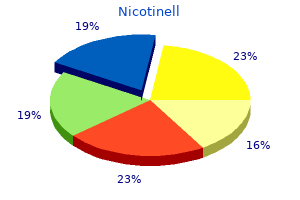
Nicotinell
"Buy generic nicotinell 52.5mg line, quit smoking body changes".
By: T. Ugolf, M.A.S., M.D.
Assistant Professor, University of Louisville School of Medicine
Diagnosing a persistent cloaca correctly is vital because 50% of infants have hydrocolpos and 90% of babies have associated urological problems quit smoking ulcerative colitis buy generic nicotinell from india. In this situation quit smoking patches order generic nicotinell pills, placement of a temporary tourniquet around the base of the tumor may be a lifesaving intervention that allows the child to make it to the operating room. The prognosis is dependent on presence of malignancy and the ability to completely resect the tumor. Growing evidence suggests that families of children with lifethreatening and chronic conditions benefit from palliative care and that earlier discussions and initiation can improve symptom management and quality of life. This statement was reaffirmed in 2007, with a policy statement in 2013 enhancing these concepts. Improved professional and social support for families in need of palliative care 5. Continued improvement of pediatric palliative care through research and education Palliative care includes pain/symptom control and management, focusing on enhancing quality of life, emphasizing the assessment and treatment of the body, mind, and spirit to prevent suffering for children and families living with life-threatening or terminal conditions. Complimentary and concurrent components to care Palliative Care in the Hospital Setting Palliative care provided in the tertiary hospital setting is best coordinated through the use of an interdisciplinary palliative care team which includes a physician, nurse and/or nurse practitioner, social worker, spiritual advisor and a child life therapist, and may include a family advocate, clinical pharmacist, dietician, bioethicist, and psychiatrist or psychologist. Because palliative care patients receive interventions from such diverse disciplines, it is important that the primary care physician/team coordinate these efforts. To obtain a consultation, please call the main Neonatology Service number, 832-826-1380. Perinatal Palliative Care Consultations are also available at Ben Taub General Hospital through an interdisciplinary team. Most are done while an expectant mother is admitted and are part of her prenatal consult, which is obtained by calling 713873-9210. A grimace may be characterized by brow lowering, eyes squeezed shut, deepening naso-labial furrow, or open lips and mouth. It is important to be able to recognize and treat all types of pain, including acute pain, chronic pain, recurring pain, procedurerelated pain, and end-of-life pain. Physiologic indicators such as vital sign changes, or behavioral indicators such as facial grimacing, may not be as reliable or may be absent in a chronically or critically ill infant. Characteristics of crying, oxygen requirement, changes in vital signs, facial expression, and sleep state are scored. To achieve adequate analgesia/sedation, medications optimally should be scheduled or given by continuous infusion with intermittent bolus doses as needed in order to avoid fluctuations in blood levels and breakthrough pain or discomfort. In addition, infants should always receive a bolus dose of narcotic or sedative prior to starting or increasing the infusion rate. Intranasal administration is an alternative option for patients who do not have intravenous access. It provides pain relief, elicits a sense of euphoria and promotes histamine release, which results in vasodilatory properties. These properties may decrease venous return, thereby decreasing cardiogenic pulmonary vascular congestion and resultant respiratory distress. Morphine may be less tolerance inducing than the synthetic opioids, given its longer half-life and therefore, should not have to be titrated up as quickly as the synthetic opioids. If a patient is habituated on an opioid infusion, the hourly dose of the infusion can be used for bolus dosing. These agents have specific anxiolytic effects in addition to sedative effects but do not provide pain relief to the patient. Sedatives - Benzodiazepines Habituated Patients If adequate sedation is difficult to achieve in a narcotic or benzodiazepine resistant patient, consultation with the Clinical Pharmacy Specialist or Anesthesia/Pain Management Service should be considered.
