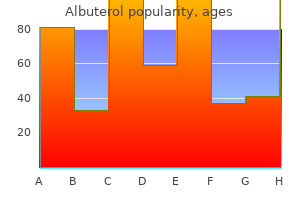
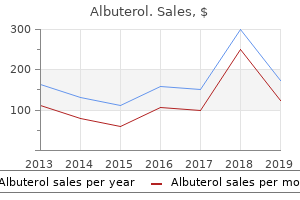
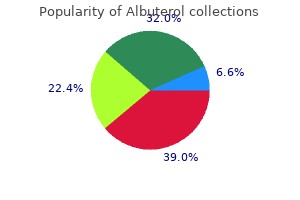
Albuterol
"Discount albuterol 100mcg visa, asthma pictures".
By: N. Ben, M.A.S., M.D.
Vice Chair, Mayo Clinic Alix School of Medicine
If a sedative is appropriate asthma symptoms vs bronchitis symptoms order albuterol visa, however asthma definition british thoracic society discount 100mcg albuterol overnight delivery, a short-acting benzodiazepine is the drug of choice such as Triazolam (Halcion) in doses of 0. Even though useful, it seems wise not to prescribe benzodiazepines for more than a few nights, while attacking the basic problem through other avenues. Recent studies also have suggested the usefulness of L-tryptophan in doses up to one to two grams at bedtime. The use of sedatives to assist sleep in sustained operations is a continuing debate. The British use of Halcion in the Falklands war increased interest and also demonstrated effectiveness when used under proper conditions. The situations that meet these criteria are those of confusion, psychosis, and impending suicide or homicide. Another way to define this is defining the patient as gravely disabled or a threat to himself or others. In treating it, the physician must distinguish between organic and functional causes and treat accordingly. Other emergency presentations and management have been discussed in the sections on treatment modalities, psychoses, mood disorders, anxiety disorders, and drug overdose. When ideation 6-38 Aviation Psychiatry presents, estimating the danger of it being translated into action is difficult. The loss of friends or relatives, or of self-esteem, or of a body part or function highly valued by the patient. Gesture and attempts may be difficult to differentiate, and in general should be taken equally seriously. Both may be associated with personality disorder and manipulation or they may be expressions of bona fide depression and a desire to be dead. Long-term treatment depends on correct diagnosis and a proper response to an estimate of the self-destructive risk. Suicide patients, even those with manipulative suicide behavior, do not belong in the operational environment. The flight surgeon should closely coordinate cases of suicidal ideation or behavior with the nearest medical treatment facility. The risk of homicide may derive either from psychiatric or organic illness and is historically nearly impossible to predict. If the etiology is functional, the following have been associated with increased homicidal risk: 6-39 U. If the illness is organic, there may be increased risk if the basic personality pattern has been paranoid. The Center for the Study of the Prevention of Violence in Los Angeles has uncovered a rather high percentage (42 percent) of soft neurological signs in studies of violent patients. In the individual case, an estimate of the following may be helpful in assessing homicidal potential: 1. Studies suggest that only a very small percentage of those presenting with homicidal risk ever act on their impulse. Treatment consists of the imposition of chemical or physical controls (in the form of hospitalization) as in suicidal potential, until the danger is over. The Tarasoff court deci- 6-40 Aviation Psychiatry sions in California has set the standard that the intended victim and police must be notified. Drug Overdose the following general principles are accepted for the treatment of drug overdose: 1. In overdose with psychotropic medications, the following steps should be taken: 1. Ensure an adequate airway - intubation or, rarely, tracheostomy if necessary in the comatose patient. Emesis in the conscious patient - syrup of ipecac, one teaspoon for a child, two for an adult. Do not attempt this in the comatose patient without intubation and cuff to preclude aspiration pneumonia.
