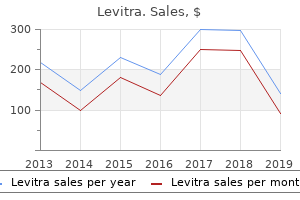
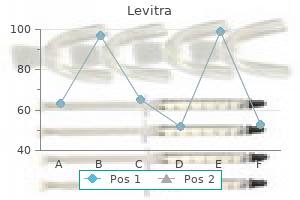
Levitra
"Order levitra with mastercard, erectile dysfunction causes mnemonic".
By: K. Abbas, M.A., M.D., M.P.H.
Medical Instructor, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine
Inhaled Corticosteroids · Inhaled corticosteroids are the most commonly prescribed maintenance therapy for asthma weight lifting causes erectile dysfunction purchase genuine levitra online. Naga · Absence of fever erectile dysfunction kegel exercises best levitra 20 mg, tachypnea, increased work of breathing, and auscultatory abnormalities, bacterial pneumonia is unlikely. Respiratory Disorders 303 · Possible causes: infection, chyle, blood, malignancy, and drug exposures. Prolonged observation (minimum 8 h) in setting able to manage respiratory failure is optimal. Pneumothorax Causes · Primary spontaneous pneumothorax Occurs without trauma or underlying cause More frequently in tall, thin male, thought to have subpleural bleb Family history is positive in many patients · Secondary pneumothorax Underlying lung disease Trauma Loud music (air pressure) Catamenial pneumothorax (unusual condition associated with menses due to passage of intra abdominal air through a diaphragmatic defect) Clinical presentation · the onset is abrupt, and the severity depends on lung collapse. Foreign Body Aspiration Background · Nuts especially peanuts are one 1/3 of cases. Complications · Retained foreign body is associated with bronchiectasis, hemoptysis and lung abscess. Congenital Pulmonary Malformations Sequestration · Extralobar: more common in males; 65 % in the left lung, covered by pleura, fed by systemic artery and drained via systemic vein, may be associated with diaphragmatic hernia and colonic duplication. Pulmonary Abscess Background · Cystic area due to necrotic lung tissue at least 2 cm in diameter. Clinical presentation · Fever · Cough · Sputum production · Hemoptysis Respiratory Disorders 305 · Treatment is surgical removal. Vascular ring/sling · May involve airway and or esophagus · Variable severity and timing of presentation · May cause stridor, cough, apnea, and dysphagia · Imaging chest is helpful, more common with right aortic arch Congenital pulmonary adenomatoid malformation, lobar emphysema, and diaphragmatic hernia · Least common · May be seen on fetal imaging (U/S) and then resolve spontaneously · May cause severe respiratory distress and require surgery · Consult pulmonology - Involvement of paranasal sinuses. Clinical presentation · Productive cough is the most common symptom of bronchiectasis. Diagnosis · Pulmonary function testing may show obstruction, restriction, and combinations depending on etiology. Clinical presentation · Hundred percent of children have productive cough, sinusitis, and otitis media. Diagnosis · the gold standard test is documentation of abnormal cilia ultrastructure (absent, abnormal dynein arms, radial spokes, doublet arrangements) on nasal and bronchial biopsies or scraping viewed on electron microscope. Treatment and prognosis · Establishing the primary cause is of critical importance and is best undertaken with direction from a pediatric pulmonologist. Pulmonary Hemosiderosis Background · Repeated episodes of intra-alveolar bleeding that lead to abnormal accumulation of iron as hemosiderin in alveolar macrophages. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Background · Recognized since 1960 following invention of positive pressure ventilation for premature infants and their survival. Cystic Fibrosis Genetics · the most common life shortening autosomal recessive disease due to mutation on the long arm of chromosome 7. The passive movement of water is decreased and airway secretions are dehydrated with very low surface liquid layer. Cilia become compressed inhibiting ciliary clearance and cough clearance, bacteria thrive; immune function is also abnormal at the airway surface. Repeated and chronic infection leads to airway damage and bronchiectasis in the lung and dysfunction of other organs. Clinical presentation · Pulmonary: Cough is the most constant symptom dry at times, frequently productive. Sarcoidosis Background · Sarcoidosis is a noncaseating granuloma multisystem disease. Clinical presentation · Approximately 5 % of cases are asymptomatic and incidentally detected by chest radiography. Respiratory Disorders 309 · Pancreatic function testing: fecal elastase preferred method. Naga · the disorder can occur at any age but is most common in the preschool age group (26 years) and adolescents. Risk factors and associated conditions · Adenotonsillar hypertrophy · Obesity · Craniofacial abnormalities, specifically midface hypoplasia and micrognathia · Hypotonia. Clinical presentation · Loud nightly snoring with observed apnea spells · Parents may note that the child is a restless sleeper · Sweats while sleeping · Sleeps in an abnormal position with the neck extended · Chronic mouth breathing with chronic nasal congestion · Morning headaches · Excessive daytime sleepiness is more common among older children. Overnight saturation monitoring can be very helpful to recognize issues that require additional support. Usefulness of chest radiographs in children with acute lower respiratory tract disease.
