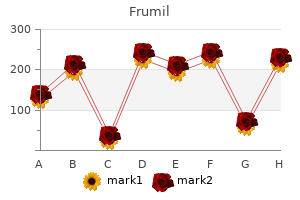
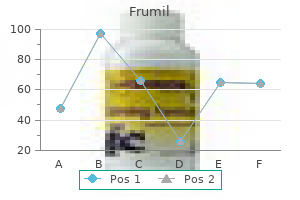
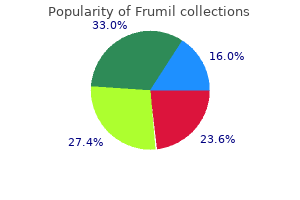
Frumil
"Purchase frumil australia, medicine x protein powder".
By: W. Rozhov, M.A.S., M.D.
Clinical Director, New York University Long Island School of Medicine
Proper use of these terms requires some knowledge of the disease entities even though their pathogenesis and relation to streptococcal infection is nearly identical 897 treatment plant rd cheap 5mg frumil with amex. However symptoms liver disease buy 5 mg frumil visa, as time goes on it is found that this child has a persistence of the murmur. This term implies there has been significant valvulitis, enough to cause valvular scarring. At one time in the early 1900s children filled the beds of hospitals dedicated to treat only rheumatic fever. In Hawaii, the ethnic groups at greatest risk are those of Polynesian heritage, with Samoan children being at greatest risk (4-6). The Samoan children also appear to be at greater risk of developing carditis (4,5). These criteria have been modified over the years since it was first developed by T. If the criteria are not used, and the patient is misdiagnosed, you may be subjecting the patient to needless penicillin injections for years. Therefore, if a child that has two Major criteria, they can fulfill Jones criteria for the diagnosis, as long as they have some evidence of streptococcal disease. On the other hand, if there is evidence of only one Major criterion, they need two minor criteria to fulfill the diagnosis, along with evidence of streptococcal infection. The symptoms may be dampened by giving aspirin or other non-steroidal antiinflammatory medications too early, thus not allowing the manifestations to fully develop. Modified Jones Criteria (two majors or one major + two minors required) (7) Major criteria: carditis, migrating polyarthritis, chorea, erythema marginatum, subcutaneous nodules. Usually one joint becomes involved and over a few days resolves, then another joint(s) becomes involved as demonstrated in our case. Occasionally, the first joint does not resolve completely by the time the second joint becomes involved, and this is termed "additive arthritis", and also fulfills a diagnosis of migrating polyarthritis. Knees and ankles are most often involved, although elbows and wrists can also be involved. Metatarsophalangeal joints can be involved and one can screen for their involvement by squeezing them together, across the foot, and eliciting pain. These findings are important to note, especially in a child with possible symptoms of orthopnea. Classic mitral insufficiency sounds like a holosystolic murmur heard at the apex which radiates to the axilla. Besides mitral insufficiency, a ventricular septic defect could be heard in the axilla, but this murmur is usually heard all over the precordium. The murmur of aortic insufficiency is a diastolic murmur (difficult to hear) that is usually heard best at the upper left sternal border. There is often a decrescendo component to this murmur that is sometimes very high pitched. One should also listen for a rub which would indicate pericarditis and a gallop for evidence of congestive heart failure. The murmur of mitral stenosis is a diastolic murmur, although it is described as occurring in mid-diastole, rather then later in diastole like aortic insufficiency. Similarly, aortic stenosis may subsequently result from initial aortic insufficiency. Thus, chorea is often termed a "subacute" phenomenon of rheumatic fever (as opposed to acute rheumatic fever). Despite this lack of evidence of inflammation these patients can develop cardiac disease. They are located over areas that tend to be more prominent and rub against surfaces causing microtrauma. For example, they can be located at the tips of the elbows, around the joints, and the bony prominences of the spinal column. It is worthwhile spending some time looking for the nodules as their presence heralds severe carditis (9). The erythema is described as an evanescent pink eruption with irregular but well-demarcated borders (9).