Hypoxia Probably the most frequently encountered hazard in aviation medicine is hypoxia asthma definition vintage discount 100 mcg albuterol otc. Records of early balloon and aircraft flights describe tragedies resulting from hypoxia asthma expert panel report 3 trusted albuterol 100 mcg, since even these primitive machines had a higher operational ceiling than the men aboard them. Considerable money has been expended on training of aviators and on procurement of equipment to prevent hypoxia. Yet, hypoxic incidents continue to occur, and the flight surgeon should be well informed concerning this problem. There is a commonly encountered misconception among aviators that it is possible to learn all of the early symptoms of hypoxia and then to take corrective measures once symptoms are noted. This concept is appealing because it allows all action, both preventive and corrective, to be postponed until the actual occurrence. Therefore, even if the early symptoms are noted, an aviator may disregard them and often does, or he may take corrective action which is actually hazardous, such as disconnecting himself from his only oxygen supply. Finally, at high altitudes, hypoxia may cause unconsciousness as the first symptom. The most common cause of the hypoxic incident is cabin or cockpit pressurization failure followed by defective oxygen equipment. In these incidents, the pilot or copilot was able to recover the aircraft and avoid a major mishap or fatality. One can only conjecture how many mishaps and fatalities in military aviation have occurred as the direct result of hypoxia. Since hypoxia episodes are still frequently encountered, and in all likelihood contribute to many major mishaps and fatalities, the flight surgeon and aviation physiologist should be well informed of every facet of the problem. Types of Hypoxia the amount and pressure of oxygen delivered to the tissues is determined by arterial oxygen saturation, by the total oxygen-carrying capacity, and by the rate of delivery to the tissues. Hypoxia, defined as an insufficient supply of oxygen, can result from any one of these factors. Hypoxic hypoxia results from an inadequate oxygenation of the arterial blood and is caused by reduced oxygen partial pressure. Anemic hypoxia results from the reduced oxygen- carrying capacity of the blood, which may be due to blood loss, any of the anemias, carbon monoxide poisoning, or by drugs causing methemogiobinemia. Stagnant hypoxia is caused by a circulatory malfunction which results, for example, from the venous pooling encountered during acceleration maneuvers. Histofoxic hypoxia results from an inability of the cells to utilize the oxygen provided when the normal oxidation processes have been poisoned such as by cyanide. This results from the reduced oxygen partial pressure in the inspired air caused by the decrease in barometric pressure. Other types may also affect aircrewmen, such as anemic hypoxia as seen in carbon monoxide poisoning and stagnant hypoxia resulting during various acceleration profiles. During ascent to altitude without supplementary oxygen equipment, the onset of hypoxia is as gradual as the rate of ascent. As soon as an inspiration is completed, the alveolar gases approach equilibrium with the inspired gases, and similarly, the arterial gases reach a very rapid equilibrium with the alveolar gases, but the change in barometric pressure is gradual between breaths. In the event of contamination or dilution of oxygen in the mask with some amount of cabin air, due to either a leaky mask or faulty tubing, onset of hypoxia is intermittent. Moreover, the effects are inconsistent because the amount of hypoxia developing varies from one breath to the next, depending on leakage rate, altitude, and body position (which may cause the aperture of a leak to be temporarily closed, partially open, or completely open). This type of hypoxia onset is difficult to trace because it is often difficult to validate that a hypoxic incident occurred, much less to determine the cause. In the case of a supply hose disconnect or other cause of exposure to ambient air, whether known or unknown, the onset of symptoms will be determined by the altitude during exposure. When rapid decompression occurs, the volume and pressure of alveolar gases become markedly higher than those of the ambient atmosphere, and sudden expulsion of the alveolar gases occurs. Symptomatology Many observations have been made on the subjective and objective symptoms of hypoxia. A detailed analysis of progressive functional impairment indicates that the effects of hypoxia fall in- 1-20 Physiology of Plight to four stages. Table l-7 summarizes the stages of hypoxia in relation to the altitude of occurrence, breathing air or breathing 100 percent oxygen, and the arterial oxygen saturation.