Diseases
- Brachydactyly small stature face anomalies
- Blepharophimosis nasal groove growth retardation
- Kennerknecht Sorgo Oberhoffer syndrome
- Iridocyclitis
- Hypokalemic periodic paralysis
- AREDYLD syndrome
Mutation of p53 is one of the most common genetic changes associated with cancer impotence of organic origin purchase levitra 20 mg free shipping, and is estimated to occur in half of all malignancies impotence injections medications generic levitra 10 mg overnight delivery. Mutation of p53 is linked to a variety of malignancies, including brain tumors (astrocytoma); carcinomas of the breast, colon, lung, cervix, and anus; and osteosarcoma. As more mutations in the genome occur, the risk for malignant transformation increases. Oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes provide the stimulatory and inhibitory signals that ultimately regulate the cell cycle. The function of the clock in normal tissue is to integrate the signal input and to determine if the cell cycle should proceed. The clock is composed of a series of interacting proteins, the most important of which are cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases. Cyclins (especially cyclin D1) and cyclin-dependent kinases promote entry into the cell cycle and are overexpressed in several 2195 cancers, including breast cancer. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors have been identified as important negative regulators of the cell cycle. In the first resting phase G1, the cell grows in size and decides to commit to the cell cycle or remain in a resting state. Next, the cell enters the second resting phase G2, in which the cell prepares to divide. Four checkpoints exist within the cell cycle, one in each phase of the cell cycle and serve as quality control checkpoints. The cell will not proceed to the next phase if all requirements for the current phase are not met. These complexes lead to the activation of other proteins that are responsible for the specific events of each phase of the cell cycle. The restriction site is controlled by retinoblastoma (Rb) complexed to a transcription factor called E2F. A cell may alternatively withdraw into the G0 phase in the presence of anti-mitogenic or the absence of mitogenic factors. The secondary defenses include apoptosis (programmed cell death or suicide) and cellular senescence (aging). Overexpression of oncogenes responsible for apoptosis may produce an "immortal" cell, which has increased potential for malignancy. The most common chromosomal abnormality found in lymphoid malignancies is the t(14;18) translocation. Translocation of this proto-oncogene to chromosome 14 in proximity to the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene leads to overexpression of bcl-2, which decreases apoptosis and confers a survival advantage to the cell. Loss of p53 disrupts normal apoptotic pathways, imparting a survival advantage to the cell. Apoptosis may also play an important role as a mechanism of inherent resistance to chemotherapy. In cancer cells, the function of telomeres is overcome by overexpression of an enzyme known as telomerase. Telomerase replaces the portion of the telomeres that is lost with each cell division, thereby avoiding senescence and permitting an infinite number of cell doublings. As information regarding the role of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes accumulated, it became evident that a single mutation is probably insufficient to initiate cancer. Thus, several detectable genetic mutations may be present in an established tumor. Early mutations are found in both premalignant lesions and in established tumors, whereas later mutations are found only in the established tumor. This theory of sequential genetic mutations resulting in cancer has been demonstrated in colon cancer. In colon cancer, the initial genetic mutation is believed to be loss of the adenomatous polyposis coli gene, which results in formation of a small benign polyp. Oncogenic mutation of the ras gene is often the next step, leading to enlargement of the polyp. Loss of p53 is thought to be a late event in the development and progression of the malignancy.
Purchase levitra pills in toronto. Erectile Dysfunction: Treatment Options Beyond Pills.
