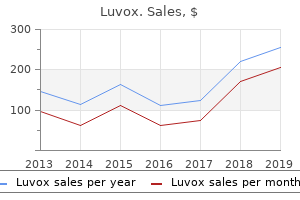
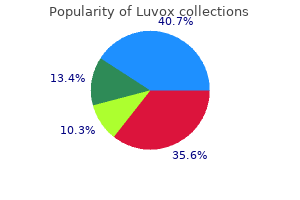
Luvox
"Buy online luvox, anxiety symptoms journal".
By: N. Renwik, M.A., Ph.D.
Program Director, University of New England College of Osteopathic Medicine
Summer-run Steelhead migrate higher in river networks anxiety 3rd trimester purchase luvox 50 mg online, entering freshwater between late spring and fall anxiety symptoms in teens cheap 100mg luvox with mastercard, and overwinter before spawning the following spring. Because they spend more time in freshwater, summer-run populations of steelhead may be more sensitive to changes in flow and temperature regimes across river networks. For example, higher temperatures will increase the metabolic costs accrued by summer-run steelhead during the several months that they hold in streams prior to spawning. For example, anadromous individuals can survive ephemeral periods of unsuitability in their natal streams while they are away at the ocean, whereas residents can survive in years where conditions are poor along migratory routes. Walleye Pollock are likely to be sensitive to increases in sea surface temperature, particularly since Puget Sound is the southern limit of their range. Cooler waters support higher levels of Walleye Pollock recruitment and larval survival because cooler waters promote increased production of primary prey species for pollock. For Walleye Pollock in the Bering Sea, it was found that though warmer spring conditions during spawning season enhanced early survival of larvae, continued higher temperatures led to poor feeding conditions and reduced recruitment the following year. Thus, predicted warming could result in decreases in prey abundance and declines in recruitment, larval survival, and productivity and potential northward range shifts of Walleye Pollock. Westslope Cutthroat Trout spawn in the spring and are thus sensitive to the timing and magnitude of snowmelt and the accompanying flood pulse. Winter floods do not pose a risk to Westslope Cutthroat Trout embryos, but it is possible that increased severity of fall and winter floods could negatively affect overwintering juveniles (although quality data on this topic are lacking due to the challenge of monitoring survival in flood prone systems). Like many stream rearing salmonids, Westslope Cutthroat Trout can be vulnerable to sub-optimally warm temperatures during base flow periods in late summer and fall. During these low flow periods, terrestrial subsidies typically comprise the dominant food source for this species, and may be critical for enabling fish to offset the elevated metabolic costs caused by higher water temperatures. Factors that mediate the magnitude of terrestrial subsidies, such as land use practices in riparian areas, can in turn mediate the sensitivity of trout to altered thermal regimes. Warming may have some positive effects by increasing the amount of high elevation habitat capable of rearing juveniles. The primary source of decline for Westslope Cutthroat Trout has been hybridization with Rainbow Trout. Genetically pure Westslope Cutthroat Trout often exist in cold tributary streams and show subtle signs of being better adapted to cold temperatures than Rainbow Trout when studied in the laboratory. This suggests warming temperatures could increase hybridization by allowing Rainbow Trout to invade cold headwater streams. However, in an analysis across a large watershed, environmental factors were not as important as demographic factors in determining levels of hybridization. Westslope Cutthroat Trout are unique among the cutthroat subspecies in that they exhibit an anadromous, coastal-roaming ecotype. Populations with this life history may be less sensitive to altered flow and thermal regimes in freshwater because there is less cumulative exposure to freshwater conditions and individuals at sea can survive ephemeral climate-related disturbance such as thermal stress events or periods of low flow. White Sturgeon likely exhibit physiological sensitivity to warmer water temperatures, and increasing temperatures may reduce spawning success and/or increase disease risk and mortality. White Sturgeon are also sensitive to declining spring and summer streamflows, which reduce spawning habitat and annual recruitment; loss of spawning habitat and reduced recruitment associated with lower streamflows is a particular concern for impounded portions of the Columbia River. Shifts in ocean conditions may also affect prey availability for young White Sturgeon in estuarine environments, and reduced prey availability has been linked with undermined White Sturgeon growth. The main sensitivity of Yelloweye Rockfish to climate change is likely to stem from changes to their prey base. Deepwater coral habitat, which is particularly preferred by Yelloweye Rockfish, may also decrease due to acidification, further reducing available habitat. Decreased oxygen levels may have direct physiological effects on Yelloweye Rockfish, leading to higher levels of mortality across various life stages. Although little is known about this species, caddisflies in the genus Allomyia are restricted to high-elevation coldwater streams in the larval and pupae stages, where they build protective cases of silk and small pieces of rock. Climate sensitivity for this species is likely tied primarily to their specialized habitat, which is particularly vulnerable to warming air and water temperatures, low summer flows, sedimentation from upstream erosion, and habitat fragmentation from nearby human activity. Goereilla Baumanni is a species of caddisfly found only in few sites and always in very low numbers in Washington, Idaho, and Montana. The close association of Goereilla Baumanni to organic muck may make this species particularly sensitive to high temperatures, drought, and precipitation changes which may make these areas more likely to dry out. Caddisflies in general are often considered an indicator of highquality streams, suggesting that they are particularly vulnerable to changes in their habitat.
