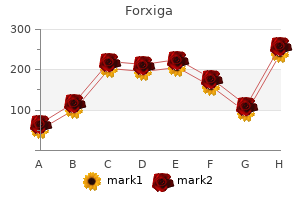
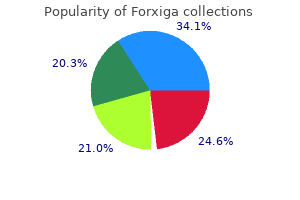
Forxiga
"Discount 10mg forxiga with mastercard, diabetes belt".
By: F. Bufford, MD
Vice Chair, Idaho College of Osteopathic Medicine
The effect of labour and maternal oxytocin infusion on fetal plasma oxytocin concentration diabetes test in pharmacy purchase forxiga 5mg with visa. The effect of early labour diabetes medications kidney disease 5mg forxiga sale, maternal analgesia and fetal acidosis on fetal plasma oxytocin concentrations. Stimulation of fetal hypothalamus induces uterine contractions in pregnant rats at term. A parturition-associated nonsynaptic coherent activity pattern in the developing hippocampus. Newborn behaviour to locate the breast when skin-to-skin: A possible method for enabling early self-regulation. Postpartum maternal oxytocin release by newborns: Effects of infant hand massage and sucking. Outcomes of planned home births and planned hospital births in low-risk women in Norway between 1990 and 2007: A retrospective cohort study. Severe adverse maternal outcomes among low risk women with planned home versus hospital births in the Netherlands: Nationwide cohort study. Outcomes associated with planned home and planned hospital births in low-risk women attended by midwives in Ontario, Canada, 2003-2006: A retrospective cohort study. Risk of severe postpartum hemorrhage in low-risk childbearing women in New Zealand: Exploring the effect of place of birth and comparing third stage management of labor. Outcomes of physiological and active third stage labour care amongst women in New Zealand. Holistic physiological care compared with active management of the third stage of labour for women at low risk of postpartum haemorrhage: A cohort study. Systematic review: the clinical effectiveness of physiological (expectant) management of the third stage of labor following a physiological labor and birth. Randomized controlled trial of early skin-to-skin contact: Effects on the mother and the newborn. Analgesic effects of skin-to-skin contact and breastfeeding in procedural pain in healthy term neonates. Mother and newborn baby: Mutual regulation of physiology and behavior-a selective review. Maternal contact differentially modulates central and peripheral oxytocin in rat pups during a brief regime of mother-pup interaction that induces a filial huddling preference. The peptide that binds: A systematic review of oxytocin and its prosocial effects in humans. Individual differences underlying susceptibility to addiction: Role for the endogenous oxytocin system. Mechanisms underlying epigenetic effects of early social experience: the role of neuropeptides and steroids. Prolactin secretion patterns: Basic mechanisms and clinical implications for reproduction. Central vasopressin and oxytocin release: Regulation of complex social behaviours. Maternal analgesia during labor disturbs newborn behavior: Effects on breastfeeding, temperature, and crying. Timing of breastfeeding initiation and exclusivity of breastfeeding during the first month of life: Effects on neonatal mortality and morbidity-a systematic review and metaanalysis. Different patterns of oxytocin, prolactin but not cortisol release during breastfeeding in women delivered by caesarean section or by the vaginal route. Short-term effects of early suckling and touch of the nipple on maternal behaviour. Breastfeeding and child cognitive development: New evidence from a large randomized trial. The burden of suboptimal breastfeeding in the United States: A pediatric cost analysis. Oxytocin, prolactin, milk production and their relationship with personality traits in women after vaginal delivery or cesarean section. Breastfeeding is associated with reduced perceived stress and negative mood in mothers. Postnatal oxytocin treatment and postnatal stroking of rats reduce blood pressure in adulthood. Separation distress call in the human neonate in the absence of maternal body contact.
