Rivastigimine
"Buy 1.5 mg rivastigimine with visa, treatment lung cancer".
By: R. Tempeck, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Co-Director, Mercer University School of Medicine
The effectiveness of dialysis is often based on a positive clinical outcome rather than on objective measurements of drug concentrations in the plasma and dialysate medicine klimt generic 4.5mg rivastigimine mastercard. When applying information from the primary literature to a specific patient medicine while pregnant buy rivastigimine discount, the specifics of the dialyzer. In addition, clinical investigators often use predialysis and postdialysis serum drug concentrations for estimating drug dialyzability without considering the contributing effects of drug metabolism and excretion on drug elimination. Drug-Specific Properties the physical and chemical characteristics of drugs can be used to predict the effectiveness of dialysis on drug removal. Newer high-flux dialyzers using polysulfone membranes more effectively remove large chemical compounds (see High-Flux Elimination the extent to which renal disease affects the elimination of a drug depends on the amount of drug normally excreted unchanged in the urine and the degree of renal impairment. Consequently, the ability to eliminate certain drugs that are renally excreted also decreases. If the dose of these drugs is not modified for patients with renal dysfunction, these drugs will accumulate, leading to an increase in the pharmacologic effect and the potential for toxicity. Characteristics of a drug that determine its ability to be filtered include its affinity for protein binding and its molecular weight. Drugs with low protein binding or those that are displaced from proteins in the setting of renal disease. Molecules with a high molecular weight (>20,000 Da) are not readily filtered because of their large size. The reasons for how renal disease selectively alters the process of glomerular filtration or tubular secretion of specific drugs are not well understood. The renal elimination of drugs in patients with renal disease usually is estimated by measuring the ability of the kidney to eliminate substances such as creatinine. Renal disease can also have an important impact on the elimination of drugs that are primarily metabolized by the liver. In patients with renal disease, these metabolites may accumulate, leading to an increase in pharmacologic activity and adverse effects. Therefore, careful dosing modifications or avoidance of these drugs are warranted in patients with renal impairment. Metabolic enzymes have been found within renal tissue, and may play a role in the metabolism of some of these drugs. In addition, the water solubility of a compound can also help predict drug dialyzability because water-soluble drugs are removed more readily than lipid-soluble compounds. A drug with a large Vd that distributes widely into the peripheral tissues resides minimally in the plasma and therefore is not substantially removed by dialysis. The plasma clearance of a drug should also be compared with the dialysis clearance. High-Flux Hemodialysis High-flux hemodialysis utilizes higher blood and dialysate flow rates compared with conventional methods. Drugs such as gentamicin and foscarnet, which are removed by conventional dialysis, are also efficiently removed by high-flux hemodialysis. The accumulated fluid and uremic byproducts diffuse from the blood into the dialysate solution, which is exchanged every 4 to 8 hours (see Chapter 32, Renal Dialysis). This is particularly useful for patients with peritonitis who require high intraperitoneal concentrations of antimicrobial agents to treat this infection. Following intraperitoneal administration of drugs, such as the aminoglycosides, plasma and intraperitoneal drug concentrations will eventually reach equilibrium. Despite systemic absorption of these drugs from the peritoneal fluid, peritoneal dialysis usually is inefficient at removing drugs from the plasma. These therapies are typically reserved for patients who are unable to tolerate hemodialysis because of hemodynamic instability. Using a hollow fiber that is made of a semipermeable membrane, water and solutes are filtered by hydrostatic pressure.
Reinforcement of the importance of continued preventive therapy that has given such remarkable success is appropriate for C treatment 7th march order generic rivastigimine line. The clinician should continue to work with her to further tailor the therapy treatment zamrud purchase generic rivastigimine on-line, including control of rhinitis, to maintain optimal outcomes at the lowest dosages and the simplest possible regimen. Recent research has further emphasized the goal of simplified regimens and achieving the lowest effective doses of anti-inflammatory therapy. A multidisciplinary group of health science center students have been invited to present a program on asthma at a local innercity high school. The small group of nursing, pharmacy, and medical students are discussing the materials they want to use in the program. What would be some key points to cover, and are there validated instruments to assess asthma control that may be helpful? Complementary and alternative approaches that have been used in the treatment of asthma include black tea, coffee, ephedra, marijuana, dried ivy leaf extract, acupuncture, meditation, and yoga. Volunteer service to help educate patients with asthma is encouraged and has the potential to make a positive difference in the lives of patients and health science center students. For patients whose asthma is not well controlled, the test scores can be a helpful tool in initiating or modifying long-term treatment. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma-update on selected topics 2002. Effects of inhaled corticosteroids on pathology in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Effects of corticosteroids on noninvasive biomarkers of inflammation in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Inhaled glucocorticoids decrease nitric oxide in exhaled air of asthmatic patients. The effect of the menstrual cycle on asthma presentations in the emergency department. Efficacy of frequent nebulized ipratropium bromide added to frequent high-dose albuterol therapy in severe childhood asthma. Effect of nebulized ipratropium on the hospitalization rates of children with asthma. Fractional deposition from a jet nebulizer: how it differs from a metered dose inhaler. Holding chambers (spacers) versus nebulisers for beta-agonist treatment of acute asthma. Costs and effectiveness of spacer versus nebulizer in young children with moderate and severe acute asthma. Comparison of albuterol delivered by a metered dose inhaler with spacer versus a nebulizer in children with mild acute asthma. Efficacy of albuterol administered by nebulizer versus spacer device in children with acute asthma. High-versus low-dose frequently administered nebulized albuterol in children with severe acute asthma. A single dose of intramuscularly administered dexamethasone acetate is as effective as oral prednisone to treat asthma exacerbations in young children. Comparative efficacy of oral dexamethasone versus oral prednisolone in acute pediatric asthma. Single-dose oral dexamethasone in the emergency management of children with exacerbations of mild to moderate asthma. Efficacy of parenteral albuterol in the treatment of asthma: comparison of its metabolic side effects with subcutaneous epinephrine. Tachyphylaxis to systemic but not to airway responses during prolonged therapy with high dose inhaled salbutamol in asthmatics. Aminophylline increases the toxicity but not the efficacy of an inhaled beta-adrenergic agonist in the treatment of acute exacerbation of asthma. Inhaled albuterol and oral prednisone therapy in hospitalized adult asthmatics: does aminophylline add any benefit? Aminophylline therapy does not improve outcome and increases adverse effects in children hospitalized with acute asthmatic exacerbations. Hospital treatment of asthma: lack of benefit from theophylline given in addition to nebulized albuterol and intravenously administered corticosteroid.
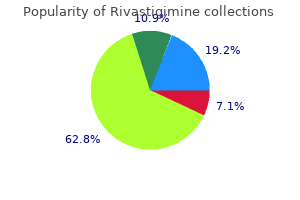
They are classified as either a hypertensive emergency (with acute or progressive targetorgan damage) or urgency (without acute or progressive targetTable 13-3 Secondary Causes of Hypertension5 organ damage) treatment yeast cheap rivastigimine 3mg visa. Goals the overarching goal of treating hypertension is to reduce associated morbidity and mortality treatment 4 high blood pressure purchase 6mg rivastigimine overnight delivery. Hypertension-associated complications are the primary causes of death in patients with hypertension. Lifestyle Modifications Lifestyle modifications are the cornerstone of management for preventing and treating hypertension. For patients who drink alcohol, limit consumption to no more than two drinks/day in men and no more than one drink/day in women and lighter-weight persons. Regular moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity; at least 30 min of continuous or intermittent 5 days/wk, but preferably daily. This can also occur in patients with hypertension and chronic kidney disease who are treated with potassium supplementation. Physical activity should occur for at least 30 minutes, at least 5 days of the week, but preferably daily. Aerobic exercise such as walking, running, cycling, swimming, and cross-country skiing, are examples of recommended physical activity. Pharmacotherapy Numerous clinical trials have demonstrated that antihypertensive pharmacotherapy generally reduces the risk of hypertension-associated complications. Some clinicians may argue that the efficacy of implementing sodium restriction in patients with hypertension may vary. They should be counseled not to add salt to foods, and to avoid or minimize ingestion of processed or packaged foods, foods with high sodium content, and nonprescription drugs containing sodium (see Chapter 18, Heart Failure). Combination therapy with two antihypertensive drugs is an option for patients with stage 1 hypertension (see Table 13-1) and is strongly recommended in patients with stage 2 hypertension. Pharmacotherapy has been evaluated in patients with one of several comorbid conditions considered compelling indications for specific pharmacotherapy. The selection of pharmacotherapy in such patients is much more prescriptive than in primary prevention patients, and is outlined in Figure 13-3. Hyperkalemia is possible, however, and potassium concentrations should be monitored. Patients with chronic kidney disease or volume depletion may be more susceptible to hyperkalemia or to further kidney dysfunction. Although this may lead to additive vasodilation by releasing nitrous oxide, bradykinin can also cause a dry cough in some patients. Because aldosterone is blocked, monitoring of potassium is important to avoid hyperkalemia. They have historically been the most commonly prescribed antihypertensive agents in the United States. When initially started, they induce a natriuresis that causes diuresis and decreases plasma volume. Diuresis usually decreases after chronic use with some of these agents, especially with thiazide diuretics. Overwhelming evidence from large outcome-based clinical trials indicates that diuretic therapy reduces morbidity and mortality rates. These effects were particularly problematic when high doses were used many years ago. Other biochemical changes in glucose and cholesterol are minimal and mostly transient with low-dose therapy. They can decrease cardiac contractility and output, lower heart rate, blunt sympathetic reflex with exercise, reduce central release of adrenergic substances, inhibit norepinephrine release peripherally, and decrease renin release from the kidney.
Cheap rivastigimine 3mg free shipping. Why Do Depression and Anxiety Go Together?.
Diseases
- Erythroplakia
- Woolly hair, congenital
- Insulinoma
- Thyroid hormone plasma membrane transport defect
- Infantile axonal neuropathy
- Kalam Hafeez syndrome
- XY Female