Overzealous resuscitation of burn patients has been an emerging problem with patients frequently receiving volumes far in excess of those predicted quit smoking using laser therapy buy nicotinell american express. Excess fluid administration has been associated with an increased incidence of compartment syndromes of the abdomen quit smoking you fool buy cheapest nicotinell, extremities, and orbit as well as pulmonary edema and significant pericardial and pleural effusions. For patients with a difficult resuscitation course, use of colloid in the later phase of resuscitation may decrease total fluid administration and the risk of abdominal compartment syndrome. Serial bladder pressure measurement should be considered for patients at risk of developing abdominal compartment syndrome. The surgical goal is to debride all dead skin and achieve coverage of the wound as soon as possible. Ideally, this should occur immediately after hemodynamic stability is achieved and within 48 hours post-burn. Beyond this time, bacterial colonization of the wound is common leading to greater blood loss and graft failure. Burn excision can result in significant blood loss so patients are at risk for familiar transfusion related complications including coagulopathy, electrolyte imbalance, immunosuppression and acute lung injury. Intensive Care Unit Management Infectious Disease Burn patients are at increased risk of infection due to loss of the barrier function of the skin and an induced state of immunosuppression. Therefore, vigilance for changes in patient condition that may suggest infection and are not easily explained by the burn injury alone are warranted. The wound should be assessed for signs of infection including conversion of partial thickness wounds to full thickness, cellulitis, rapid eschar separation and frank tissue necrosis. Quantitative tissue culture and histologic analysis may be considered for diagnosis of wound infection. Pharmacokinetic changes are frequently observed in burn patients with altered volume of distribution and clearance leading to less than predicted serum levels and risk for inadequate antimicrobial therapy. The considerations for timing of tracheostomy in burn patients are similar to those for any critically ill patient requiring mechanical ventilation and are often subject to institutional bias given an overall lack of evidence. Evidence suggests that alterations in amino acid transport contribute to ongoing proteolysis and negative nitrogen balance. Hypermetabolism and catabolism persists nine months to as long as three years post injury. Nutritional needs are high but provision of optimal nutrition does not prevent loss of lean body mass. Use of early enteral feeding may be beneficial and careful attention should be paid to minimize the interruption of nutrition for operative procedures. Overfeeding is not beneficial and may lead to complications including fatty liver. Hyperglycemia is common and peak serum glucose concentrations and duration of hyperglycemia have been associated with increased mortality. Some studies have associated even modest levels of hyperglycemic with an increased risk of infection in burn patients. Pharmacologic interventions to address hypermetabolism include the anabolic steroid oxandrolone and the beta blocker propranolol. Oxandrolone has been demonstrated to improve wound healing and decrease hospital length of stay. Propranolol has been reported to attenuate the inflammatory response and decrease catabolism. The use of immunonutrition remains controversial with trials reporting mixed results. Transfusion the currently available data suggest that restrictive transfusion strategies are beneficial in burn patients. Conclusions 452 Critical care of the burn patient is challenging, resource intensive and multidisciplinary. In spite of an increased understanding of the pathophysiology and wide range of clinical factors that affect the care of burn patients, many questions regarding the best strategies for intensive care management of the thermally injured remain unanswered. Rae L, Fidler P, Gigran N: the Physiologic Basis of Burn Shock and Need for Aggressive Fluid Resuscitation. Immunonutrition has been demonstrated to improve survival in large prospective randomized trials.
Prophylactic intrapar tum antibiotics given intravenously to the mother can prevent group B streptococcus infection in the newbornbaby quit smoking lower blood pressure purchase generic nicotinell. Nosocomially acquired infections are an inherent risk in a neonatal unit quit smoking 6 years buy nicotinell 35mg mastercard,andallstaffmustadherestrictlytoeffectivehand hygienemeasurestopreventcrossinfection. Inneona tal intensive care, the main sources of infection are indwelling central venous catheters for parenteral nutrition,invasiveprocedureswhichbreaktheprotec tivebarrieroftheskin,andtrachealtubes. Coagulase negative staphylococcus (Staphylococcus epidermidis) is the most common pathogen, but the range of Listeria monocytogenes infection Fetal or newborn Listeria infection is uncommon butserious. Theorganismistransmittedtothemother in food, such as unpasteurised milk, soft cheeses 174 and undercooked poultry. It causes a bacteraemia, often with mild, influenzalike illness in the mother, and passage to the fetus via the placenta. Maternal infection may cause spontaneous abortion, preterm deliveryorfetal/neonatalsepsis. Characteristicfeatures aremeconiumstainingoftheliquor,unusualinpreterm infants, a widespread rash, septicaemia, pneumonia andmeningitis. If the skin surrounding the umbilicus becomes inflamed, systemic antibiotics are indicated. This can be removed by applying silver nitrate while protecting the surrounding skin to avoid chemical burns,orbyapplyingaligaturearoundthebaseofthe exposedstump. Gram-negative infections Earlyonset infection is acquired in the same way as groupBstreptococcalinfection. Lateonsetinfectionis usually from infected central venous lines, but occa sionally from seeding to the circulation from the intestines. Theriskto aninfantborntoamotherwithaprimarygenitalinfec tion is high, about 40%, while the risk from recurrent maternalinfectionislessthan3%. Pres entationisatanytimeupto4weeksofage,withlocal ised herpetic lesions on the skin or eye, or with encephalitisordisseminateddisease. Mortalitydueto localiseddiseaseislow,but,evenwithaciclovirtreat ment, disseminated disease has a high mortality with considerablemorbidityafterencephalitis. Ifthemother is recognised as having primary disease or develops genitalherpeticlesionsatthetimeofdelivery,elective Caesarean section is indicated. Women with a history ofrecurrentgenitalinfectioncanbedeliveredvaginally as the risk of neonatal infection is low and maternal treatment