Ultrasonography is not reliable for detection of central venous pathologies asthma kitty purchase line albuterol, owing to difficult access to these vessels asthma and pregnancy buy albuterol with a mastercard. In addition enlarged collateral veins and nonocclusive thrombi may cause false negative results. Sensitivity can be improved with the demonstration of normal cardiac pulsatility and respiratory phasicity within the examined vessels (read Thrombosis, vein brachial). Synonyms Malignant central venous obstruction; Malignant central venous thrombosis Occlusion, Venous Central, Malignant. Table 1 Kishi scoring system for superior vena cava obstruction with the total score for signs and symptoms calculated as the sum of the highest grades in each category Signs and symptoms grade Neurologic symptoms Stupor, coma, or blackout 4 Blurry vision, headache, dizziness, or amnesia 3 Changes in mentation 2 Uneasiness 1 Laryngopharyngeal or thoracic symptoms Orthopnea or laryngeal edema 3 Stridor, hoarseness, dysphagia, glossal edema, or shortness of breath 2 Cough or pleural effusions 1 Nasal and facial signs or symptoms Lip edema, nasal stiffness, epistaxis, or rhinorrhea 2 Facial swelling 1 Venous dilatation Neck vein or arm vein distension, upper extremity swelling, or upper body plethora 1 Definition Acute or chronic thrombotic uni- or bilateral occlusion of one or more central veins. Pathology/Histopathology the central venous vasculature, in particular the superior caval venous system, may be obstructed by two types of lesions. Bronchogenic carcinoma is the most common causative malignant tumor and often leads to edema of the upper thorax, shortness of breath, cough, dysphagia, hemoptysis, and headaches. Less often, direct extension or compression due to the primary tumor or by invasion of the mediastinal lymph nodes is triggered by lymphoma, extra-thoracic tumors, mesothelioma, and lymph node metastases (1). Clinical manifestations of venous obstruction can be extremely serious, requiring prompt treatment (also see Benign central venous occlusion). Although the primary diagnostic suspicion can be rendered clinically, imaging is required for demonstrating the extent of the pathology. Imaging Contrast venography for decades has been the standard of reference for benign and malignant central venous Nowadays contrast enhanced spiral or preferably multislice computed tomography is employed to define the site of the obstruction and the presence of possible thrombosis and reveal surrounding soft tissue alterations (3). Another drawback of digital subtraction angiography is that it can only evaluate one single venous drainage system for each injection and other major draining vessels, for instance the internal jugular veins, may remain indeterminate. If a percutaneous therapy is anticipated, naturally, digital subtraction venography should be carried out immediately prior to , during, and after the intervention. Diagnosis Due to the deficiencies of a clinical diagnosis, imaging techniques need to be incorporated in the diagnostic process. Interventional Radiological Treatment Especially in acute central venous obstruction, traditional treatment methods in malignancy have been nonoperative, such as steroids, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. These however may require up to 4 weeks to show an effect and thus often are too time consuming (5). In benign and malignant lesions, anticoagulation alone is not efficient but may be used combined with other treatment modalities (6). In early chronic and chronic occlusions, thrombolysis is outright unsatisfactory (7). If a stenosis is the trigger for thrombosis, sole lysis will also be inefficient (8). In conclusion, an approach which offers urgent and rapid nonoperative relief should be the preferred treatment of choice. Admittedly, with balloon angioplasty alone early restenosis can be expected; plus, interventional success is limited because of the well-known fibrous and elastic features of venous lesions (6, 8). It however can be valuable before stenting by allowing the stent to uncomplicatedly cross relatively tight lesions. For all the above mentioned reasons percutaneous endovascular stenting of obstructive central venous lesions, which are symptomatic and caused by benign or malignant lesions, is an effective therapeutic option with acceptable patency rates and proven efficacy (9). Stenting results in a rapid and consistent relief and maintains patency throughout the life span of most patients suffering from malignant tumors. Different vascular access sites like the femoral vein, internal jugular vein, subclavian vein, and basilic vein are possible. The obstruction may require predilation after safe passage through the segment, but only if presence of thrombus material can be excluded. Next, a stent which is flexible enough to allow implantation even in kinked vessels should be introduced. Coverage of the obstructed segment is advised to be at least 1 cm free at the proximal and distal end to cover beyond the obstruction. Sometimes the placement of an additional stent may be necessary, especially if there is obstruction of both anonymous veins and the superior vena cava.
Discount albuterol 100 mcg on-line. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Asthma or Both.
