justify in international law than are preventive strikes in response to future threats, since the latter but not the former provide some time for the target to implement alternative strategies in response to the threat. On the ethical and legal dimensions of preemption and prevention, see Doyle (2008). Goldstein (1988) also proposes a long-cycle theory based on changes in the global political economy, but he gives less attention to system management within a hierarchical order. For a summary of additional system-level theories and evidence on war, see Rasler and Thompson (forthcoming). They questioned whether system structures could explain enough of the variance in war, peace, and other international behaviors and outcomes. That disillusionment has led in several directions, including a growing interest in dyadic-level theories focusing primarily on the interactions of pairs of states rather than on broader system-level structures and patterns. The interest in dyadic-level theories derived in part from the success of theories of the democratic peace in uncovering some very strong empirical regularities (the near-absence of war between democratic states) that had previously been neglected. The hope was that by focusing on dyads rather than on the system as a whole, researchers might uncover additional patterns that had previously been obscured. Quantitative researchers were also encouraged by the success of early work at the dyadic level that used regime type, territorial conflicts, and the dyadic balance of power to explain the frequency of war between pairs of states (Bremer, 1992; Bennett and Stam, 2004). Contributing further to interest in dyadic-level phenomena was some new work on international rivalries. This work emphasized the impact of the history of the interactions between pairs of states on their evolving relationships, and introduced a new dynamic element in the study of international interactions. There are many dyadic-level theories, just as there are many system-level theories, and we cannot survey them all here. Among the most important are theories of international rivalry, the "steps-to-war" model, the bargaining theory of war, and theories of economic interdependence and peace. None of these is exclusively dyadic in character, but each places primary emphasis on causal variables relating to the interactions of pairs of states. Of course, there are some obvious caveats on the "other things being equal" modifier. Assuming they had some reason to become involved in a conflict, neither state has the capability to project armed force across the Atlantic that a war would require. But since they are unlikely to have much contact with each other in the first place, they are also not too likely to have conflicting interests. Another reasonable caveat is that very weak states do not usually take on very strong states. We could make the situation even more extreme by matching states that lack an army (Iceland, Costa Rica) with states that have large armies and forecast fairly safely that states without armies are unlikely to attack states with armies.
Buy trazodone 100mg low price. USMLE Respiratory 12: Lung Infections (Pneumonia TB and more!).