The tip of the pig-tail catheter will curl up within the air cavity and helps hold the drain in (Fig anxiety head pressure buy discount luvox 50 mg on line. Stitches are not usually required anxiety blanket order 50 mg luvox with mastercard, but the drain can be dressed with opposing clear adhesive dressings. The passage of meconium often indicates fetal distress, but in the breech presentation may be normal. The response of the infant to intrapartum asphyxia is to gasp, and if meconium is present it will be aspirated deep into the bronchi. Once respiration begins, distal migration of the meconium into small airways occurs. Typically, the infant is born covered in meconium-stained liquor and has meconium staining of the umbilical cord, skin and nails. Respiratory distress may be mild initially, becoming rapidly more severe after several hours. If asphyxia has occurred, the baby may also show signs of early-onset encephalopathy (see Chapter 22). Pathogenesis and aetiology Meconium causes a number of anatomical and physiological problems that make lung function worse: Plugging of the airways, with consequent atelectasis. Radiology Chest radiographs show hyperinflation (flat diaphragms, widening of rib spaces) with diffuse patchy opacities throughout both lung fields (Fig. There is controversy as to whether a neonatal paediatrician should attend every delivery where there is meconium staining of the liquor. It is important, however, that an experienced neonatal paediatrician be present for the delivery if thick meconium is present, especially if there are signs of intrapartum fetal distress. In such cases, the baby is intubated with a wide-bore suction catheter or endotracheal tube and the trachea is suctioned clear. Treatment of established meconium aspiration syndrome the treatment will be the same as for respiratory distress (see above). Particular emphasis or consideration should be given to the following points: Humidification of inspired oxygen. Postural drainage positioning, suctioning of airways and chest percussion are of unproven benefit. Both conventional and high-frequency ventilation can be used with multiple strategies to achieve normal gaseous exchange and prevent complications such as air trapping and air leaks, which are common in such infants. In some centres lavage with surfactant is practiced, but its efficacy is not fully established. Pulmonary hypoplasia For adequate fetal lung development the fetus must be able to make breathing movements and move a column of amniotic and lung fluid up and down the trachea and main bronchi. Hypoplasia may therefore be due to: Failure of fetal breathing (neuromuscular disorders). Lack of liquor (oligohydramnios) due to renal or urethral abnormalities or prolonged preterm rupture of the membranes causing leakage of amniotic fluid. Clinical features the infant develops severe respiratory distress from birth, with marked hypoxia, hypercapnia and metabolic acidosis. The lungs are very stiff and there is little chest movement with mechanical ventilation. Severe lung hypoplasia is incompatible with life, and less severe forms contribute towards chronic ventilator dependency and bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Management and prognosis Management of lung hypoplasia starts antenatally if diagnosed earlier, and includes counselling by the obstetrician, neonatologist, clinical geneticist and surgeon (if appropriate). Pulmonary hypoplasia results from a large number of different conditions, and hence the prognosis is governed mainly by the aetiology and associated anomalies. Lung biopsy may be difficult to perform safely while the infant is alive, and hence postmortem studies should be made where possible. Where permission for a full autopsy is not granted an open or needle biopsy of the lung obtained soon after death may provide a tissue diagnosis. Pulmonary haemorrhage Pulmonary haemorrhage has a characteristic clinical presentation in newborn infants, with cardiovascular collapse associated with an outpouring of bloodstained fluid from the trachea and mouth.
Order 100mg luvox fast delivery. No More Free Consultancy About Anxiety And Depression In || اردو || हिंदी.