Vision Anatomy Vision is the special sense of sight that is based on the transduction of light stimuli received through the eye diabetes prevention program nejm purchase forxiga australia. The primary structure associated with vision is the eyeball but there are also several accessory structures that are critical for our ability to see the world around us diabetes test for last 3 months forxiga 10mg overnight delivery. The bony orbit surrounds the eyeball, protecting it and serving as an anchor for soft tissues that support the eyeball. Eyelids, with lashes at their leading edges, help to protect the eye from abrasions by blocking particles that may land on the surface of the eye. The inner surface of each eyelid contains a thin membrane called the palpebral conjunctiva which is continuous with the ocular conjunctiva which extends over the white areas of the eye, connecting the eyelids to the eyeball. The production of tears by the lacrimal gland washes the surface of the eyeball to prevent the accumulation of foreign material and nourish the cells of the cornea. The lacrimal gland, found in the superolateral portion of the orbit, releases fluid through lacrimal ducts onto the surface of the eye where the fluid flows to the medial corner of the eye and is collected via the lacrimal punctum. The collected fluid moves through the lacrimal canaliculus, into the lacrimal sac, through the nasolacrimal duct, into the back of the nasal cavity, and down into the throat. Muscles of the Eye Movement of the eye within the orbit is accomplished via contraction of six extraocular muscles that originate from the bones of the orbit and insert into the surface of the eyeball (Figure 25. Four of the muscles are arranged at the cardinal points around the eye and are named for those locations. However, the tendon of the oblique muscles thread through a pulley-like piece of cartilage known as the trochlea. The angle of the tendon through the trochlea means that contraction of the superior oblique rotates the eye medially. The inferior oblique muscle originates from the floor of the orbit and inserts into the inferolateral surface of the eye. When it contracts, it laterally rotates the eye, in opposition to the superior oblique. When the eye looks up or down, the eye must also rotate slightly to compensate for the superior rectus pulling at approximately a 20-degree angle, rather than straight up. The lateral rectus, which causes lateral movement of the eye, is innervated by the abducens nerve. The motor nuclei of these cranial nerves all connect to the brain stem which coordinates eye movements. The Eyeball Layers of the Eyeball the eyeball itself is a hollow sphere composed with three layers of tissue forming the walls (Figure 25. The outermost layer is the fibrous tunic, which includes the white sclera and transparent cornea. The middle layer of the eye is the vascular tunic, composed of, from posterior to anterior, the choroid, ciliary body, and iris. The choroid is a layer of highly vascularized connective tissue that provides a blood supply to the other layers of the eyeball. Anterior to the choroid is the ciliary body, a muscular structure that attaches to the lens by suspensory ligaments. The ciliary body and suspensory ligaments change the shape of the lens, allowing it to focus light onto specific regions at the back of the eye. The iris contains layers of smooth muscle that either open or close the pupil, which is the hole at the center of the eye that allows light to enter the eyeball. The innermost layer of the eye is the neural tunic, or retina, which contains the receptor cells and other nervous tissue responsible for photoreception and is described further below. Cavities of the Eyeball the eyeball is also divided into two cavities: the anterior cavity and the posterior cavity (Figure 25. The anterior cavity is the space between the cornea and lens, bound by the iris and ciliary body on the posterior side. The posterior cavity is the space behind the lens that extends to the posterior side of the interior eyeball and is filled with a viscous fluid called the vitreous humor. The Retina the retina is composed of several layers and contains specialized cells for the initial processing of visual stimuli. There are two types of photoreceptors-called rods and cones-which contain two parts, the inner segment and the outer segment (Figure 25.

The knee joint has multiple ligaments that provide support diabetes symptoms of breast cancer buy forxiga 10 mg without prescription, particularly in the extended position (see Figure 10 blood sugar keeps going up best forxiga 5mg. Outside of the articular capsule, located at the sides of the knee, are two extrinsic ligaments. The fibular collateral ligament (lateral collateral ligament) is on the lateral side and spans from the lateral epicondyle of the femur to the head of the fibula. The tibial collateral ligament (medial collateral ligament) of the medial knee runs from the medial epicondyle of the femur to the medial tibia. Inside the knee are two intracapsular ligaments, the anterior cruciate ligament and posterior cruciate ligament. These ligaments are anchored inferiorly to the tibia at the intercondylar eminence, the roughened area between the tibial condyles. The cruciate ligaments are named for whether they are attached anteriorly or posteriorly to this tibial region. In this position, the posterior cruciate ligament prevents the femur from sliding anteriorly off the top of the tibia. The anterior cruciate ligament becomes tight when the knee is extended, and thus resists hyperextension. The superior aspect of the talus bone is square-shaped and has three areas of articulation. The sides of the talus are firmly held in position by the articulations with the medial malleolus of the tibia and the lateral malleolus of the fibula, which prevent any side-to-side motion of the talus. The ankle is thus a uniaxial hinge joint that allows only for dorsiflexion and plantar flexion of the foot. The joints between the talus and navicular bones and the calcaneus and cuboid bones are also important contributors to these movements. Like the hinge joints of the elbow and knee, the talocrural joint of the ankle is supported by several strong ligaments located on the sides of the joint. These ligaments extend from the medial malleolus of the tibia or lateral malleolus of the fibula and anchor to the talus and calcaneus bones. They also prevent abnormal sideto-side and twisting movements of the talus and calcaneus bones during eversion and inversion of the foot. The talocrural (ankle) joint is a uniaxial hinge joint that only allows for dorsiflexion or plantar flexion of the foot. Movements at the subtalar joint, between the talus and calcaneus bones, combined with motions at other intertarsal joints, enables eversion/inversion movements of the foot. In this lesson you will learn about the nerves that innervate the muscles of the leg. All of the spinal nerves include axons of neurons carrying both sensory information toward the central nervous system and motor information away from the central nervous system. The anatomy and organization of spinal nerves is discussed in detail in Lesson 22. Spinal nerves can continue to directly form peripheral nerves or axons from different spinal nerves can be reorganized to follow different courses in the periphery. Axon reorganization happens at four places along the length of the vertebral column, each identified as a nerve plexus. Nerve Plexuses Of the four nerve plexuses, two are found at the cervical level (discussed in Lesson 16), one at the lumbar level, and one at the sacral level (Figure 11. The lumbar plexus arises from all of the lumbar spinal nerves and gives rise to nerves innervating the pelvic region and the anterior leg. Nerves of the Leg the major peripheral nerves of the leg diverge and spread in order to innervate structures of the leg including leg muscles (Figure 11. The femoral nerve supplies innervation to the muscles of the anterior thigh region which includes the hip flexors and the knee extensors. The tibial nerve supplies innervation the posterior aspect of the calf, as well as the lateral and plantar regions of the foot. The common fibular nerve does not innervate any muscles directly before it splits into the superficial and deep fibular nerves. The superficial fibular nerve supplies innervation the muscles of the lateral aspect of the calf, while the deep fibular nerve supplies innervation to the anterior aspect of the calf. Both fibular nerves provide some innervation to the dorsal region of the foot as well.
