Prazosin
"Order cheap prazosin line, cholesterol test can i drink coffee".
By: D. Emet, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Co-Director, The Ohio State University College of Medicine
Long-term observation of patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis treated with rituximab cholesterol medication names canada buy generic prazosin 5 mg on-line. Antiproteinase 3 antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies and disease activity in Wegener granulomatosis cholesterol eggs purchase prazosin with visa. Long-term outcome of anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody disease treated with plasma exchange and immunosuppression. Therapy of anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody disease: analysis of prognostic significance of clinical, pathologic and treatment factors. Management of idiopathic crescentic and diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis: evidence-based recommendations. Characteristics and prognosis of Chinese patients with anti-glomerular basement membrane disease. Clinical outcome of patients with coexistent antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies and antibodies against glomerular basement membrane. Anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody disease in Japan: part of the nationwide rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis survey in Japan. Recurrence of circulating antiglomerular basement membrane antibody three years after immunosuppressive treatment and plasma exchange. Formulating questions and locating primary studies for inclusion in systematic reviews. Suggested protocol for the further investigation of an individual demonstrating a positive reagent strip test for albuminuria/proteinuria or quantitative albuminuria/proteinuria test Figure 17. Distribution of the probability of nonlinearity with three example trajectories demonstrating different probabilities of nonlinearity Figure 19. Grade A B C D Quality of evidence High Moderate Low Very low Meaning We are confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect. Equations expressed for specified sex and serum creatinine level Gender Female Female Male Male Serum creatinine p0. Equations expressed for serum cystatin C level Serum cystatin C Female or male Female or male p0. Equations expressed for specified sex, serum creatinine, and serum cystatin C level Gender Female Female Male Male Serum creatinine p0. Metric units g/dl mg/dl mg/dl ml/min g/dl mg/dl pg/ml mg/dl mg/dl ng/ml Conversion factor 10 0. Every health-care professional making use of these recommendations is responsible for evaluating the appropriateness of applying them in any particular clinical situation. Single photocopies may be made for personal use as allowed by national copyright laws. Special rates are available for educational institutions that wish to make photocopies for non-profit educational use. We hope to accomplish this, in the short term, by helping clinicians know and better understand the evidence (or lack of evidence) that determines current practice. By providing comprehensive evidence-based recommendations, this guideline will also help define areas where evidence is lacking and research is needed. However, clinicians still need to make decisions in their daily practice, and they often ask, ``What do the experts do in this setting These recommendations are often rated with a low strength of recommendation and a low quality of evidence, or were not graded. It is important for the users of this guideline to be cognizant of this (see Notice). Adeera Levin and Paul Stevens, along with all of the Work Group members who volunteered countless hours of their time developing this guideline. We also thank the Evidence Review Team members and staff of the National Kidney Foundation who made this project possible. The development of the guideline followed an explicit process of evidence review and appraisal. Treatment approaches are addressed in each chapter and guideline recommendations are based on systematic reviews of relevant trials. Practical comments or statements which serve as educational purposes are ungraded, but included as important information for the readership.
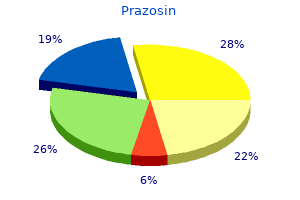
This framework helps an individual facing an ethical quandary to determine "what should I do Their work was subsequently validated and employed by numerous researchers (Barnett and Schubert 2002; Cullen new cholesterol medication guidelines discount 2.5 mg prazosin mastercard, Victor cholesterol and vitamin d buy prazosin 5mg cheap, and Bronson 1993; Peterson 2002; Trevino, Butterfield, and McCabe 1998; Vardi 2001; Weber 1995; Weber and Gerde 2011; Weber and Seger 2002). They are egoism, which stresses self-interest; benevolence, which stresses joint interests; and principle, which stresses adherence to a moral code or principle (Victor and Cullen 1988, 104). The second dimension is the locus of analysis which is a referent group that is the "source of moral reasoning" (Victor and Cullen 1988, 105). Based on sociological theories of reference groups and their roles, this dimension has three components: individual, in which the source of reasoning is personal ethics or self-interest; local, in which the source is the immediate surrounding organization; and cosmopolitan, in which the source extends beyond the organization to include others such as members of a shared profession or an abstract influence such as a body of law or ethical code (Victor and Cullen 1988, 106). It was also found to be associated with unethical conduct (Peterson 2002; Trevino, Butterfield, and McCabe 1998), including theft and falsification of reports (Weber, Kurke, and Pentico 2003). Their work validated its applicability to military organizations by surveying 10 different military work groups of U. Both are affected by the behavior and values of its members, perhaps more strongly so than by the formal values espoused by the larger, formal organization. In the fall of 2010, the Navy Personnel Command invited Michael Josephson of the Josephson Institute of Ethics to speak on the topic of ethics. As part of the seminar, senior and midgrade officers and civilian employees participated in a survey on ethics and values. Josephson queried 300 persons, and 100 responded which yielded a strong response rate of 33%. The survey participants were asked about a series of behaviors and whether in their opinion this conduct was so frequent or serious that it should be addressed more consistently by the Navy. Officers overlooking poor or mediocre performance of subordinates - 59% agreement 3. Looking the other way at improper conduct by high level officers - 55% agreement 5. Willingness to lie, deceive, or conceal for personal advantage or avoidance of negative consequences - 53% agreement 6. Arrogance or abuse of power with respect to subordinates - 52% agreement (Josephson 2010). In "The Bathsheba Syndrome: the Ethical