Algorithm for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in established disease (>6 months) impotence nutrition buy levitra with amex. Monitor liver injury tests periodically erectile dysfunction laser treatment cheap generic levitra uk, but a liver biopsy is recommended during therapyonlyinpatientswithpersistentlyelevatedhepaticenzymes. The drugs contain a black-box warning about increased risk of lymphoproliferative and other cancers in children and adolescents treated with thesedrugs. BindingofrituximabtoBcells results in nearly complete depletion of peripheral B cells, with a gradual recovery overseveralmonths. Corticosteroids ·Corticosteroids have anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties. They interfere with antigen presentation to T lymphocytes, inhibit prostaglandin and leukotriene synthesis, and inhibit neutrophil and monocyte superoxide radical generation. Depotforms(triam- cinolone acetonide,triamcinolone hexacetonide,and methylprednisolone acetate) provide 2 to 6 weeks of symptomatic control. In patients 42 acute coronary Syndromes chapter 5 75yearsandolder,giveenoxaparin0. Arterial dilation also relieves coronary artery vasospasm and improves myocardialbloodflowandoxygenation. Theusual dose is5to10mcg/minby continuousinfusion,titratedup to 100mcg/minuntil reliefofsymptomsorlimitingsideeffects(eg,headacheorhypotension). Avoid nifedipine because it causes reflex sympatheticactivation,tachycardia,andworsenedmyocardialischemia. P2Y12 Inhibitors ·When an initial invasive strategy is selected, there are two initial options for dual antiplatelettherapydependingonchoiceofP2Y12inhibitor: 1. Other arrhythmias that usually do not require drug therapy are not discussed here (eg, prematureatrialcomplexes,sinusarrhythmia,sinustachycardia). Additionalassociated disorders include acute pulmonary embolus and chronic lung disease, resulting in pulmonaryhypertensionandcorpulmonale,andstatesofhighadrenergictonesuch asthyrotoxicosis,alcoholwithdrawal,sepsis,andexcessivephysicalexertion. First, evaluate need for acute treatment (usually with drugs that slow ventricular rate). For patients at low risk for stroke, either no antithrombotictherapyoraspirinisrecommended;however,notherapyispreferred. Algorithm for the treatment of acute (top portion) paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia and chronic prevention of recurrences (bottom portion). Note: For empiric bridge therapy prior to radiofrequency ablation procedures, do not use calcium channel blockers (or other atrioventricular [aV] nodal blockers) if the patient has aV reentry with an accessory pathway. It is highly effective and curative, rarely resultsincomplications,obviatesneedforchronicantiarrhythmicdrugtherapy,and iscosteffective. If ineffective,institutestrategiestoincreaseheartrateandshortenventricularrepolarization (ie, temporary transvenous pacing at 105120 beats/min or pharmacologic pacingwithisoproterenolorepinephrineinfusion). Otherdrugsthat have been used successfully (with or without -blockers) include fludrocortisone, anticholinergics (scopolamine patches and disopyramide), -adrenergic agonists (midodrine),adenosineanalogues(theophyllineanddipyridamole),andselective serotoninreuptakeinhibitors(sertralineandparoxetine). P econdary: results from respiratory failure in which lack of ventilation leads to S severehypoxemia,hypotension,andcardiacarrest. Potentiallyreversiblecausesinclude:(1)hypovolemia,(2)hypoxia,(3)acidosis, (4) hyper- or hypokalemia, (5) hypothermia, (6) hypoglycemia, (7) drug overdose,(8)cardiactamponade,(9)tensionpneumothorax,(10)coronarythrombosis, (11)pulmonarythrombosis,and(12)trauma. Raise the head of the bedto30degreestoreduceriskforaspiration,ventilator-associatedpneumonia,and cerebraledema. Secondary forms of dyslipidemia also exist, and severaldrug classesmay affect lipid levels (eg, progestins, thiazidediuretics,glucocorticoids,-blockers,isotretinoin,proteaseinhibitors,cyclosporine,mirtazapine,andsirolimus). Encouragephysicalactivityofmoderateintensity30minutesaday for most days of the week. Carbohydrates should derive from foods rich in complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Takingtheniacin dose with meals and slowly titrating the dose upward may minimize these effects.
Apricot Fruit (Apricot). Levitra.
- How does Apricot work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Dosing considerations for Apricot.
- Asthma, cough, constipation, bleeding, and infertility.
- What is Apricot?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96915