On the other hand asthma treatment ramdev buy albuterol 100 mcg lowest price, the interactions between leukocytes and albumin microbubbles are mediated largely by leukocyte b2 integrin asthmatic bronchitis joke cheap albuterol 100mcg free shipping. In the presence of a strong negative shell-surface charge, nonspecific adhesion and accumulation of microbubbles on the vascular endothelium has been noted (1, 2). Lymph flow transport: Passive targeting of lymph nodes was demonstrated after interstitial injection of small microbubbles (1 mm) consisting of a low-solubility gas or air-microbubbles stabilized with a polymeric hardshell by using gray scale or color Doppler ultrasound. Interstitial injected microbubbles enter the lymph vessels through gaps between lymphatic endothelial cells or by transcellular endo- or exocytosis and is transported by the lymph flow to the respective regional lymph node. This can be done either by direct coupling of the ligand to shell-forming molecules or by covalent or noncovalent attachment of ligands to preformed microbubbles. Because of the size of microbubbles (mm-range), they are not able to move through the endothelium and thus do not usually leave the Targeted Microbubbles. The conjugation of a targeting moiety with the signaling moiety results in target-specific microbubbles. For passive targeting, intrinsic chemical or electrostatical properties of the shell can be used to carry microbubbles to the target. Active-targeted microbubbles can be produced by different coupling strategies depending on the targeting moiety. Therefore, selective targeting with microbubbles is generally directed (limited) to specific receptors of physiological or pathological conditions on the surface of the vascular endothelium. However, the endothelium in a human adult has a total mass of about 1,000 g (like the liver mass) and mediates a wide variety of messages from local tissue to the systemic system. The rapid blood clearance guarantees a strong signal-to-noise ratio for specific accumulated microbubbles at the target site. The exceptional ultrasound sensitivity of microbubbles allows the detection of signals from single bubbles and their quantification at the target even in high concentrations. The late phase effect (bubble retention) allows contrast imaging in these organs long after blood-pool enhancement has disappeared and is used for the detection of neoplastic lesions. Another example is the use of Imagent (Alliance Pharmaceuticals, San Diego, California) for passive lymph node targeting after their interstitial administration (3). The nonspecific targeting of activated leukocytes could be shown in preclinical settings with different types of microbubbles, which provides a new approach for ultrasound imaging, the detection of acute inflammation including ischemiareperfusion injuries. The targeting of myocardial endothelial cells has been achieved in anesthetized dogs with negative-charged microbubbles indicating that those types of agents could provide information on myocardial perfusion and viability (1, 2). However, each of the broad variety of molecules expressed on the endothelial surface can potentially be targeted with specific microbubbles. Only recently, a new method has been reported allowing the in vivo quantification of targeted microbubbles even in high concentrations. Neuroimage 27:26778 Targeted Optical Contrast Agents Molecular Probes, Optical Probes Bibliography 1. Bioconjug Chem 16:97 Targeted Probes Molecular Probes, Optical Probes Temporal Bone, Inflammatory Diseases, Acute, Chronic 1789 Targeted Specific Ultrasound Contrast Agents Targeted Microbubbles Targeted Tumor Imaging Receptor Studies, Neoplasms of the external, middle, and inner ear, including the associated complications and the sequelae. The infections can be of microbial or viral origin and include a series of clinical entities for which several classifications have been proposed. The first distinction must be made between acute and chronic inflammatory, where chronic is defined as an inflammation that does not resolve itself within three months from its appearance. The inflammatory diseases of the temporal bone are generally classified according to the site of origin: external ear, middle ear and mastoid, inner ear, and petrous apex. In acute middle ear and mastoid inflammation the mucopurulent fluid is a result of vasodilatation, increasing glandular secretion with mucous production, and polymorphonuclear reaction occurring from the neutrophil cells. Resolution frequently occurs, but, if for some reason, the condition is prolonged, such as inability of the secretions to be drained out of the eustachian tube, the number of glands and goblet cells increases. The areas formerly covered by a cuboidal or flat epithelium change into areas of a less differentiated pseudostratified columnar epithelium. Localized areas of the mucosa become hyperplastic with invasion of fibroblasts, capillaries, macrophages, plasma cells, and lymphocytes. Chronic middle otitis can be distinguished into two main groups according to the integrity of the tympanic membrane: (a) otitis with integrity of the tympanic membrane, which generally represents serous-mucous otitis; (b) otitis with open tympanum, which includes chronic suppurative otitis, chronic noncholesteatomatous otitis with ossicular erosion, and cholesteatomatous otitis. In serous-mucous chronic otitis the aerial cavities of the middle ear are filled by a transuded serous and serousmucous fluid that can change into an exudate due to bacterial superimposition. Chronic noncholesteatomatous otitis is characterized by a tympanic perforation with otorrhea and a range of irreversible modifications that can involve the mucous membrane, the temporal bone, the ossicular chain, the mastoid air cells, and the eustachian tube.