Failure of Successful Leaders," Ludwig and Longenecker place the responsibility squarely on failed leaders. In their assessment, leaders are placed in danger of ethical failure due to four conditions produced by success. While there is merit in their observations of the freedom that accompanies achieving a pinnacle position, their perspective ignores the organizational culture and any values or expectations of leaders that it imposes, falling short by excluding this noteworthy aspect. Navy Culture the official organizational culture of the Navy, as defined by Jermier et al. Employ the global reach and persistent presence of forward-stationed and rotational forces to secure the Nation from direct attack, assure Joint operational access and retain global freedom of action. With global partners, protect the maritime freedom that is the basis for global prosperity. Foster and sustain cooperative relationships with an expanding set of allies and international partners to enhance global security. They go on to describe manifestations of this culture as including "myths, values, ideologies; stories and heroes; slogans, rituals, rites, and ceremonies" (1991,170). All these things are thoroughly embraced within the military, perhaps more so than other organizations due to the need to instill loyalty, espirit de corps, and discipline. For example, the Navy reveres the heroes, "the hallowed dead," of its past (Karsten 1972, 27). Their heroic deeds and victories in battle are taught as lessons in leadership and service, and their names, such as John Paul Jones, Stephen Decatur, and Arleigh Burke, grace the hulls of modem warships. The Navy holds ceremonies full of pomp and martial music for the commissioning and decommissioning of ships and for changes of command.
In a recent review Barakat677 attempts to address a number of these issues by outlining the most common presentations of a child with significant renal disorders cholesterol levels ratio order discount prazosin. Barakat and Chesney also suggest a number of specific areas in terms of initial investigations high cholesterol medication uk buy 2.5 mg prazosin otc, management, and follow-up where the primary care physician can legitimately play a role in the care of the child with renal disease and provides a list of suggested referral triggers. Similarly, the need for education in progressive conditions, performance of and interpretation of renal biopsies, and allaying parental/patient anxiety would also be acceptable reasons for referral. The other metric of interest chosen by these authors to evaluate the possible detrimental effect of late referral was the likelihood of a given child having a pre-emptive transplant. The underlying concept of referral to a pediatric nephrologist in the face of rapid progression of renal failure is of course applicable in full. However, no current validated risk of progression tool exists in pediatric nephrology. All efforts to slow decline in renal function would still be of vital importance in every individual. The recommendations are intended to model best practices but it is appreciated that different health-care systems, geographical issues, and economic considerations will have variable abilities to implement these recommendations. While the studies had different variables of interest and used slightly different approaches for comparison of results between their groups, both demonstrated a reduction in the rate of decline in estimated renal function, improved Hb levels, and improvement in at least some aspect of bone mineral metabolism control in their respective cohorts cared for in the multidisciplinary era. In addition, both studies also demonstrated a decrease in resource utilization by patients in the multidisciplinary clinic as measured by median length of stay682 and number of unplanned admissions per patient per year. International Relevance Standardized and culturally appropriate protocols should be considered. While it is recognized that resources may vary across and within jurisdictions, recommendations here are based on principles of care, which should be relevant across the globe. Therefore models of care should be developed that integrate the complexity of the clinical conditions involved, patient-centered philosophies, and the health-care environment. The principles of care are universal but implementation may be customized to specific circumstances. Thus, the statement as written should help the clinician to balance symptoms with laboratory values in decision making. It aims to reflect the need for risk-benefit assessment of preemptive renal transplantation in all individuals. Although there was a small gain in survival time over 3 years after start of dialysis for the timely start group (2. Subsequent observational studies, including large dialysis registry studies from around the globe, have all suggested increased mortality when dialysis is started early. In an even healthier subset of 35,665 subjects with serum albumin concentrations of 3. International Relevance the availability of resources for formal multidisciplinary teams, educational materials, and access to specialized counseling for diet, advance directives, access planning, and pre-emptive transplantation varies around the world. The need for education, planning, and appropriate expertise for the management of this patient group is internationally relevant. The methods, frequency, and tools with which this can be accomplished will be region specific. Individual assessment and availability of resources will dictate specific timing of therapies. As might be expected, information as to the proper timing for initiation of dialysis does not exist for children. Thus, it would seem reasonable to follow the guidelines as set out for the adults. A review by Greenbaum and Schaefer700 provides the reader with generally agreed upon absolute and relative indications for initiation of dialysis in the child. The absolute indications listed are those of neurologic consequences attributable to uremia; hypertension that fails to respond to antihypertensive therapy; pulmonary edema unresponsive to diuretics; pericarditis; bleeding tendency; and refractory nausea or vomiting. However, the authors clearly state that there is no current consensus as to the validity of the relative indications and specifically the level at which each engenders the need for 117 chapter 5 dialysis. Relative indications to commence dialysis include less severe uremic symptoms, hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, malnutrition, and growth failure. While there is little doubt as to the benefit in overall lifespan accrued by a child who is transplanted as opposed to one maintained on standard dialysis therapies during their childhood (average life expectancy of 63 versus 38 years respectively),701 the issue as to what level of residual function is sufficient to justify delay or conversely proceeding to transplant is simply not readily available.