before delivery minimises the presence of virusatdelivery. A more troublesome discharge with redness of the eye may be due to staphylococcal or streptococcal infection and can be treated with a topicalantibioticeyeointment,e. Purulent discharge with conjunctival injection and swellingoftheeyelidswithinthefirst48hoflifemay beduetogonococcalinfection. Thedischargeshould be Gramstained urgently, as well as cultured, and treatment started immediately, as permanent loss of vision can occur. Chlamydia trachomatis eye infection usually presents with a purulent discharge, together with swellingoftheeyelids(Fig. The vaccination course needs to be completed during infancyandantibodyresponsechecked. Hypoglycaemia Hypoglycaemiaisparticularlylikelyinthefirst24hof lifeinbabieswithintrauterinegrowthrestriction,who are preterm, born to mothers with diabetes mellitus, 1 2 3 Neonatal medicine 175 4 10 Neonatal medicine are largefordates, hypothermic, polycythaemic or ill foranyreason. Growthrestrictedandpreterminfants have poor glycogen stores, whereas the infants of a diabetic mother have sufficient glycogen stores, but hyperplasiaoftheisletcellsinthepancreascauseshigh insulin levels. Manybabiestoleratelowbloodglucose levels in the first few days of life, as they are able to utiliselactateandketonesasenergystores. In infants at increased risk of hypoglycaemia, blood glucose is regularly monitored at the bedside. The concentration of the intravenous dextrose may need to be increased from 10% to 15% or even 20%. High concentrationintravenousinfusionsofglucoseshould begivenviaacentralvenouscathetertoavoidextrava sationintothetissues,whichmaycauseskinnecrosis and reactive hypoglycaemia. If there is difficulty or delayinstartingtheinfusion,orasatisfactoryresponse is not achieved, glucagon or hydrocortisone can be given. Typically, there are repetitive, rhythmic (clonic) movements of the limbs whichpersistdespiterestraintandareoftenaccompa nied by eye movements and changes in respiration. Ongoingorrepeated seizures are treated with an anticonvulsant, although their efficacy in suppressing seizures is much poorer thaninolderchildren.
It may be used to determine detection thresholds quit smoking you fool order nicotinell with paypal, understand resolution and assess and track linearity of detectors quit smoking quebec purchase nicotinell visa. Beads are suitable for labeling with mouse antibodies conjugated with violet fluorochromes, and for use as a compensation or general reference standard for detectors off of the violet laser. The Simply Cellular anti-Mouse for Violet Laser standard is supplied as 2 populations: 1 blank and 1 high-binding antiMouse IgG (Fc specific) population. Labeled microspheres may be used as single-population reference standards or in conjuction with an unlabeled population for compensation purposes. Bangs Flow Cytometry Standards are 7-9m in diameter (unless otherwise noted) to approximate the size of human lymphocytes. Our Small Bead Calibration Kits allow operators to verify the resolution capabilities of the flow cytometer, and to establish appropriate instrument settings for these analyses. Particle Concentration Nanobead Calibration Kit (50nm, 100nm) Submicron Bead Calibration Kit (0. These beads fluoresce over a broad range of the spectrum, allowing them to be used as count standards in multiple detectors. We hope that you find this catalog to be helpful as you consider products for your work, and invite you to contact us if we may address any questions or be of assistance in formulating solutions to meet your specific needs. As there are many varieties of microspheres available, it is important to think about the demands of the application when selecting a microsphere. Physical and optical properties should be considered in the context of handling and detection, and thought should also be given to requirements for diameter and size distribution, composition, surface chemistry and any other needed properties. Property Size Composition Surface chemistry Special properties Considerations Diameter, Uniformity / distribution Density, Refractive index, Hydrophobicity / -philicity, Nonspecific binding, Autofluorescence Reactive groups, Level of functionalization, Charge Visible dye / fluorophore, Superparamagnetic Particle Size Microsphere size may be critical to the proper function of an assay, or it may be secondary to other characteristics. Considering traditional diagnostic methods, the test or assay format commonly dictates particle size, such as the use of very small spheres (~0. In magnetic separations, particularly those involving capture and elution of target, the exact size of the magnetic particle may be unimportant provided that the particles are in some general size range and offer desired separation characteristics. Small-diameter spheres present more surface area per unit mass, while larger spheres present more surface area per bead. Size also affects ease of handling, process considerations (such as the method used for separations [centrifugation, dialysis, filtration]) and the amount of reagent needed for coating. For most products, the mean diameter of your particles will be printed on the label with the standard deviation. These materials possess different physical and optical properties, which may present advantages or limitations for different applications. Polymer beads are generally hydrophobic, and as such, have high protein binding abilities. During synthesis, functional monomers may be co-polymerized with styrene to develop beads with reactive surface groups. Functional groups may be used in covalent binding reactions and also aid in stabilizing the suspension. Consequently, aqueous silica suspensions rarely require the use of surfactants or other colloidal stabilizers. Carboxyl- and amine-functionalized silica spheres are available for use in common covalent coating protocols, and plain silica microspheres may be modified using a variety of silanes to generate functional groups or alter surface properties. Polymer spheres (and some polymer-based magnetic spheres) are often internally dyed via organic solvent swelling and many standard products are available. Many surface- or internally-labeled fluorescent beads are also available as specialized flow cytometry standards. Various types of superparamagnetic microparticles are available, with different matrices, magnetite content, surface groups, etc. For new assays or applications, magnetic beads should be evaluated with application demands in mind. Handling and Storage Our microspheres are synthesized in water and should be stored in aqueous environments. Deionized water is the best suspending medium for uncoated spheres as high concentrations of ions may result in aggregation.