The majority of apnea events in premature infants are typically mixed (central and obstructive) in origin medicine ketorolac 5 mg frumil with amex. The airway obstruction is usually the result of upper airway collapse or laryngeal closure symptoms hypoglycemia buy cheap frumil 5mg. The response of the respiratory system to chemical stimuli (the primary process by which the respiratory center controls respirations) can be modulated by methylxanthines. This drug has been shown to reduce the severity and frequency of central apnea and periodic breathing in premature infants. This is a disorder of angiogenesis that could potentially lead to blindness secondary to retinal detachment. The American Academy of Pediatrics and the American Academy of Ophthalmologists have jointly recommended a schedule for screening high risk premature infants for this disorder. Later on in life, prematurely born infants are at higher risk for refractive errors and, therefore, need to be closely monitored. It is recommended that they have a comprehensive ophthalmologic examination at 6 months to one year of age. Premature infants are at the same risk for developing anemia of infancy as are term infants. In addition, premature infants are at higher risk for protracted anemia, because they are born with lower body iron stores. This situation is further compounded by significant phlebotomy losses in the neonatal period related to hospitalization after birth. Anemia of prematurity may at least partially be overcome by the use of erythropoietin, which is used to stimulate erythropoiesis. In this respect, the iron supplementation during therapy should be at the levels used in the treatment of anemia at any other age (up to 6 mg/kg/d of elemental iron). The primary source of immunity for the neonate is passively derived antibodies from the mother and this tends to occur primarily in the third trimester. Thus, the relative amount of antibody transferred is affected by the duration of gestation. All of these factors contribute to the increased risk of infections in this population. This mandates close monitoring for infectious complications, both during hospitalization, in the immediate neonatal period, and in subsequent months during the first year of life. Given their propensity for infections, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that all childhood immunizations be administered to premature infants at the appropriate chronological age. Despite lower titers of antibody response in these infants, there is no recommendation for additional doses of specific immunizations. The most current recommendation is published in the Red Book 2003 of the American Academy of Pediatrics. These infants will also benefit from receiving influenza immunization at 6 months chronological age during the cooler winter months (3). The premature infant is ready for discharge when he/she is able to fulfill the following criteria: 1) ability to appropriately regulate their temperature without the need for technological support, 2) ability to ingest adequate calories to achieve consistent growth, and 3) to have demonstrated other parameters of global physiologic stability (the absence of clinically significant apnea, bradycardia, or hypoxemia). In addition, and most importantly, it is critical that the parents/caregivers feel comfortable with the care of the infant in the home environment. Thus, the process of discharge of the infant is a continuum that begins several days to weeks prior to the actual discharge of the infant. Many of these infants will have additional needs and it is important that all of these needs and appropriate community resources are identified prior to discharge. At the time of discharge, the routine mandated screening for hearing and metabolic diseases should be completed with the results forwarded to the primary care physician. The long term outcome of premature infants is inversely related to gestational age (better outcomes in older infants), and directly related to the clinical course in the neonatal period, and the associated morbidities and diagnoses during their hospitalization. In general, these infants need close neurodevelopmental monitoring and early interventions for identified problems. They are at increased risk for repeated hospitalization for various residual problems of prematurity such as bronchopulmonary dysplasia, failure to thrive, and feeding problems.
Regulating blood pressure the kidneys: produce and secrete renin in response to a decline (actual or perceived) in extracellular fluid volume treatment 4 lung cancer purchase cheap frumil line. Regulating vitamin D and calcium formation the kidneys help convert vitamin D to its active form symptoms 1 week before period discount frumil express. Renal disorders Acute tubular necrosis-destruction of the tubular segment of the nephron, causing renal failure and uremia Benign prostatic hyperplasia-enlarged prostate gland that compresses the urethra and causes urinary obstruction Glomerulonephritis-bilateral inflammation of the glomeruli, commonly following a streptococcal infection Hydronephrosis-abnormal dilation of the renal pelvis and the calyces of one or both kidneys Prostatitis-inflammation of the prostate gland Renal calculi-substances that normally dissolve in the urine precipitate to form "kidney stones" Renal failure, acute-sudden interruption of renal function caused by obstruction, poor circulation, or kidney disease Renal failure, chronic-irreversible deterioration of tissue and eventual loss of kidney function Quick quiz 1. This is because creatinine is only filtered by the glomeruli and not reabsorbed by the tubules. One such condition, prerenal azotemia, accounts for between 40% and 80% of all cases of acute renal failure. Depending on the size of the enlarged prostate and resulting complications, the obstruction may be treated surgically or symptomatically. Your ability to concentrate, absorb, and secrete data about the kidneys is amazing! Pumped by the heart, it continuously circulates through the blood vessels, carrying vital elements to every part of the body. A problem with any of these components may have serious and even deadly consequences. Plasma Plasma is a clear, straw-colored fluid that consists mainly of the proteins, albumin, globulin, and fibrinogen held in aqueous suspension. Other components in plasma include glucose, lipids, amino acids, electrolytes, pigments, hormones, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. These components regulate acid-base balance and immune responses as well as carry nutrients to tissues and help to mediate coagulation. About 80% to 90% of erythropoietin is made in the kidneys; the remainder comes from the liver. The making of an erythrocyte Erythrocyte formation begins with a precursor, called a stem cell. Development requires vitamin B12, folic acid, and minerals, such as copper, cobalt, and-especially-iron. Iron is found in food and, when consumed, is absorbed in the duodenum and upper jejunum. After iron is absorbed, it may be transported to the bone marrow for hemoglobin synthesis. Iron may also be transported to needy tissues such as muscle for myoglobin synthesis. They surround and digest invading organisms and other foreign matter by phagocytosis. They also migrate to tissues where they develop into cells called macrophages that participate in immunity. Platelets Platelets are small (2 to 4 microns in diameter), colorless, diskshaped cytoplasmic cells split from cells in bone marrow. Platelets perform three vital functions to help minimize blood loss: They help constrict damaged blood vessels. They form hemostatic plugs in injured blood vessels by becoming swollen, spiky, sticky, and secretory. When tissue injury occurs, blood vessels at the injury site constrict and platelets mesh or clump to help prevent hemorrhage. Bone marrow cells and their precursors are especially vulnerable to physiologic changes that can affect cell production. Bringing some order to blood disorders Blood disorders may be primary or secondary and quantitative or qualitative. A secondary bleeding disorder results from a cause other than a defect in the blood. Qualitative blood disorders stem from intrinsic cell abnormalities or plasma component dysfunction. Quantitative blood disorders result from increased or decreased cell production or cell destruction.