Patients with no improvement in the initial weeks of treatment generally need an earlier adjustment of treatment diabetes symptoms in children type 2 discount forxiga online american express. For these patients diabetes test strips cvs order forxiga 10 mg on line, the psychiatrist should consider changing to another antidepressant rather than increasing the dose of the medication. For some antidepressant medications, the exact relationships between doses and major depressive disorder symptom response have not been rigorously investigated with fixed-dose studies, and minimum effective doses have not been clearly established; moreover, for other antidepressant medications, some studies have failed to show doseresponse relationships (230, 231). Therefore, the initial doses and usual adult doses in Table 6 are intended to serve as general guidelines, and actual doses may vary from individual to individual. In general, patients who are older, are medically compromised, or have decreased ability to metabolize and clear antidepressant medications will require lower doses. In such patients, reduction of initial and therapeutic doses to 50% of usual adult doses is often recommended, and dose escalations should be made at a slower rate than for younger and healthier adults. Medication doses should also be tailored to individual patients depending on the potential for pharmacokinetic alterations and drug-drug interactions. Patients who have started taking an antidepressant medication should be carefully and systematically monitored to assess their response to treatment, the emergence of side effects, their clinical condition, safety, and adherence to treatment. Visits should also be frequent enough to monitor and address suicide risk and to actively promote treatment adherence, since attrition from treatment continues to be a major hurdle in maximizing outcomes. Patients in clinical trials appear to benefit from monitoring once a week or more. This frequency of monitoring enhances adherence rates and likely helps patients avoid the demoralization that may occur before the onset of beneficial effects (216). In clinical practice, the frequency of monitoring during the acute phase of pharmacotherapy may vary and can be as often as multiple times per week in more complex circumstances. When such medications are given, obtaining blood drug levels can be particularly informative when patients have not responded to treatment with an adequate dose of antidepressant medication for an adequate duration; when patients are particularly vulnerable to the toxic effects of a medication and require the lowest possible effective dose; when there are concerns about patient adherence; and when there is concern that drug-drug interactions are adversely affecting antidepressant medication levels. In time, genetic testing may help guide selection or dosing of antidepressants, but data are currently insufficient to justify the cost of such tests (229). Ingestion of a 10-day supply of a tricyclic agent administered at a dose of 200 mg/day is often lethal. Early on in treatment, it is prudent to dispense only small quantities of such antidepressant medications and keep in mind the possibility that patients can hoard medications over time. Electroconvulsive therapy may be particularly beneficial and can be considered as a first-line treatment option for severe major depressive disorder when it is coupled with psychotic features (240, 241), catatonia (239, 242), suicide risk (243), or food refusal leading to nutritional compromise, as well as in other situations when a particularly rapid antidepressant response is required (240), such as with severely ill inpatients (239). Electroconvulsive therapy is also indicated as a first-line treatment for patients who have previously shown a positive response to this treatment modality or who prefer it (239). Side effects of electroconvulsive therapy Electroconvulsive therapy is a very safe treatment, and there are no absolute contraindications to its use (239). Risks of morbidity and mortality, in general, do not exceed those associated with anesthesia alone (239, 244, 245). Electroconvulsive therapy may have cardiovascular side effects, mediated by changes in the autonomic nervous system with the initial stimulus and subsequent seizure activity (239). Retrograde amnesia also improves over time, typically resolving within 6 months (248, 252), although some patients report incomplete recovery of memories, particularly for events around the time of the treatment (247, 254). Rarely, patients report more pervasive and persistent cognitive disruption, the basis of which is uncertain (252, 255). Although data supporting this practice are still few, it does not appear to increase side effects and may augment response (259, 260). Electroconvulsive therapy may be administered either unilaterally or bilaterally (using a bitemporal or bifrontal electrode placement). Compared with patients who receive bilateral treatment, most patients who receive right unilateral electrode placement with low stimulus intensities experience fewer cognitive effects but less therapeutic benefit (253). Failure to induce an adequate seizure should be followed immediately by restimulation at higher energies until an adequate seizure is elicited.
Generic forxiga 5mg otc. PROTECT YOUR HEART TAKE GOOD CARE OF YOUR DIABETES FOR LIFE.