Select and self the monosomic F anxiety symptoms skipped heart beats discount 100 mg luvox overnight delivery, plants and determine the segregation ratios for the F2 generation anxiety symptoms 6 dpo buy luvox 100 mg with mastercard. Aratio of approximately 97 resistant:3 susceptible indicates the resistance gene is located on that chromosome. Only one out of the 21 crosses (21 monosomics) will segregate in an abnormal manner. The ratio may vary slightly depending on the chromosome involved and the environment where the plants were grown. Susceptible plants occur at a very low frequency (approximately 3%) in the F2 population of the critical cross because male gametes with 20 chromosomes have approximately a 3% fertilization frequency and gametes with 21 chromosomes have a frequency of 97%. The F2 plants can be advanced to obtain F3 lines, which is more desirable when the resistance is recessive. The response of the F3 lines can be correlated with the chromosome constitution of the parental F2 plants. Other low frequency chromosome arrangements in each of the response classes are possible-for example, spontaneous monosomics for other chromosomes and secondary aneuploids. Monotelosomic (deficient in one entire chromosome and one arm of the homolog) plants, if available, are preferred to monosomic plants because they minimize the chances of monosomic shift. In addition, the F1 hybrids with 2N = 41 + a telosome can be used to locate the gene in a chromosome arm and to estimate the distance of the gene from the centromere (336). A new resistance gene must be located on the chromosome before allocating a permanent designation. Although the individual plants in a line may be homozygous, an unselected parent line may be genetically heterogenous. Keep selfed seed of the parent plant for comparison with segregating progenies and with the original unspecified bulk line. Keep the number of races low (ideally one) in the mixture to be used for field inoculations. It is often useful to determine if the rust in the nursery has the same virulence as the isolates used to inoculate the nursery. Parents Monosomic (susceptible) X Resistant cultivar Q Resistant d Select monosomic F, plants 3 Resistant: 1 Susceptible Resistance gene not on the monosomic chromosome or About 97 Resistant: 3 Susceptible Resistance gene on the monosomic chromosome Figure 18. The pattern lor Inheritance of resistance lor monosomic wheats crossed with a resistant cultivar. Many gene pyramids have been successful, although some have quickly been rendered ineffective. At least in a few cases, Lr13 and 16 (332), Lr2a and 16 (117), Lr13 and 34 (101), Lr27 and 31 (351), and undesignated genes for stripe rust resistance (118, 344) seem to have an additive effect in combination. Such durable resistance can be combined with other genes to provide some diversity. The breeding methodology for developing gene pyramids involves the identification of genetically different sources of resistance, followed by the incorporation of these resistances into a high yielding and adapted background. This can be accomplished by any selection methodology (pedigree or bulk breeding) following simple, top (three-way), or double crosses. Two to three thousand plants are space2 grown in well watered, high fertility conditions under rust epidemics. Individual plants are identified on the basis of rust resistance and agronomic suitability. Progeny of selected F2 plants are grown in solid stands in 2-m, two or three-row plots. Selection is based on the plot and then individual selected spikes in the plot are bulked. Individual plants are selected on the basis of rust resistance, acceptable agronomic characters, and spike fertility.
In experimental practice anxiety symptoms definition generic 100mg luvox with amex, this air-bridge can be achieved by placing on-chip wirebonds which go over the center pin but connect the lower and upper ground planes anxiety symptoms constipation buy luvox master card. We can perform simple 4 K transmission experiments with Nb resonators to demonstrate the effect of the wirebonding. By adding on-chip wirebonds at the center of the sample and repeating the measurements, we find the transmission spectrum given by figure 5. Other resonances are due to copper traces on the sample board holder as well as the sample box, which will be the subject of the next section. We need both a sample holder and box which suppress parasitic resonances and can be easy to use and convert into microwave coaxial cable lines for input and output through the cryostat. The upper and bottom ground planes are connected by copper coated vias (mil hole size) which are drilled throughout. These vias reduce the parasitic modes which can arise due to imbalances in the top and bottom copper ground planes. This resonance corresponds to a whispering gallery mode of the box, removable by filling up the three-dimensional cavity within the sample holder. A lot of the structure is actually removed from the system by modifying the octobox with a flip-chip combined with a larger copper back plate. This makes the geometry more symmetric and limits any modes which may arise due to differences in the dielectric on top and below the copper traces. The larger copper back plate serves to fill up up most of the volume within the box, removing whispering gallery and other 3D resonator modes. This particular copper octobox is designed to fill up the entire space in between the box and the sample lid. The development of this flip-chip and reduced mode volume is now incorporated into all of our experiments. The key details of the cryogenic setup pertain to the reduction of heat and noise that can reach the sample from room temperature or microwave cryogenic amplifiers. The long cryogenic lines give an additional dB resulting in a total line attenuation of dB. This is suppressed with the use of the flip-chip and filled octobox design, with which we measure the transmission spectra shown in (b). It is not advisable here to use attenuation between the output port of the cavity and the amplifier as the whole point of the amplifier is to increase the amount of signal. However, a microwave circulator allows for the signal to pass through to the amplifier without being attenuated, while taking all the reflected noise off of the amplifier and dumping it in a termination instead of reaching the sample. The location of the microwave circulator can affect the mean photon number in the cavity. The mean photon number was extracted using fits to strongly driven vacuum Rabi spectra []. The dB at K is chosen to afford enough current for biasing the transmon across a single. There are a total of four cryogenic lines: input, output, left flux-bias and right flux-bias. Normally, the qubit frequencies are detuned from the cavity frequency, and hence the qubit drives are off-resonant and need to be higher in power. When performing heterodyne detection, a further digital demodulation is performed known as digital homodyne. The outputs are then a digital I and a digital Q, which can then be combined to give an amplitude A = I + Q or a phase = tan- (I/Q). Although such a piece of hardware is not the only way of producing good dual-quadrature control pulses, it is very reliable in terms of timing, bandwidth, and linearity. Current investigations are being performed to build a piece of hardware that takes a single carrier frequency, splits it into two signals in quadrature, and mixes in a modulated pulse shape. Overall, the fabrication techniques are quite simple and reliable to within % of all parameters.