Some patients with hypercalcemia have as their first symptom a mild diffuse encephalopathy with headache symptoms quotes cheap frumil 5mg with amex. Delusions and changes in affect can be prominent medicine buy frumil 5mg without prescription, so that many such patients have been initially treated for a psychiatric disorder until the blood calcium level was measured. The posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome (see page 215) has been reported in association with severe hypercalcemia. Hypercalcemia should be suspected in a delirious patient who has a history of renal calculi, recent immobilization, cancer, or evidence of any other systemic disease known to cause the condition. The cardinal peripheral manifestations of hypocalcemia are neuromuscular irritability and tetany, but these may be absent when hypocalcemia develops insidiously. Accordingly, patients with hypoparathyroid hypocalcemia can sometimes present with a mild diffuse encephalopathy as their only symptom. With more severe cases, excitement, delirium, hallucinations, and stupor have been reported. This hypocalcemic pseudotumor cerebri apparently is a direct effect of the metabolic abnormality, but the precise mechanism remains unexplained. To avoid making this extrapolation, if there is any question about the calcium level, the free serum calcium should be measured. Chronic hypocalcemia may cause chorea and parkinsonism, along with calcifications in the basal ganglia. Five years later following reconstructive surgery on her leg, she complained of numbness and tingling of both hands and arms spreading into the face and followed by spasms of her arms, which lasted several hours. Other attacks followed but were milder until 2001; while the patient was in bed with a viral illness, the symptoms were so severe that she was taken to an emergency department where sedation was again applied. Voluntary hyperventilation for 2 minutes reproduced the carpal spasms and paresthesias in both hands. Comment: Cisplatin and ifosfamide are drugs that can cause calcium- and magnesium-losing nephropathy. Both low magnesium (see below) and low ionized calcium that result from a magnesium loss can cause hyperventilation that further lowers ionized calcium, presumably by increasing the binding of calcium to albumin, thus causing tetany. However, of the four disorders of systemic acidbase balance (respiratory and metabolic acidosis and respiratory and metabolic alkalosis), only respiratory acidosis acts as a direct cause of stupor and coma with any regularity. Metabolic acidosis, the most immediately medically dangerous of the acid-base disorders, by itself only rarely produces coma. Usually, metabolic acidosis is associated with delirium or, at most, confused obtundation. Instead, it is more likely is that the metabolic defect responsible for the acid-base disturbance. A useful clinical clue to the presence and possible cause of metabolic acidosis or certain other electrolyte disorders comes from estimating the anion gap from the measured blood Other Electrolytes Hypo- and hypermagnesemia are rare causes of neurologic symptomatology. Because hypomagnesemia and hypocalcemia often occur together, it is sometimes difficult to determine which is the culprit. It is mainly seen in the obstetric suite when eclampsia is treated with intravenous infusion of magnesium sulfate. If high levels persist, they may equilibrate across the blood-brain barrier, resulting in lethargy and confusion and rarely coma. Hypophosphatemia can occur during nutritional repletion, with gastrointestinal malabsorption, use of phosphate binders, starvation, diabetes mellitus, and renal tubular dysfunction. Hyperphosphatemia can occur with rhabdomyolysis or during the tumor lysis syndrome, but does not appear to cause neurologic symptoms. The calculation is based on the known electroneutrality of the serum, which requires the presence of an equal number of anions (negative charges) and cations (positive charges). For practical purposes, sodium and potassium (or sodium alone) represent 95% of the cations, whereas the most abundant and conveniently measured anions, chloride and bicarbonate, add up to only 85% of the normal total. Thus, hyperthermia is more damaging to injured brain, for example, after traumatic brain injury, than it is to normal brain, for example, after heat stroke. Hypothermia Hypothermia results from a variety of illnesses including disorders of the hypothalamus, myxedema, hypopituitarism, and bodily exposure. In the absence of any underlying disease that may be causing both coma and hypothermia, there is a rough correlation among the body temperature, cerebral oxygen uptake, and state of consciousness.
Cheap frumil 5 mg without prescription. Burning skin anxiety symptom commentary by Jim Folk president of anxietycentre.com.