In a young quit smoking now for free order cheap nicotinell line, healthy patient with unilateral iliac artery occlusive disease quit smoking marijuana purchase nicotinell with visa, when angioplasty is not a treatment option, an aortofemoral bypass offers excellent long-term relief. Aortobifemoral bypass, while clearly the most risky of the treatment options offered, provides the best long-term patency. In elderly patients with severe comorbidities who are considered at high risk for complications, extra-anatomic bypasses (femorofemoral or axillofemoral bypasses) offer fair long-term patencies while not subjecting the patient to the risks of general anesthesia. Femorofemoral bypass offers the additional benefit of not disturbing sexual function; however, femorofemoral bypass is not an option in a patient with bilateral iliac artery disease. Neither common femoral and profunda femoral endarterectomies nor femoropopliteal bypass is beneficial in this patient who has aortoiliac disease. Which of the following is the recommended treatment for stage A (superficial and submucosal) transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder Which of the following is the optimal management of bilateral undescended testicles in an infant Chorionic gonadotropin therapy for 1 month; operative placement into the scrotum before age 2 if descent has not occurred c. Observation until age 2; operative placement into the scrotum if descent has not occurred d. Observation until age 5; if no descent by then, plastic surgical scrotal prostheses before the child enters school. No therapy; reassurance of the parent that full masculinization and normal spermatogenesis are likely even if the testicle does not fully descend 436. Which of the following is the most accurate method in obtaining a diagnosis of testicular cancer On physical examination, he is noted to have a high-riding, firm, and markedly tender left testis. Manual detorsion of the left testicle with external rotation toward the thigh; orchiopexy if the condition recurs b. Manual detorsion of the left testicle with internal rotation toward the thigh; orchiopexy if the condition recurs c. A 45-year-old woman presents with a 7-cm renal cell carcinoma with radiologic evidence of abdominal lymph node involvement with no distant metastases. A 60-year-old man seeks medical attention because of recurrent urinary tract infections. The patient also reports a history of increasing difficulty in urination (decreased flow, straining, and hesitancy) over the last several months. The left ureter is partially transected (50% of circumference) during the course of a difficult operation on an unstable, critically ill patient. Placement of an external stent through the proximal ureteral stump with delayed reconstruction b. Placement of a catheter from the distal ureter through an abdominal wall stab wound d. Immediate placement of a Foley catheter through the urethra into the bladder to align and stent the injured portions c. Immediate reconstruction of the ruptured urethra after initial stabilization of the patient d. Immediate exploration of the pelvis for control of hemorrhage from pelvic fracture and drainage of pelvic hematoma. Upon further questioning he also complains of frequency, urgency, dysuria, and a decreased urinary stream. Digital rectal examination demonstrates exquisite tenderness on the anterior aspect. Laboratory examination reveals leukocytosis and findings on urinalysis are consistent with a bacterial infection. It is most prevalent among men with a history of heavy smoking and is usually multifocal and superficial, even when recurrent. When the disease is still superficial, transurethral resection of visible lesions and intravesicular chemotherapy are most often recommended. More radical surgical resection, systemic chemotherapy, and radiation are reserved for advanced stages of the disease. This procedure is completely noninvasive and uses a device that delivers convergent shockwave energy to the stone under fluoroscopic guidance.
Nicotinell 17.5mg on-line. Quitting Smoking - Day 2 (2014).