At the same time the military began a process of professionalization which it conducted in virtual isolation from civil influence cholesterol in scrambled eggs buy prazosin 2.5 mg mastercard. It was at this time cholesterol test diy purchase prazosin 5 mg mastercard, possibly from the Prussian example the Army began to study, there arose a notion within the officer corps that political participation and military professionalism were incompatible (Johnson and Metz 1995,198). According to Huntington "not one in five hundred military officers ever voted" (1957, 258). It was also during this time the Navy embarked on a campaign of intellectual growth, creating the Naval Institute "as a forum for the advancement of professional, literary, and scientific knowledge in the Navy" (Bradford 2000, 63). These J were significant efforts to increase the level of professionalism among naval officers, raising them from merely proficient mariners to innovators in naval warfare. This was shown by the later creation and deployment of the Great White Fleet by then President Roosevelt (Bradford 2000, 69). With this notable exception, when it came to the development of policy and strategy on a national scale, the military did not desire a role. The years 1939-1945 saw enormous changes in the character of civil-military relations in the country. Roosevelt, who was widely regarded as one of the most astute, influential, and active Commandersin-Chief in our history. Analysts differ widely on the conditions of relations between the military and civilian authority during this time. Hendrickson finds relations "though judged defective, were relatively harmonious and reasonably effective" (1988, 27). Weigley attributes the harmony to "remarkably silent military acquiescence" (1993,43). Huntington (1957, 315-320) and Stoler (1991, 62-65) both find that the relative weakness or ineffectiveness of the civilian service secretaries and the State Department provided the military with this opportunity for playing a new and greater role. For all the successes of the Service Chiefs, Roosevelt had been unwilling to institutionalize their existence or his relationship with them. It was not until the National Security Act o f 1947, that the Joint Chiefs were officially sanctioned and simultaneously relegated to a purely "military" role. The act transferred the responsibility of advising the President on national security to the National Security Council, composed of civilians. This act was indicative of the tenuous equilibrium between the need for military input and the desire to control the military that marks the Cold War era. The Joint Chiefs had foreseen the possibility of future conflict with the Soviet Union and had pressed for a world-wide system of air and naval bases to ensure our national security. There would be no complete post-war demobilization but the maintenance o f sufficient forces and bases to counter an enemy such as a resurgent Germany or Japan or possibly a hostile Soviet Union. The country entered a period of "perpetual semi-mobilization that transformed the traditional civil-military equation" (Bacevich 1994-1995, 78). Countering the pressure to quarantine the military from policy-making were three factors: first, the Soviet military threat; second, the popularity and prestige of the military (Huntington 1957, 354); and third, the dramatic increase in military spending which made it a vital component of the economy (Johnson and Metz 1995, 200; Kohn 1994, 5). It was during this time President Eisenhower warned the nation of the nowfamous "military-industrial complex" and its impact on national policy (Bacevich 2011; Janiewski 2011; Kampmark 2011; Schlesinger 2011). In his January 17, 1961 farewell address, Eisenhower asserted that the government "must guard against the acquisition of unwarranted influence, whether sought or unsought, by the military industrial complex" (Kampmark 2011, 11; Schlesinger 2011). During his presidency, the Korean War and the rising power of the Soviet Union had resulted in Eisenhower engaging in "bruising battles to constrain military budgets" (Janiewski 2011, 681), as he struggled with the "unstated alliance of interested parties: generals, defense officials, military contractors, and members of Congress" (Bacevich 2011, 76). When Kennedy assumed power, the nuclear stockpile contained 24,000 warheads, and by the end of the decade, it had grown to 31,000 (Bacevich 2011, 76). The factors behind the tension were numerous, but the primary concerns were nuclear weapons strategy and the Vietnam War. Kohn views the nuclear capability as threatening civilian control making it "imperative to take authority to use these weapons away from the military, lest operational commanders displace Congress and the President in determining whether the country would go to war" (1994, 5). Kohn also cites civilian concern over potential friction between United States (U. During the 1950s there had been an inordinate amount of inter-service discord and competition over roles and missions, such as the Air Force and Navy conflict over the procurement of B-36 bombers or "supercarriers," and the Air Force-Army conflict over control of an intermediate range ballistic missile (Hendrickson 1988, 39).
Effective prazosin 2.5 mg. Anderson Fitness Institute- Cholesterol Myth.